In telecommunications, RS-232, Recommended Standard 232 refers to a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports.

In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It has two analog input terminals and and one binary digital output . The output is ideally

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function and the amplifying function ; it is the same naming convention used in resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and diode–transistor logic (DTL).
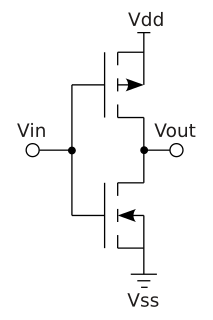
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. Frank Wanlass patented CMOS in 1967 while working for Fairchild Semiconductor.

Low-voltage differential signaling, or LVDS, also known as TIA/EIA-644, is a technical standard that specifies electrical characteristics of a differential, serial communications protocol. LVDS operates at low power and can run at very high speeds using inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables. LVDS is a physical layer specification only; many data communication standards and applications use it and add a data link layer as defined in the OSI model on top of it.

In electronics, emitter-coupled logic (ECL) is a high-speed integrated circuit bipolar transistor logic family. ECL uses an overdriven BJT differential amplifier with single-ended input and limited emitter current to avoid the saturated region of operation and its slow turn-off behavior. As the current is steered between two legs of an emitter-coupled pair, ECL is sometimes called current-steering logic (CSL), current-mode logic (CML) or current-switch emitter-follower (CSEF) logic.
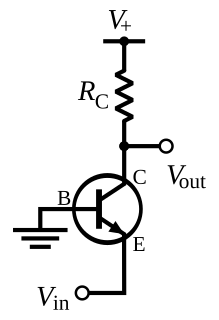
In electronics, a common-base amplifier is one of three basic single-stage bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier topologies, typically used as a current buffer or voltage amplifier.

In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input signal to a digital output signal. The circuit is named a "trigger" because the output retains its value until the input changes sufficiently to trigger a change. In the non-inverting configuration, when the input is higher than a chosen threshold, the output is high. When the input is below a different (lower) chosen threshold the output is low, and when the input is between the two levels the output retains its value. This dual threshold action is called hysteresis and implies that the Schmitt trigger possesses memory and can act as a bistable multivibrator. There is a close relation between the two kinds of circuits: a Schmitt trigger can be converted into a latch and a latch can be converted into a Schmitt trigger.
Resistor–transistor logic (RTL) is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices. RTL is the earliest class of transistorized digital logic circuit used; other classes include diode–transistor logic (DTL) and transistor–transistor logic (TTL). RTL circuits were first constructed with discrete components, but in 1961 it became the first digital logic family to be produced as a monolithic integrated circuit. RTL integrated circuits were used in the Apollo Guidance Computer, whose design was begun in 1961 and which first flew in 1966.

A buffer amplifier is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another, with the aim of preventing the signal source from being affected by whatever currents that the load may produce. The signal is 'buffered from' load currents. Two main types of buffer exist: the voltage buffer and the current buffer.
Stub Series Terminated Logic (SSTL) is a group of electrical standards for driving transmission lines commonly used with DRAM based DDR memory IC's and memory modules. SSTL is primarily designed for driving the DDR (double-data-rate) SDRAM modules used in computer memory; however, it is also used in other applications, notably some PCI Express PHYs and other high-speed devices.
In computer engineering, a logic family may refer to one of two related concepts. A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compatible logic levels and power supply characteristics within a family. Many logic families were produced as individual components, each containing one or a few related basic logical functions, which could be used as "building-blocks" to create systems or as so-called "glue" to interconnect more complex integrated circuits. A "logic family" may also refer to a set of techniques used to implement logic within VLSI integrated circuits such as central processors, memories, or other complex functions. Some such logic families use static techniques to minimize design complexity. Other such logic families, such as domino logic, use clocked dynamic techniques to minimize size, power consumption and delay.
RS-485, also known as TIA-485(-A), EIA-485, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in serial communications systems. Electrical signaling is balanced, and multipoint systems are supported. The standard is jointly published by the Telecommunications Industry Association and Electronic Industries Alliance (TIA/EIA). Digital communications networks implementing the standard can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments. Multiple receivers may be connected to such a network in a linear, multidrop bus. These characteristics make RS-485 useful in industrial control systems and similar applications.
The media-independent interface (MII) was originally defined as a standard interface to connect a Fast Ethernet media access control (MAC) block to a PHY chip. The MII is standardized by IEEE 802.3u and connects different types of PHYs to MACs. Being media independent means that different types of PHY devices for connecting to different media can be used without redesigning or replacing the MAC hardware. Thus any MAC may be used with any PHY, independent of the network signal transmission media.

Current mode logic (CML), or source-coupled logic (SCL), is a differential digital logic family intended to transmit data at speeds between 312.5 Mbit/s and 3.125 Gbit/s across standard printed circuit boards.
Gunning transceiver logic or GTL is a type of logic signaling used to drive electronic backplane buses. It has a voltage swing between 0.4 volts and 1.2 volts—much lower than that used in TTL and CMOS logic—and symmetrical parallel resistive termination. The maximum signaling frequency is specified to be 100 MHz, although some applications use higher frequencies. GTL is defined by JEDEC standard JESD 8-3 (1993) and was invented by William Gunning while working for Xerox at the Palo Alto Research Center.

Parallel SCSI is the earliest of the interface implementations in the SCSI family. SPI is a parallel data bus; There is one set of electrical connections stretching from one end of the SCSI bus to the other. A SCSI device attaches to the bus but does not interrupt it. Both ends of the bus must be terminated.

An open collector is a common type of output found on many integrated circuits (IC), which behaves like a switch that is either connected to ground or disconnected.

P-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses p-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. PMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in an n-type transistor body. This inversion layer, called the p-channel, can conduct holes between p-type "source" and "drain" terminals.
Low voltage complementary metal oxide semiconductor (LVCMOS) is a low voltage class of CMOS technology digital integrated circuits.














