This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2021) |

The following is a list of historical military colours, standards and guidons in different countries that do not exist today.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2021) |

The following is a list of historical military colours, standards and guidons in different countries that do not exist today.

During the Middle Ages, units did not have specific colours attached to them; rather, they often wore the heraldry of their lord. The armies of France often used the fleur-de-lis, a symbol of the Capetian dynasty. The King of France also had an official battle standard, the Oriflamme: a special flag, red with gold, and the motto "Montjoie Saint-Denis". When the Oriflamme was taken into battle, it signified that there would be no quarter given to the enemy. English soldiers during the same time period sometimes wore Saint George's Cross as a symbol of identification.
The French colours of the Ancien Régime got the same design: a white cross, the Cross of France (vertical cross, but sometimes it was a St Andrew's cross, like the "Royal Deux Ponts" Régiment's flag). The rest of the standard was depending on the regiment. Often, the Cross of France divided the flag in four equal quarters. The quarters could have the same colour (specially for the Marine troops's flags). Sometimes, there were two colours: the top-left and the bottom-right quarters of one colour, the top-right and the bottom-left of another. In the most part of the time, lys flowers were on the Cross of France, with an inscription or a motto. The regiment often got the name of their province: Picardie (the oldest regiment of Europe), Normandie, Piemont, Provence... but were also called with special names, like "Régiment de la Reine" (Queen's regiment), which had a dark green and black quartered flag, with the cross of France. Each regiment had its flag. The colonel, at the head of the regiment, had a special flag: it also had the white Cross of France, but the four quarters were white too (white was the colour of the French monarchy). The actual flag of Quebec has exactly the design of the French colours of this time. The same pattern was used by regiments made up of foreign nationals who served with the Royal Army infantry.
In 1794, the French Army was reorganised following the Revolution. Regiments were renamed demi-brigades, with three battalions in each. The 1st Battalion of each was raised from the volunteers, while the 3rd Battalion were conscripts. These two received identical colours. The 2nd Battalion meanwhile was formed from a regiment of the old Royal Army, and received a different colour from the 1st Battalion. The colours of all of the 2nd Battalions were identical to each other (except for the demi-brigade's number), while the 1st Battalions all received different colours.
In the Imperial Army under Napoleon I, regiments received new colours, which were called aigles (eagles), from the eagle that was mounted atop the pole. The designs differed per speciality.
Up to 1812, the colours of infantry regiments resembled the colours of the Revolutionary Army, specifically the 1st Demi-Brigade of infantry, with a white diamond and the corners filled in (from clockwise top left) red-blue-red-blue. The name of the regiment was written in gold on the obverse, and the words Valeur et Discipline, together with the battalion number, on the reverse. The regiment's number was written in gold in the four corners. In 1812, a new pattern of colours was authorised; this used the French Tricolour, fringed in gold, and with various regimental and imperial devices forming a frame around the gold writing. The obverse bore the name of the regiment, while the reverse saw listed its battle honours. However, only those actions in which the Emperor himself had participated were permitted to be displayed, so some regiments had nothing on the reverse of their colours. Only the 1st Battalion of each regiment was issued with this Colour; subsequent battalions were issued with plain, coloured marker flags (a practice that began in 1809); although the regulations issued specifically prohibited the addition of any inscriptions or insignia, many battalions did so to allow them to stand out.
From 1804 to 1812, the cavalry and artillery of the Imperial Army used similar designs for the unit standards. The line heavy cavalry regiments (cuirassiers and carabiniers) and all hussar formations, as well as the foot artillery companies, carried standards with similar inscriptions as the infantry while the line cavalry regiments of dragoons and the lancers and Chasseurs-à-Cheval, as well as the horse artillery, all had swallowtailed guidons. In 1812 the designs were unified, with both now having unit standards of the same design as the infantry with the battle honours. The regiments of engineers, as well as the pontoon units attached to the artillery, also carried infantry-style colours. The artillery and logistics trains, till 1812, carried swallowtailed guidons due to their mounted role.
In 1810, the standards and guidions of Imperial Guard cavalry formations raised before 1809 carried grenades or hunting horns in their colours depending on their role.
King Frederick II - known to history as Frederick the Great - ascended the throne of Prussia in 1740. Shortly thereafter he began to issue colours of a new pattern to the infantry regiments of the Prussian Army. Under the new regulations, each regiment received two flags per battalion. The first battalion carried the King's Colour (leibfahne) and one Regimental Colour (regimentsfahne), while the second battalion carried two regimentsfahnen. The Leibfahne had a white field and the Regimentsfahne had a field in the distinguishing colour of the regiment. In the center of both colours was a circular tablet bearing the crowned Prussian eagle under a scroll inscribed Pro Gloria et Patria (For Glory and Fatherland), all within a wreath surmounted by the royal crown. The corners were decorated with crowned royal cyphers (FR for Fredericus Rex) The colours of the wreath, crown and cyphers could be either gold or silver. Unusually, Prussian infantry colours were longer at the hoist than on the fly, measuring 140 by 120 centimetres. Cords and tassels were silver and black. The colours were made of silk, with insignia painted on. The colours of the regular infantry regiments remained virtually unchanged from 1742 until 1806, when catastrophic defeat at the hands of Napoleon all but destroyed the once-proud Prussian Army. When new flags were issued to the reconstituted army beginning in 1811-12, their design was based on the original pattern, but with a number of modifications.
In cavalry formations, the same pattern prevailed, with the 1st Squadron or Battalion of cavalry (Cuirassier and Hussar since 1744) regiments carrying the King's Standard (Leibstandarte) and a Squadron Standard (Eskadronsstandarte). Dragoon regiments had swallowtailed standards (Leibfahne and Eskadronsfahne) in unit colours. The Garde du Corps had a Roman styled vellixum standard carried solely by the 1st squadron, while the other squadrons carried lances with the eagle finial.

In Mongolia, the Tug is generally regarded as a type of historical military symbol that is the equivalent to a military colour. It is a circular pole with attached horse or yak tail hairs arranged at the top. It was introduced and was flown during the period of the Mongol Empire, and was later adopted by Turco-Mongol, Turkic khanates and the Ottoman Empire. [2]

During the period of the Constitucional Monarchy (1834-1910), each of the regiments and other independent units of the Portuguese Army had a regimental colour, which was the variant of the then Flag of Portugal, the field being vertically divided in blue and white, with the Royal coat of arms in the centre, surrounded by two golden olive branches tied by a red ribbon carrying the Order of Christ Cross, and the royal cypher at each corner. Under the arms there was a white ribbon containing the number of the unit in the obverse of the colour and the regimental title in the verse. The colour was square with 130 cm each side.
The flags of the mounted units were similar, but were named "standards" and were smaller, with 80 cm each side.
Colours in the Imperial Russian Army were introduced in the 18th century. Large regimental flags were reserved for infantry units while small, easy to carry flags were used in the cavalry and horse artillery. Regulations in 1797 were introduced to give the military a guideline when awarding colours. New designs for regular infantry units were made, with the state color consisting of white with the state emblem and the assigned colors of the company/battalion/regiment using a different emblem.
In 1812 the former tradition, a Russian adaptation of the British practice, was replaced with the use of the regimental colour or standard as the sole colour for all units.
Each unit in the armed forces of the Soviet Union had its own Regimental Colour, which was produced to a standard design from the 1930s onward:
All the Colours were red with gold fringe and square in form.
The former designs (issued from 1925) had a red star on the reverse with the name of the Central Executive Committee and later, the Supreme Soviet of the USSR surrounding it, and the obverse had the unit inscription below the State Emblem of the Soviet Union, which had the Soviet Union state motto ("Workers of the world, unite!") and the red star with the hammer and sickle inside (both were on the flag of the Soviet Union) above it (the latter was near the hoist). (Distinguished units would be given a second colour, the Revolutionary Red Banner of Honour, by the all-Union CEC (before 1924 by the All-Russian Central Executive Committee).)
The Naval Flags used by the Soviet Navy are white with a bottom blue stripe and were based on the naval ensign. Above it are the USSR's national symbols, the hammer and the sickle, beside the red star. If a naval unit is a recipient of the Order of the Red Banner, the medal of the order replaced the star.
The Colours of those regiments that were classed as 'Guards' was slightly different. These had the portrait of Lenin, the Za nashu motto and the abbreviation "USSR" (СССР) on the obverse and the small star with hammer and sickle in its centre, unit's name and a motto on the reverse. The mottoes were different for different regiments (for example, those regiments made Guards in the Great Patriotic War bore the motto 'Death to the German Invaders!'). Naval Guards units had a Guards ribbon included in the Naval ensign whenever a ship becomes a Guards ship.
An army regulation of July 1810 stated that line infantry regiments of the Spanish army would bear two colours. The first battalion would carry the coronela (King's Colour), which was white and bore the Royal Coat of Arms in the centre, sometimes on top of a burgundy Cross , surrounded by various regimental devices, while the second battalion (and independent battalions of light infantry) would carry the sencilla (Regimental Colour), which would have a burgundy cross with the provincial coat of arms at the four corners, and the name of the regiment in the top half. In 1843, the regulations introduced a new pattern for regimental colours, with the sencilla replaced by the batallona. This was a flag that adopted the national colours of red-yellow-red horizontal stripes, with a simplified royal coat of arms in the centre atop a small burgundy cross and the name of the regiment encircling it.
Following the victory of General Franco in the Spanish Civil War, the Spanish army adopted the policy of using only a single colour, the batallona, with the new coat of arms in its centre replacing the Royal arms, and the name of the regiment encircling it.

In military organizations, a colour guard is a detachment of soldiers assigned to the protection of regimental colours and the national flag. This duty is highly prestigious, and the military colour is generally carried by a young officer (ensign), while experienced non-commissioned officers are assigned to the protection of the national flag. These non-commissioned officers, accompanied in several countries by warrant officers, can be ceremonially armed with either sabres or rifles to protect the colour. Colour guards are generally dismounted, but there are also mounted colour guard formations as well.

The Royal Regiment of Fusiliers is an infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Queen's Division. Currently, the regiment has two battalions: the 1st Battalion, part of the Regular Army, is an armoured infantry battalion based in Tidworth, Wiltshire, and the 5th Battalion, part of the Army Reserve, recruits in the traditional fusilier recruiting areas across England. The Royal Regiment of Fusiliers was largely unaffected by the infantry reforms that were announced in December 2004, but under the Army 2020 reduction in the size of the Army, the 2nd Battalion was merged into the first in 2014.

A stable belt is a striped coloured belt worn at times by the armed forces of the United Kingdom, other Commonwealth countries, and a few other countries including Denmark, Brazil and Lebanon. The stripes vary by regiment and corps, identifying the wearer's unit. In Brazil and Lebanon they are known as gymnastic belts.

In military organizations, the practice of carrying colours, standards, flags, or guidons, both to act as a rallying point for troops and to mark the location of the commander, is thought to have originated in Ancient Egypt some 5,000 years ago. The Roman Empire also made battle standards reading SPQR a part of their vast armies. It was formalized in the armies of Europe in the High Middle Ages, with standards being emblazoned with the commander's coat of arms.

The Life Guards is a combined Swedish Army cavalry/infantry regiment. Its responsibilities include the defence of Stockholm as well as provision of the royal guard of honour for the King of Sweden and the Stockholm Palace. With traditions dating from 1521, the regiment is one of the oldest military units in continuous operational existence in the world. It was established in its present form in July 2000, following a merger of the Svea Life Guards and the Life Guard Dragoons. Headquarters are mainly located in Brunna north of Kungsängen in Upplands-Bro Municipality and at the "Cavalry Barracks 1" in central Stockholm.

The Norrbotten Regiment, designation I 19, is a Swedish Army arctic armoured, light infantry and commando regiment that traces its origins back to the 19th century. The regiment's soldiers were originally recruited from the province of Norrbotten, and it is currently garrisoned in Boden, Norrbotten. The regiment has the responsibility for training two armoured and one special recon battalion, as well as number of Arctic light infantry battalions from the home guard as well as running the army's winter unit.

Queen Alexandra's Mounted Rifles (QAMR) is an armoured regiment of the New Zealand Army and forms part of the Royal New Zealand Armoured Corps. The regiment was formed in 1864 and is currently an armoured cavalry unit equipped with NZLAV.
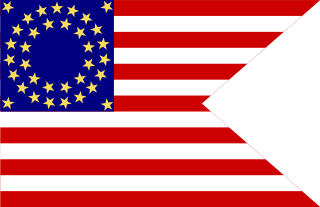
In the United States Armed Forces, a guidon is a military standard or flag that company/battery/troop or platoon-sized detachments carry to signify their unit designation and branch/corps affiliation or the title of the individual who carries it. A basic guidon can be rectangular, but sometimes has a triangular portion removed from the fly.

A battle honour is an award of a right by a government or sovereign to a military unit to emblazon the name of a battle or operation on its flags ("colours"), uniforms or other accessories where ornamentation is possible.

The Regulation Colours are the standard colours used in the armed forces of the countries of the Commonwealth of Nations.

A facing colour, also known as facings, is a common tailoring technique for European military uniforms where the visible inside lining of a standard military jacket, coat or tunic is of a different colour to that of the garment itself. The jacket lining evolved to be of different coloured material, then of specific hues. Accordingly, when the material was turned back on itself: the cuffs, lapels and tails of the jacket exposed the contrasting colours of the lining or facings, enabling ready visual distinction of different units: regiments, divisions or battalions each with their own specific and prominent colours. The use of distinctive facings for individual regiments was at its most popular in 18th century armies, but standardisation within infantry branches became more common during and after the Napoleonic Wars.

The uniforms of La Grande Armée, the army of Napoleon I, are described in this article.
Quartermaster sergeant (QMS) is a class of rank or appointment in some armed forces, especially those of the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth, and formerly also in the United States.

The British Army during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars experienced a time of rapid change. At the beginning of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1793, the army was a small, awkwardly administered force of barely 40,000 men. By the end of the Napoleonic Wars, the numbers had vastly increased. At its peak, in 1813, the regular army contained over 250,000 men. The British infantry was "the only military force not to suffer a major reverse at the hands of Napoleonic France."

The 211th Military Police Battalion is a unit of the Massachusetts Army National Guard. Its Headquarters and Headquarters Detachment is descended from the First Corps of Cadets, initially formed in 1741. It is one of several National Guard units with colonial roots. Its motto is Monstrat Viam – "It Points the Way." While it has served in five wars, the sub-unit's primary contribution to Massachusetts and to the United States was as an officer-producing institution for new regiments from the Revolutionary War through World War II.

The Infantry Branch is a branch of the United States Army first established in 1775.

The following battle honours were awarded to units of the British Army and the armies of British India and the Dominions of the British Empire. From their institution until the end of the Second World War, awards were made by, or in consultation with, the British government, but, since 1945, the individual countries of the former British Empire have awarded battle honours to their forces independently.
During the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, three main patterns of flags were used by the army of the Habsburg monarchy. From 1768 until 1805, each infantry regiment carried two flags per battalion: the 1st or Leib Battalion carried the white Leibfahne and one yellow Ordinarfahne, while the others used two Ordinarfahnen. As the new organisation was implemented under Karl Mack von Leiberich, an Imperial Decree of 22 June 1805 reduced the flags to one per battalion, the Grenadier carrying the white Leibfahne as it was the senior battalion and the others carrying one Ordinarfahne each. When the army reverted to its former organisation on 6 December 1806, so did the flags, i.e.: Leibfahne plus one Ordinarfahne for 1st (Leib) Battalion, two Ordinarfahnen for the others. A further change in 1808 reduced the numbers of flags to one per battalion again. Grenadier battalions carried one Ordinarfahne except in 1805, usually but not necessarily from the senior parent regiment depot. The post-1808 Jäger battalions never carried flags. The Grenzers used the usual system, except that after 1807, all battalions appear to have carried one Ordinarfahne. It is not clear whether they carried the flag in war, although one was captured from 9. Peterwardein Grenzer at the Battle of Eckmühl in April 1809.

The President's Colour Award is the highest honour that can be bestowed upon any military unit of India. It is also known as Nishaan, which is an emblem that is worn by all unit officers on the left-hand sleeve of their uniform.