Related Research Articles

The minstrel show, also called minstrelsy, was an American form of theater developed in the early 19th century. The shows were performed by mostly white actors wearing blackface make-up for the purpose of comically portraying racial stereotypes of African-Americans by playing the role of black minstrels. There were also some African-American performers and black-only minstrel groups that formed and toured. Minstrel shows stereotyped blacks as dim-witted, lazy, buffoonish, cowardly, superstitious, and happy-go-lucky. Each show consisted of comic skits, variety acts, dancing, and music performances that depicted people specifically of African descent.

Fernando Wood was an American Democratic Party politician, merchant, and real estate investor who served as the 73rd and 75th Mayor of New York City. He also represented the city for several terms in the United States House of Representatives.
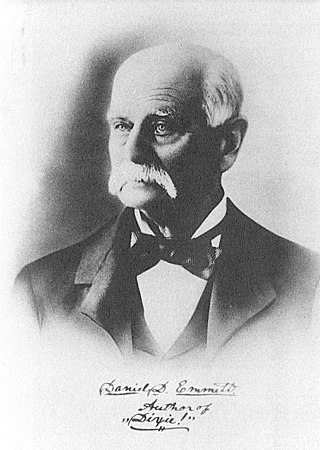
Daniel Decatur Emmett was an American composer, entertainer, and founder of the first troupe of the blackface minstrel tradition, the Virginia Minstrels. He is most remembered as the composer of the song "Dixie".

The New Christy Minstrels are an American large-ensemble folk music group founded by Randy Sparks in 1961. The group has recorded more than 20 albums and scored several hits, including "Green, Green", "Saturday Night", "Today", "Denver" and "This Land Is Your Land". The group's 1962 debut album, Presenting the New Christy Minstrels, won a Grammy Award and remained on the Billboard 200 albums chart for two years.

Christy's Minstrels, sometimes referred to as the Christy Minstrels, were a blackface group formed by Edwin Pearce Christy, a well-known ballad singer, in 1843, in Buffalo, New York. They were instrumental in the solidification of the minstrel show into a fixed three-act form. The troupe also invented or popularized "the line", the structured grouping that constituted the first act of the standardized three-act minstrel show, with the interlocutor in the middle and "Mr. Tambo" and "Mr. Bones" on the ends.

Edwin Pearce Christy was an American composer, singer, actor and stage producer. He is more commonly known as E. P. Christy, and was the founder of the blackface minstrel group Christy's Minstrels.

"Dixie", also known as "Dixie's Land", "I Wish I Was in Dixie" and other titles, is a song about the Southern United States first made in 1859. It is one of the most distinctively Southern musical products of the 19th century. It was not a folk song at its creation, but it has since entered the American folk vernacular. The song likely cemented the word "Dixie" in the American vocabulary as a nickname for the Southern U.S.

Thomas Dilward was an entertainer who appeared in blackface minstrel shows from 1853 until the early 1880s under the name Japanese Tommy. He was also sometimes billed as "The African 'Tom Thumb'" and the "African Dwarf Tommy". Dilward is one of only two known African-Americans to have performed with white minstrel companies before the American Civil War.
Charles Barney Hicks was an American advance man, manager, performer, and owner of blackface minstrel troupes composed of African-American performers. Hicks himself was a minstrel performer who could sing and play challenging roles such as the minstrel-show interlocutor or endmen. However, he was most interested in the business side of minstrelsy. Over the course of his career, he worked with most successful black minstrel troupes as manager, owner or both. The white-dominated minstrel market proved hostile to a black owner, and Hicks had to travel abroad or manage for white owners in order to make a reliable living. Nevertheless, both white and black rivals came to respect him. One observer in 1891 wrote, "This man Hicks was a dangerous man to all outside managers and they all were afraid of him." In 1912, Hicks was the sole African American listed on M. B. Leavitt's list of "best known advance agents during the last fifty years".
Bryant's Minstrels was a blackface minstrel troupe that performed in the mid-19th century, primarily in New York City. The troupe was led by the O'Neill brothers from upstate New York, who took the stage name Bryant.

Mechanics' Hall was a meeting hall and theatre seating 2,500 people located at 472 Broadway in New York City, United States. It had a brown façade. Built by the Mechanics' Society for their monthly meetings in 1847, it was also used for banquets, luncheons, and speeches held by other groups.

William M. Whitlock was an American blackface performer. He began his career in entertainment doing blackface banjo routines in circuses and dime shows, and by 1843 he was well known in New York City. He is best known for his role in forming the original minstrel show troupe, the Virginia Minstrels.
Adeline Miller, alias Adeline Furman, was an American madam and prostitute. According to her contemporary George Templeton Strong, Miller was active in New York City prostitution from the late 1810s. By 1821, she was running a brothel on Church Street, where she had accumulated personal effects worth at least $500.

Hokum is a particular song type of American blues music—a song which uses extended analogies or euphemistic terms to make humorous sexual innuendos. This trope goes back to early dirty blues recordings, enjoyed a huge commercial success in 1920s and 1930s, and is used from time to time in modern American blues and blues rock.

Lew Dockstader was an American singer, comedian, and vaudeville star, best known as a blackface minstrel show performer. Dockstader performed as a solo act and in his own popular minstrel troupe.
George H. Coes was an American minstrel music performer. He appeared in numerous minstrel shows in California and throughout the Northeastern United States.
The Nativity of Our Blessed Lady is a Roman Catholic parish church under the authority of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New York, located at 1510 East 233rd Street and the corner of Secor Avenue, Bronx, New York in the Eastchester neighborhood of the northern Bronx. The church was designed by Don Shepherd, a designer and not an architect. The AIA Guide to New York City described it as "a minor work but one which calls attention to itself because of its location and the rusted steel crucifix that dominates the corner of the site."

Milt G. Barlow was an American blackface comedian and actor popular in minstrel and vaudeville shows over the latter half of the 19th century.
The Theatre Comique, formerly Wood's Minstrel Hall, was a venue on Broadway in Manhattan, New York City. It was built in 1862, replacing a synagogue on the site.
References
- 1 2 Monarchs of minstrelsy, from "Daddy" Rice to date, p. 74-75 (1911)
- ↑ (21 January 1878). A New Library Building, The New York Times