Antofagasta de la Sierra is a volcanic field in Argentina. The main type of volcanic edifice in the area are scoria cones, it is formed by the La Laguna, Jote and Alumbrera volcanoes. The first and last of these form a sub-group which is better researched. Various dating methods have yielded ages from several million to several hundred thousand years ago, but some vents appear to be of Holocene age.

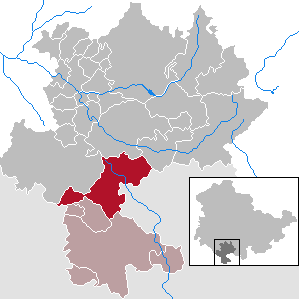
Baunach is a town in the Upper Franconian district of Bamberg and the seat of the administrative community (Verwaltungsgemeinschaft) of Baunach. Until administrative reform in 1972, Baunach belonged to the Lower Franconian district of Ebern.

Ampato is a dormant 6,288-metre (20,630 ft) stratovolcano in the Andes of southern Peru. It lies about 70–75 kilometres (43–47 mi) northwest of Arequipa and is part of a north-south chain that includes the volcanoes Hualca Hualca and Sabancaya, the last of which has been active in historical time.
Puyuhuapi Volcanic Group is a volcanic group of cinder cones located at the head of Puyuhuapi Channel, in the Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region of Chile.
The Bridge River Cones, sometimes referred to as the Lillooet Cones and Salal Creek Cones, is the name given to a volcanic field located on the north flank of the upper Bridge River, about 40 km (25 mi) west of the town of Gold Bridge. The cones are in the lee of the Lillooet Icecap and sit astride a group of passes between the Bridge River, which flows W-E to their south, and the Lord River, which flows north to the Taseko Lakes in the Chilcotin District.

West Crater is a small lava dome with associated lava flows in southern Washington, United States. Located in Skamania County, it rises to an elevation of 4,131 feet (1,259 m), and forms part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It is also part of the Marble Mountain-Trout Creek Hill volcanic field, a little-known Quaternary volcanic field in the southern Cascades of Washington state. The area can be hiked, and can be accessed by roads in the Gifford Pinchot National Forest.

San Pedro is a Holocene composite volcano in northern Chile and one of the tallest active volcanoes in the world. Part of the Chilean Andes' volcanic segment, it is part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, one of the four tracts of the Andean Volcanic Belt. This region of volcanism includes the world's two highest volcanoes Ojos del Salado and Llullaillaco. San Pedro, like other Andean volcanoes, was formed by the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South America Plate. It has a neighbouring volcano, San Pablo, and is itself formed by two separate edifices usually known as the Old Cone and the Young Cone. These edifices are formed by rocks ranging from basaltic andesite over andesite to dacite and are emplaced on a basement formed by Miocene volcanic rocks.

Nevado San Francisco, or Cerro San Francisco, is a stratovolcano on the border between Argentina and Chile, located just southeast of San Francisco Pass. It is considered extinct and is one of the several 6,000 m (19,700 ft) peaks in the area, of which the chief is the Ojos del Salado.

The volcanic history of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province presents a record of volcanic activity in northwestern British Columbia, central Yukon and the U.S. state of easternmost Alaska. The volcanic activity lies in the northern part of the Western Cordillera of the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Extensional cracking of the North American Plate in this part of North America has existed for millions of years. Continuation of this continental rifting has fed scores of volcanoes throughout the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province over at least the past 20 million years and occasionally continued into geologically recent times.

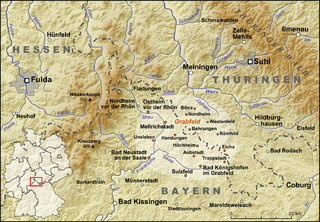
The Zeilberg is a hill, 463 m above NHN, in the Haßberge Nature Park and county of Haßberge in eastern Lower Franconia, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) east of Maroldsweisach. It is one of the few still recognisable volcanoes of the Heldburger Gangschar and gives its name to the Zeilberge, which are the highest part of the Itz-Baunach Hills that are geologically part of the actual Haßberge to the west, but are separated from them by the Baunach valley.

Ash Hill is a volcano in Wiri, in the Auckland volcanic field. A low tuff cone with an explosion crater about 150m wide, it is now covered by industrial development. It peaked at roughly 30 metres above sea level.
The Franconian Keuper-Lias Plains or Franconian Keuper-Lias Lands are a major natural region in the South German Scarplands in Upper Franconia and to a lesser extent in the north, in the Thuringian district of Hildburghausen. As the name betrays, the term embraces both the Keuper landscapes and lias landscapes in Franconia. In addition, the foreland of the Franconian Jura, in which part of the Brown Jurassic occurs, as well as parts of the former volcanic region of Heldburger Gangschar belong to this region.

The Heldburger Land was the historical, Saxon, administrative district (Amtsbezirk) of Heldburg and is today the southernmost part of the Free State of Thuringia and the district of Hildburghausen, between the towns of Coburg, Hildburghausen and Bad Königshofen. The region known now as the Heldburger Land is referred to administratively as the Heldburger Unterland, and sometimes in the vernacular as the Heldburger Zipfel.

Heldburg Fortress is a high medieval hilltop castle in the 16th Century was rebuilt into a renaissance castle. It rises on a former volcanic region to 'Heldburger Gangschar' counted, 405-metre-high volcanic cone, 113 metres above the town of Heldburg in the Heldburger Land, the southern tip of the district Hildburghausen in Thuringia. The Veste Heldburg, once a secondary residence and hunting lodge of the Dukes of Coburg, dominates the little town of Heldburg on the Thuringian border with Bavaria. From it can be seen across the Thuringian border the sister-castle Veste Coburg,, once the residence of the Dukes of Coburg, now located in Bavaria.

The Gleichberge, which mainly comprise the Großer and Kleiner Gleichberg, are a small, inselberg-like mountain range, up to 679 m above sea level (NHN), in the southwestern part of the German state of Thuringia. They rise just east of the little ancient town of Römhild in the county of Hildburghausen.

Pali-Aike volcanic field is a volcanic field in Argentina which straddles the border with Chile. It is part of a province of back-arc volcanoes in Patagonia, which formed from processes involving the collision of the Chile Rise with the Peru–Chile Trench. It lies farther east than the Austral Volcanic Zone, the volcanic arc which forms the Andean Volcanic Belt at this latitude.