Related Research Articles

The Rhön Mountains are a group of low mountains in central Germany, located around the border area where the states of Hesse, Bavaria and Thuringia come together. These mountains, which are at the extreme southeast end of the East Hesse Highlands, are partly a result of ancient volcanic activity. They are separated from the Vogelsberg Mountains by the river Fulda and its valley. The highest mountain in the Rhön is the Wasserkuppe, which is in Hesse. The Rhön Mountains are a popular tourist destination and walking area.
Rhenish Hesse or Rhine Hesse is a region and a former government district in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. It is made up of territories west of the Upper Rhine river that were part of the Grand Duchy of Hesse and its successor in the Weimar Republic, the People's State of Hesse from 1816 to 1945. The hilly countryside is largely devoted to vineyards, comprising the Rheinhessen wine region.

Gladenbach [German pronunciation:[ˈɡlaːdn̩ˌbax] ] is a town in Hesse, Germany, in the west of Marburg-Biedenkopf district.
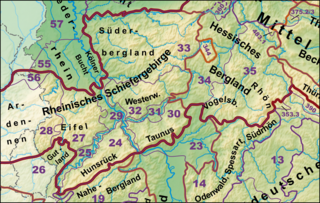
The Rhenish Massif, Rhine Massif or Rhenish Uplands is a geologic massif in western Germany, eastern Belgium, Luxembourg and northeastern France. It is drained centrally, south to north by the river Rhine and a few of its tributaries.
The term Upper Hesse originally referred to the southern possessions of the Landgraviate of Hesse, which were initially geographically separated from the more northerly Lower Hesse by the County of Ziegenhain.

The West Hesse Highlands, also known as the West Hessian Lowlands and Highlands, are a heavily forested region of the Central Uplands in Germany. These highlands lie mainly within the state of Hesse, between that part of the Rhenish Massif right of the Rhine in the west, the Weser Uplands to the north, the Hessian Central Uplands to the east and the Wetterau to the south.

The West Hesse Depression is part of the West Hesse Highlands and Lowlands region in the north of the German state of Hesse. Like the East Hesse Depression, it is a series of separate depressions that form a natural corridor and have been an important historical trade route.
The East Hesse Highlands describes a heavily wooded range of hills lying mainly in the German state of Hesse, but also extending a little way into Lower Saxony to the north, Thuringia to the east and Bavaria to the southeast. The region is sandwiched between the West Hesse Depression to the west, the Weser Uplands to the north, the Thuringian Basin to the northeast, the northwestern edge of the Thuringian Forest to the east, the Spessart to the south and the Wetterau to the southwest.

The Gladenbach Uplands, named after their central town of Gladenbach, is a range of hills up to 609 m high in the Rhine Massif in Germany, on the junction of the Rothaar Mountains, Westerwald (southwest), (Eastern) Hintertaunus and West Hesse Highlands in the east. It lies in Central Hesse within the districts of Marburg-Biedenkopf, Lahn-Dill and Gießen within the so-called Lahn-Dill-(Dietzhölze-) loop. Small parts of the Upper Lahn Valley in the northwest belong, together with the town of Bad Laasphe, also to the district of Siegen-Wittgenstein, North Rhine-Westphalia.
The Oberwälder Land is a natural region in the extreme east of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia with small elements parts in Hesse and Lower Saxony. It consists of Muschelkalk upland, heavily dissected by the Nethe and its tributaries, between the Eggegebirge to the west, the Lippe Uplands to the north, the Weser Valley around Holzminden to the east, the West Hesse Depression to the southeast and the Warburg Börde to the south. This natural region is part of the upper Weser Uplands and hence the German Central Uplands.
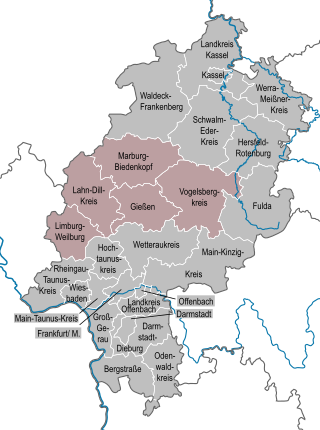
The region of Middle Hesse is one of three planning regions in the German state of Hesse, alongside North and South Hesse. Its territory is identical with that of the administrative province of Gießen and covers the counties of Limburg-Weilburg, Lahn-Dill-Kreis, Gießen, Marburg-Biedenkopf and Vogelsbergkreis. The Middle Hesse Regional Assembly, which decides on the regional plan, currently consists of 31 members chosen by the five counties and the three towns with special status: Gießen, Marburg and Wetzlar. The regional assembly has tasked the governing president (Regierungspräsident) with delivering regional management. The Mid-Hesse Regional Management Association was founded on 22 January 2003.
The East Hesse Depression is one of two fault troughs trending from north-northeast to south-southwest in the state of Hesse, Germany. Like the West Hesse Depression, it is a series of separate depressions that form a natural corridor and have been an important historical trade route.
The Hesse Highlands, Hessian Highlands or Hessian Highlands and Lowlands, are a largely densely forested low mountain area in the German state of Hesse that lies between the Rhenish Massif and the western edge of the Thuringian Basin. The Hesse Highlands are both part of the German Central Uplands and the Rhine-Weser Watershed.

The Upper Hessian Ridge or Upper Hesse Ridge is a hill chain in the West Hesse Highlands in North and Middle Hesse, which lies on the Rhine-Weser watershed and links the montane Central Upland ranges of the Kellerwald and the Vogelsberg in a north-south direction. The swell is divided into the Gilserberg Heights in the north, the central Neustadt Saddle and the Northern Vogelsberg Foreland in the south.

The is a large volcanic mountain range in the German Central Uplands in the state of Hesse, separated from the Rhön Mountains by the Fulda river valley. Emerging approximately 19 million years ago, the Vogelsberg is Central Europe's largest basalt formation, consisting of a multitude of layers that descend from their peak in ring-shaped terraces to the base.

The Salzungen Werra Upland is a natural region in Germany that forms part of the East Hesse Highlands in the German states of Hesse and Thuringia.

The Seulingswald is a hill range in the German Central Uplands which reaches heights of up to 480.3 m above sea level (NHN). It is part of the Fulda-Werra Uplands in the East Hesse Highlands within the Hessian county of Hersfeld-Rotenburg; small ridges extend into the Thuringian county of Wartburgkreis. It is a sandstone range and one of the largest contiguous woodland areas in Hesse.
The Fulda-Werra Uplands are a major natural regional unit in the East Hesse Highlands in East and North Hesse and, with small elements in the southeast, in the German state of Thuringia. Most of the range lies right of the River Fulda and left of the Werra. The uplands extend from the Rhön mountains northwards, to the River Weser near Hann. Münden.
The Söhre is a forested hill range of the German Central Uplands and a subordinate natural region of the Fulda-Werra Uplands in North Hesse, Germany.
References
- 1 2 Elkins, T H (1972). Germany (3rd ed.). London: Chatto & Windus, 1972, p. 223. ASIN B0011Z9KJA.
- ↑ Dickinson, Robert E (1964). Germany: A regional and economic geography (2nd ed.). London: Methuen, p. 512. ASIN B000IOFSEQ.