Related Research Articles

Oxfordshire is a ceremonial county in South East England. The county is bordered by Northamptonshire and Warwickshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the east, Berkshire to the south, and Wiltshire and Gloucestershire to the west. The city of Oxford is the largest settlement and county town.

Abingdon-on-Thames, commonly known as Abingdon, is a historic market town and civil parish on the River Thames in the Vale of the White Horse district of Oxfordshire, England. The historic county town of Berkshire, the area was occupied from the early to middle Iron Age and the remains of a late Iron Age and Roman defensive enclosure lies below the town centre. Abingdon Abbey was founded around 676, giving its name to the emerging town. In the 13th and 14th centuries, Abingdon was an agricultural centre with an extensive trade in wool, alongside weaving and the manufacture of clothing. Charters for the holding of markets and fairs were granted by various monarchs, from Edward I to George II.

The Vale of White Horse is a local government district of Oxfordshire in England. It was historically part of Berkshire. The area is commonly referred to as the 'Vale of the White Horse'. It is crossed by the Ridgeway National Trail in its far south, across the North Wessex Downs AONB at the junction of four counties. The northern boundary is defined by the River Thames. The name refers to Uffington White Horse, a prehistoric hill figure.

The Diocese of Oxford is a Church of England diocese that forms part of the Province of Canterbury. The diocese is led by the Bishop of Oxford, and the bishop's seat is at Christ Church Cathedral, Oxford. It contains more church buildings than any other diocese and has more paid clergy than any other except London.

Abingdon Abbey was a Benedictine monastery in Abingdon-on-Thames in the modern county of Oxfordshire in the United Kingdom. Situated near to the River Thames, it was founded in c.675 AD and was dedicated to Mary, mother of Jesus. It was disestablished in 1538 during the dissolution of the monasteries. A few physical remnants of the Abbey buildings survive within Abingdon-on-Thames.
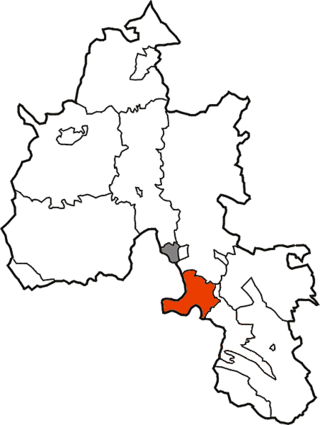
Culham was a rural district in Oxfordshire, England, from 1894 to 1932. It was formed under the Local Government Act 1894 from the part of the Abingdon Rural Sanitary District in the administrative county of Oxfordshire. The remainder of the sanitary district, in the administrative county of Berkshire, became Abingdon Rural District. The rural district council continued to be based at Abingdon, holding meetings in the workhouse of the poor law union.
Abingdon was a rural district in the administrative county of Berkshire from 1894 to 1974.
Abingdon was a municipal borough embracing the town of Abingdon-on-Thames in the county of Berkshire from 1835 to 1974. From 1894 it was nearly entirely surrounded by Abingdon Rural District. It was abolished in 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972, and merged with other districts to form the new Vale of White Horse district of Oxfordshire.
Cholsey Abbey was an Anglo-Saxon nunnery in Cholsey in the English county of Berkshire, which was founded in 986.

The Church of Saint Nicolas is a Church of England parish church in Abingdon in the English county of Oxfordshire.

St. Helen and St. Katharine is a private girls' day school in Abingdon, Oxfordshire.
St. Mary's Abbey, also known as the Nunnaminster, was a Benedictine nunnery in Winchester, Hampshire, England. It was founded between 899 and 902 by Alfred the Great's widow Ealhswith, who was described as the 'builder' of the Nunnaminster in the New Minster Liber Vitae. The first buildings were completed by their son, Edward the Elder. Among the house's early members was Edward's daughter Edburga.
Bromhall Priory was a nunnery of Benedictine nuns at Sunningdale in the English county of Berkshire.
Reading Nunnery was a nunnery in Berkshire, England that existed during the Anglo-Saxon period.

Christ's Hospital of Abingdon is a charity with a long history, based in Abingdon-on-Thames, Oxfordshire.

St Helen's Church is a Church of England parish church in Abingdon on the bank of the River Thames in Oxfordshire, England. The church is thought to occupy the site of the Anglo-Saxon Helenstowe Nunnery.
Hormer was an ancient hundred of Berkshire, England. It consisted of the area immediately west of Oxford within the bend of the River Thames, all of which was transferred to Oxfordshire on 1 April 1974 in accordance with the Local Government Act 1972. It included the ancient parishes of
Shippon is a village in Oxfordshire, England, 1 mile west of Abingdon. It is the largest village in the civil parish of St. Helen Without, in Vale of White Horse District. It was in Berkshire until it was transferred to Oxfordshire in 1974. The Dalton Barracks are located in the village. The name was recorded in the Domesday Book as Scipene, meaning "cattle-shed". It was a manor in the large parish of St Helen's, Abingdon, and was held by Abingdon Abbey until the Dissolution in 1538. It was then acquired by the Duchy of Cornwall, which still owns it. Shippon became a separate ecclesiastical parish in 1865. The parish church of St Mary Magdalene was built in 1855 to a design of Gilbert Scott.

Dry Sandford is a village in the Vale of White Horse district of England, about 3 miles (5 km) north-west of Abingdon. It is one of two villages in the civil parish of St Helen Without. It was part of Berkshire until the 1974 boundary changes transferred the Vale of White Horse to Oxfordshire.
Fyfield and Tubney is a civil parish in The Vale of White Horse district of Oxfordshire, England. It includes the village of Fyfield which is about 4.5 miles (7 km) west of Abingdon and Tubney, which is about 4 miles (6 km) west of Abingdon. The parish was formed in 1952 when the parish of Fyfield was merged with the parish of Tubney. It was part of Berkshire until the 1974 boundary changes transferred it to Oxfordshire.
References
- ↑ Ford, David Nash (2010). "Abingdon: St. Helen's Church". Royal Berkshire History. Retrieved 7 April 2011.
51°40′03″N1°16′58″W / 51.6676°N 1.2829°W