
The Indian flapshell turtle is a freshwater species of turtle found in South Asia. The “flap-shelled” name stems from the presence of femoral flaps located on the plastron. These flaps of skin cover the limbs when they retract into the shell. It is unclear what protection the flaps offer against predators. Indian flapshell turtles are widespread and common in the South Asian provinces.

Phyllorhiza punctata is a species of jellyfish, also known as the floating bell, Australian spotted jellyfish, brown jellyfish or the white-spotted jellyfish. It is native to the western Pacific from Australia to Japan, but has been introduced widely elsewhere. It feeds primarily on zooplankton. P. punctata generally can reach up to 50 centimetres (20 in) in bell diameter, but in October 2007, one 72 cm (28 in) wide, perhaps the largest ever recorded, was found on Sunset Beach, North Carolina.
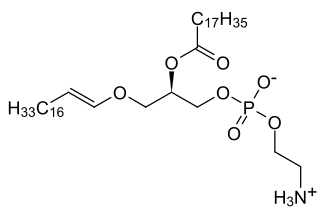
Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata is a rare developmental brain disorder characterized by systemic shortening of the proximal bones, seizures, recurrent respiratory tract infections and congenital cataracts. The affected individuals have low levels of plasmalogens.
Conradi–Hünermann syndrome is a rare type of chondrodysplasia punctata. It is associated with the EBP gene and affects between one in 100,000 and one in 200,000 babies.
Chondrodysplasia punctata is a clinically and genetically diverse group of rare diseases, first described by Erich Conradi (1882–1968), that share the features of stippled epiphyses and skeletal changes.
The European White Elm cultivar Ulmus laevis 'Punctata' was mentioned in 1873, 1889, and later in 1903 as U. effusa f. punctata, but without description.
The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Folia Alba-Punctata' was first identified by C. de Vos in 1867, as Ulmus campestris fol. albo punctatis. The tree is assumed to be U. minor by Green.
X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata is a type of chondrodysplasia punctata that can involve the skin, hair, and cause short stature with skeletal abnormalities, cataracts, and deafness.

Arylsulfatase E, also known as ARSE, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ARSE gene.
Keratosis punctata of the palmar creases is a common skin disorder that occurs most often in black patients, with skin lesions that are 1 to 5mm depressions filled with a comedo-like keratinous plug.

Monarda punctata is a herbaceous plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae, that is native to eastern Canada, the eastern United States and northeastern Mexico. Common names include spotted beebalm and horsemint.

Ransoniella punctata, common name the brown-spotted cowry, is a species of sea snail, a cowry, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Cypraeidae, the cowries.

Homonoeini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the Lamiinae subfamily. It was described by Thomson in 1864.
Heteroclytomorpha is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Heteroclytomorpha inaequalis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1908 and is known from Papua New Guinea.
Heteroclytomorpha simplex is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Lacordaire in 1872.
Heteroclytomorpha singularis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1950. It is known from Fiji.
Heteroclytomorpha sormeoides is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1908.
Metopivaria brunnea is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1923, originally under the genus Heteroclytomorpha.
The field elm cultivar 'Punctata' [:'spotted', the leaf] first appeared in the 1886–87 catalogue of Simon-Louis of Metz, France, as U. campestris punctata. It was distributed by the Späth nursery, Berlin, in the 1890s and early 1900s as U. campestris punctataSim.-Louis, the Späth catalogue listing it separately from U. campestris fol. argenteo-variegata and from U. campestris fol. argenteo-marginata. Green considered it possibly a synonym of the Field Elm cultivar 'Argenteo-Variegata'.








