Related Research Articles
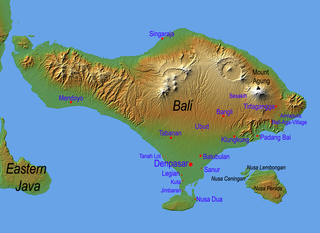
Bali is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nusa Ceningan. The provincial capital, Denpasar, is the most populous city in the Lesser Sunda Islands and the second-largest, after Makassar, in Eastern Indonesia. The upland town of Ubud is considered Bali's cultural centre. The province is Indonesia's main tourist destination, with a significant rise in tourism since the 1980s. Tourism-related business makes up 80% of its economy.

Sulawesi, also known as Celebes, is one of the four Greater Sunda Islands. It is governed by Indonesia. The world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago. Within Indonesia, only Sumatra, Borneo and Papua are larger in territory, and only Java and Sumatra have larger populations.

Hinduism in Southeast Asia had a profound impact on the region's cultural development and its history. As the Indic scripts were introduced from India, people of Southeast Asia entered the historical period by producing their earliest inscriptions around the 1st to 5th century CE. Today, the only practicing Hindus in Southeast Asia other than Overseas Indians are the Balinese and Tenggerese minorities in Indonesia, and the Cham minority in Cambodia and southern Vietnam.
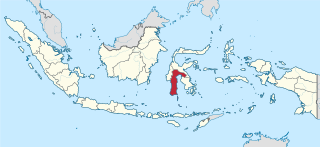
South Sulawesi is a province in the southern peninsula of Sulawesi. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital is Makassar. The province is bordered by Central Sulawesi and West Sulawesi to the north, the Gulf of Bone and Southeast Sulawesi to the east, Makassar Strait to the west, and Flores Sea to the south.

Balinese Hinduism is the form of Hinduism practiced by the majority of the population of Bali. This is particularly associated with the Balinese people residing on the island, and represents a distinct form of Hindu worship incorporating local animism, ancestor worship or Pitru Paksha, and reverence for Buddhist saints or Bodhisattava.

The culture of Indonesia has been shaped by long interaction between original indigenous customs and multiple foreign influences. Indonesia is centrally-located along ancient trading routes between the Far East, South Asia and the Middle East, resulting in many cultural practices being strongly influenced by a multitude of religions, including Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, and Islam, all strong in the major trading cities. The result is a complex cultural mixture very different from the original indigenous cultures.

Hinduism has historically been a major religious and cultural influence in Java. In recent years, it has also been enjoying something of a resurgence, particularly in the eastern part of the island.

The Balinese people are an Southeast Asian ethnic group and nation native to the Indonesian island of Bali. The Balinese population of 4.2 million live mostly on the island of Bali, making up 89% of the island's population. There are also significant populations on the island of Lombok and in the easternmost regions of Java.

The Torajans are an ethnic group indigenous to a mountainous region of South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Their population is approximately 1,100,000, of whom 450,000 live in the regency of Tana Toraja. Most of the population is Christian, and others are Muslim or have local animist beliefs known as aluk. The Indonesian government has recognised this animistic belief as Aluk To Dolo.

Hinduism in Indonesia, as of the 2018 census, is practised by about 1.74% of the total population, and almost 87% of the population in Bali. Hinduism is one of the six official religions of Indonesia. Hinduism came to Indonesia in the 1st-century through traders, sailors, scholars and priests. A syncretic fusion of pre-existing Javanese folk religion, culture and Hindu ideas, that from the 6th-century also synthesized Buddhist ideas as well, evolved as the Indonesian version of Hinduism. These ideas continued to develop during the Srivijaya and Majapahit empires. About 1400 CE, these kingdoms were introduced to Islam from coast-based Muslim traders, and thereafter Hinduism mostly vanished from many of the islands of Indonesia.
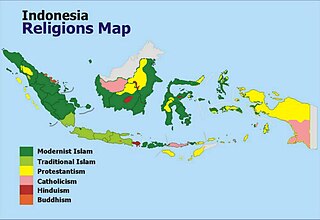
Indonesia is officially a republic with a compromise made between the ideas of a secular state and an Islamic state. Indonesia has the world's largest Muslim population and the first principle of Indonesia's philosophical foundation, Pancasila requires its citizens to "believe in the one and only God". Consequently, atheists in Indonesia experience official discrimination in the context of registration of births and marriages and the issuance of identity cards. In addition, Aceh officially enforces Sharia law and is notorious for its discriminatory practices towards religious and sexual minorities. There are also pro-Sharia and fundamentalist movements in several parts of the country with overwhelming Muslim majorities.

The architecture of Indonesia reflects the diversity of cultural, historical and geographic influences that have shaped Indonesia as a whole. Invaders, colonizers, missionaries, merchants and traders brought cultural changes that had a profound effect on building styles and techniques.

Christianity is Indonesia's second-largest religion, after Islam. Indonesia also has the second-largest Christian population in Southeast Asia after the Philippines, the largest Protestant population in Southeast Asia, and the fourth-largest Christian population in Asia after the Philippines, China and India. Indonesia's 28.6 million Christians constitute 10.72% of the country's population in 2018, with 7.60% Protestant (20.25 million) and 3.12% Catholic (8.33 million). Some provinces in Indonesia are majority Christian.

Dance in Indonesia reflects the country's diversity of ethnicities and cultures. There are more than 1,300 ethnic groups in Indonesia. Austronesian roots and Melanesian tribal forms are visible, and influences ranging from neighboring Asian and even western styles through colonization. Each ethnic group has its own dances: there are more than 3,000 original dance forms in Indonesia. The old traditions of dance and drama are being preserved in the many dance schools which flourish not only in the courts but also in the modern, government-run or supervised art academies.

Prehistoric Indonesia is a prehistoric period in the Indonesian archipelago that spanned from the Pleistocene period to about the 4th century CE when the Kutai people produced the earliest known stone inscriptions in Indonesia. Unlike the clear distinction between prehistoric and historical periods in Europe and the Middle East, the division is muddled in Indonesia. This is mostly because Indonesia's geographical conditions as a vast archipelago caused some parts — especially the interiors of distant islands — to be virtually isolated from the rest of the world. West Java and coastal Eastern Borneo, for example, began their historical periods in the early 4th century, but megalithic culture still flourished and script was unknown in the rest of Indonesia, including in Nias, Batak, and Toraja. The Papuans on the Indonesian part of New Guinea island lived virtually in the Stone Age until their first contacts with modern world in the early 20th century. Even today living megalithic traditions still can be found on the island of Sumba and Nias.

A hyang is an unseen spiritual entity that has supernatural power in ancient Indonesian mythology. This spirit can be either divine or ancestral. The reverence for this spiritual entity can be found in Sunda Wiwitan, Kejawen, Kapitayan, and Balinese Hinduism. In modern Indonesian, this term tends to be associated with gods, devata, or God. The realm where the hyangs reside is called kahyangan, the abode of gods, now a synonym for svarga or heaven in modern Indonesian.

Hinduism is a major and most-followed religion in Asia, that was more than 26% of Asia's total population. In 2010, the total number of Hindus in Asia is more than 1.1 billion. Asia constitute in absolute terms the world's Hindu population and about 99.2% of the world's Hindus live in Asia, with India having the absolute proportion of Hindus having 94% of global Hindu population. Other Asian nations with notable Hinduism population includes, Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and United Arab Emirates. Asia is home to the largest Hindu population, mainly in the Indian subcontinent region.

The mythology of Indonesia is very diverse, the Indonesian people consisting of hundreds of ethnic groups, each with their own myths and legends that explain the origin of their people, the tales of their ancestors and the demons or deities in their belief systems. The tendency to syncretize by overlying older traditions with newer foreign ideas has occurred. For example, the older ancestral mythology might be merged with foreign mythology, such as Hindu, Islam, or Christian biblical mythology.

The Greater Sunda Islands are four tropical islands situated within Southeast Asia, in the Pacific Ocean. The islands, Borneo, Java, Sulawesi and Sumatra, are internationally recognised for their ecological diversity and rich culture. Together with the Lesser Sunda Islands to their southeast, they comprise the archipelago known as the Sunda Islands.
References
- ↑ Geography - North Sulawesi
- ↑ Great Expectations: Hindu Revival Movements in Java, Indonesia Archived 2004-08-20 at the Wayback Machine Swaveda - May 13, 2005
- ↑ "Consulate General of India, Bali, Indonesia : Southeast Sulawesi".
- ↑ Guest Editor IIAS No. 23