The Percopsiformes are a small order of ray-finned fishes, comprising the trout-perch and its allies. It contains just ten extant species, grouped into seven genera and three families. Five of these genera are monotypic
The Amiiformes order of fish has only one extant species, the bowfin.

The Lamniformes are an order of sharks commonly known as mackerel sharks. It includes some of the most familiar species of sharks, such as the great white and extinct megalodon, as well as more unusual representatives, such as the goblin shark and megamouth shark.

Lates is a genus of lates perches belonging to the family Latidae. The generic name is also used as a common name, lates, for many of the species.

The Lamnidae are the family of mackerel or white sharks. They are large, fast-swimming sharks, found in oceans worldwide. The name of the family is formed from the Greek word, lamna, which means fish of prey, and was derived from the Greek legendary creature, the Lamia.

Squalicorax is a genus of extinct lamniform shark known to have lived during the Cretaceous period.

Cidaris is a genus of pencil sea urchins.

Isurus is a genus of mackerel sharks in the family Lamnidae, commonly known as the mako sharks.

Carcharias is a genus of sand tiger sharks belonging to the family Odontaspididae.
Ptychodus is a genus of extinct hybodontiform sharks. As well as a genus of durophagous (shell-crushing) sharks from the Late Cretaceous. Fossils of Ptychodus teeth are found in plenty in many of the Late Cretaceous marine sediments. There are many species among the Ptychodus that have been uncovered on all the continents around the globe. Such species are Ptychodus mortoni, P. decurrens, P. marginalis, P. mammillaris, P. rugosus and P. latissimus to name a few. They died out approximately 85 million years ago in the Western Interior Sea, where a majority of them were found. A recent publication found that Ptychodus are classified as neoselachian versus hybodont or batoid.

Turbinella is a genus of very large sea snails with an operculum, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Turbinellidae.

Eoophyla is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. It was described by Charles Swinhoe in 1900.

Nymphicula is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.

Epidendrum sect. SchistochilaRchb.f. (1861) is a section of the subgenus E. subg. AmphiglottiumLindl. (1841) of the Genus Epidendrum of the Orchidaceae. E. sect. Schistochila differs from the section E. sect. Holochila in that the species in E. sect. Holochila have undivided lips; the species in E. sect. Schistochila have lobate lips. The species in both E. sect. Schistochila and E. sect. Holochila have racemose inflorescences, unlike those in E. sect. Polycladia, which have truly paniculate inflorescences. Like the other sections of E. subg. Amphiglottium, the members of E. sect. Schistochila are sympodial orchids bearing thin stems with alternate leaves, a long peduncle covered with thin, imbricating sheathes, and a lip adnate to the very end of the column.
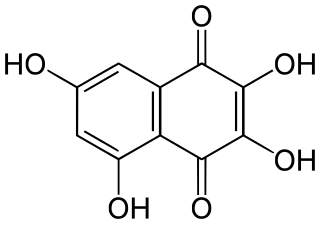
2,3,5,7-Tetraahydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione, also called 2,3,5,7-tetrahydroxynaphthoquinone or spinochrome B, is an organic compound with formula C
10H
6O
4, formally derived from 1,4-naphthoquinone through the replacement of four hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups.

Acanthocardia is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Cardiidae. Like most other bivalves, these mollusks are suspension feeders. This genus is present from the Upper Oligocene to the Recent.

The rough cockle is a species of saltwater clam, a cockle, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Cardiidae. The genus Acanthocardia is present from the Upper Oligocene to the Recent.

Boltenia is a genus of ascidian tunicates in the family Pyuridae.

Rotundaria tuberculata, commonly called the purple wartyback, is a freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk.
























