Related Research Articles

Anemia is a decrease in the total amount of red blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin in the blood, or a lowered ability of the blood to carry oxygen. When anemia comes on slowly, the symptoms are often vague and may include feeling tired, weakness, shortness of breath, and a poor ability to exercise. When the anemia comes on quickly, symptoms may include confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia must be significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Additional symptoms may occur depending on the underlying cause. For people who require surgery, pre-operatve anemia can increase the risk of requiring a blood transfusion following surgery.
Aplastic anemia is a disease in which the body fails to produce blood cells in sufficient numbers. Blood cells are produced in the bone marrow by stem cells that reside there. Aplastic anaemia causes a deficiency of all blood cell types: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
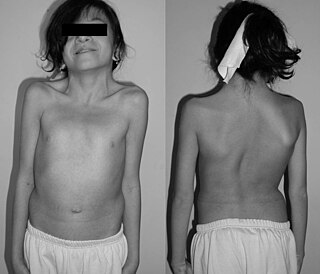
A webbed neck, or pterygium colli, is a congenital skin fold that runs along the sides of the neck down to the shoulders. There are many variants.

Thomas Addison was an English physician and scientist. He is traditionally regarded as one of the "great men" of Guy's Hospital in London.

George Richards Minot was an American medical researcher who shared the 1934 Nobel Prize with George Hoyt Whipple and William P. Murphy for their pioneering work on pernicious anemia.

Fanconi anaemia (FA) is a rare genetic disease resulting in impaired response to DNA damage. Although it is a very rare disorder, study of this and other bone marrow failure syndromes has improved scientific understanding of the mechanisms of normal bone marrow function and development of cancer. Among those affected, the majority develop cancer, most often acute myelogenous leukemia, and 90% develop bone marrow failure by age 40. About 60–75% of people have congenital defects, commonly short stature, abnormalities of the skin, arms, head, eyes, kidneys, and ears, and developmental disabilities. Around 75% of people have some form of endocrine problems, with varying degrees of severity.

Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, of which pernicious anemia (PA) is a type, is a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of vitamin B12. The most common initial symptom is feeling tired. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, pale skin, chest pain, numbness in the hands and feet, poor balance, a smooth red tongue, poor reflexes, depression and confusion. Without treatment some of these problems may become permanent.

Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes on physical examination.

Hookworm infection is an infection by a type of intestinal parasite known as a hookworm. Initially, itching and a rash may occur at the site of infection. Those only affected by a few worms may show no symptoms. Those infected by many worms may experience abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and tiredness. The mental and physical development of children may be affected. Anemia may result.

Aase syndrome or Aase–Smith syndrome is a rare inherited disorder characterized by anemia with some joint and skeletal deformities. Aase syndrome is thought to be an autosomal recessive inherited disorder. The genetic basis of the disease is not known. The anemia is caused by underdevelopment of the bone marrow, which is where blood cells are formed.
Cytopenia is a reduction in the number of mature blood cells. It is common in cancer patients being treated with radiation and/or chemotherapy.
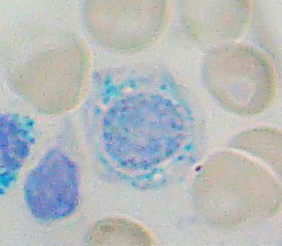
Sideroblastic anemia, or sideroachrestic anemia, is a form of anemia in which the bone marrow produces ringed sideroblasts rather than healthy red blood cells (erythrocytes). In sideroblastic anemia, the body has iron available but cannot incorporate it into hemoglobin, which red blood cells need in order to transport oxygen efficiently. The disorder may be caused either by a genetic disorder or indirectly as part of myelodysplastic syndrome, which can develop into hematological malignancies.

Ancylostoma duodenale is a species of the roundworm genus Ancylostoma. It is a parasitic nematode worm and commonly known as the Old World hookworm. It lives in the small intestine of hosts such as humans, cats and dogs, where it is able to mate and mature. Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus are the two human hookworm species that are normally discussed together as the cause of hookworm infection. They are dioecious. Ancylostoma duodenale is abundant throughout the world, including Southern Europe, North Africa, India, China, southeast Asia, some areas in the United States, the Caribbean, and South America.

Hypochromic anemia is a generic term for any type of anemia in which the red blood cells are paler than normal. A normal red blood cell has a biconcave disk shape and will have an area of pallor in its center when viewed microscopically. In hypochromic cells, this area of central pallor is increased. This decrease in redness is due to a disproportionate reduction of red cell hemoglobin in proportion to the volume of the cell. Clinically the color can be evaluated by the mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) or mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). The MCHC is considered the better parameter of the two as it adjusts for effect the size of the cell has on its amount of hemoglobin. Hypochromia is clinically defined as below the normal MCH reference range of 27–33 picograms/cell in adults or below the normal MCHC reference range of 33–36 g/dL in adults.

Koilonychia, also known as spoon nails, is a nail disease that can be a sign of hypochromic anemia, especially iron-deficiency anemia. It refers to abnormally thin nails which have lost their convexity, becoming flat or even concave in shape. In a sense, koilonychia is the opposite of nail clubbing. In early stages nails may be brittle and chip or break easily.
Necatoriasis is the condition of infection by Necator hookworms, such as Necator americanus. This hookworm infection is a type of helminthiasis (infection) which is a type of neglected tropical disease.
Nutritional anemia refers to types of anemia that can be directly attributed to nutritional disorders. Examples include Iron deficiency anemia and pernicious anemia. It is often discussed in a pediatric context.

Ceftaroline fosamil (INN), brand name Teflaro in the US and Zinforo in Europe, is a cephalosporin antibiotic with anti-MRSA activity. It is active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other Gram-positive bacteria. It retains some activity of later-generation cephalosporins having broad-spectrum activity against Gram-negative bacteria, but its effectiveness is relatively much weaker. It is currently being investigated for community-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and skin structure infection.
Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia type I is a disorder of blood cell production, particularly of the production of erythroblasts, which are the precursors of the red blood cells (RBCs).
Bone marrow failure occurs in individuals who produce an insufficient amount of red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets. Red blood cells transport oxygen to be distributed throughout the body’s tissue. White blood cells fight off infections that enter the body. Bone marrow also contains platelets, which trigger clotting, and thus help stop the blood flow when a wound occurs.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
| This cutaneous condition article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |