
A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions between networks and on the global Internet. Data sent through a network, such as a web page or email, is in the form of data packets. A packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute an internetwork until it reaches its destination node.
A network switch is networking hardware that connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.
A virtual local area network (VLAN) is any broadcast domain that is partitioned and isolated in a computer network at the data link layer. In this context, virtual refers to a physical object recreated and altered by additional logic, within the local area network. VLANs work by applying tags to network frames and handling these tags in networking systems – creating the appearance and functionality of network traffic that is physically on a single network but acts as if it is split between separate networks. In this way, VLANs can keep network applications separate despite being connected to the same physical network, and without requiring multiple sets of cabling and networking devices to be deployed.
A virtual private network (VPN) is a mechanism for creating a secure connection between a computing device and a computer network, or between two networks, using an insecure communication medium such as the public Internet.
A multilayer switch (MLS) is a computer networking device that switches on OSI layer 2 like an ordinary network switch and provides extra functions on higher OSI layers. The MLS was invented by engineers at Digital Equipment Corporation.
Networking hardware, also known as network equipment or computer networking devices, are electronic devices that are required for communication and interaction between devices on a computer network. Specifically, they mediate data transmission in a computer network. Units which are the last receiver or generate data are called hosts, end systems or data terminal equipment.
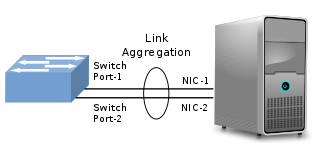
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods. Link aggregation increases total throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and provides redundancy where all but one of the physical links may fail without losing connectivity. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports.

Catalyst is the brand for a variety of network switches, wireless controllers, and wireless access points sold by Cisco Systems. While commonly associated with Ethernet switches, a number of different types of network interfaces have been available throughout the history of the brand. Cisco acquired several different companies and rebranded their products as different versions of the Catalyst product line. The original Catalyst 5000 and 6000 series were based on technology acquired from Crescendo Communications. The 1700, 1900, and 2800 series Catalysts came from Grand Junction Networks, and the Catalyst 3000 series came from Kalpana in 1994.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.

The physical-layer specifications of the Ethernet family of computer network standards are published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which defines the electrical or optical properties and the transfer speed of the physical connection between a device and the network or between network devices. It is complemented by the MAC layer and the logical link layer. An implementation of a specific physical layer is commonly referred to as PHY.
The current portfolio of PowerConnect switches are now being offered as part of the Dell Networking brand: information on this page is an overview of all current and past PowerConnect switches as per August 2013, but any updates on current portfolio will be detailed on the Dell Networking page.
Dell Force10, was a United States company that developed and marketed 10 Gigabit and 40 Gigabit Ethernet switches for computer networking to corporate, educational, and governmental customers. It had offices in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific region.
The Cisco Nexus series switches are modular and fixed port network switches designed for the data center. Cisco Systems introduced the Nexus Series of switches on January 28, 2008. The first chassis in the Nexus 7000 family is a 10-slot chassis with two supervisor engine slots and eight I/O module slots at the front, as well as five crossbar switch fabric modules at the rear. Beside the Nexus 7000 there are also other models in the Nexus range.
Juniper M series is a line of multiservice edge routers designed and manufactured by Juniper Networks, for enterprise and service provider networks. It spans over M7i, M10i, M40e, M120, and M320 platforms with 5 Gbit/s up to 160 Gbit/s of full-duplex throughput. The M40 router was the first product by Juniper Networks, which was released in 1998. The M-series routers run on JUNOS Operating System.
Linksys manufactures a series of network routers. Many models are shipped with Linux-based firmware and can run third-party firmware. The first model to support third-party firmware was the very popular Linksys WRT54G series.

Ethernet Routing Switch 3500 series and Ethernet Routing Switch 2500 series or ERS 3500 and ERS 2500 in data computer networking terms are stackable routing switches designed and manufactured by Avaya.
Dell Networking is the name for the networking portfolio of Dell. In the first half of 2013, Dell started to rebrand their different existing networking product brands to Dell Networking. Dell Networking is the name for the networking equipment that was known as Dell PowerConnect, as well as the Force10 portfolio.

The Avaya Virtual Services Platform 8000 Series, or VSP 8000, is a standalone Ethernet Switch, manufactured by Avaya and intended for use in Campus network and Data Center deployment scenarios.

Fiber to the office (FTTO) is an alternative cabling concept for local area network (LAN) network office environments. It combines passive elements and active mini-switches to provide end devices with Gigabit Ethernet. FTTO involves centralised optical fibre cabling techniques to create a combined backbone/horizontal channel; this channel is provided from the work areas to the centralised cross-connect or interconnect by allowing the use of pull-through cables or splices in the telecommunications room.







