
A turbocharger, colloquially known as a turbo, is a turbine-driven, forced induction device that increases an internal combustion engine's efficiency and power output by forcing extra compressed air into the combustion chamber. This improvement over a naturally aspirated engine's power output is because the compressor can force more air—and proportionately more fuel—into the combustion chamber than atmospheric pressure alone.

Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation and military aviation. Its headquarters are in East Hartford, Connecticut. As one of the "big three" aero-engine manufacturers, it competes with General Electric and Rolls-Royce, although it has also formed joint ventures with both of these companies. In addition to aircraft engines, Pratt & Whitney manufactures gas turbines for industrial and power generation, and marine turbines. In 2017, the company reported that in 2014 they had 38,737 employees supporting more than 11,000 customers in 180 countries around the world. In 2013, Pratt & Whitney's revenue totaled $14.5 billion. The company remained in the umbrella of its parent company after the merger of United Technologies and Raytheon.

A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous and internal combustion engine. The main elements common to all gas turbine engines are:

An auxiliary power unit (APU) is a device on a vehicle that provides energy for functions other than propulsion. They are commonly found on large aircraft and naval ships as well as some large land vehicles. Aircraft APUs generally produce 115 V alternating current (AC) at 400 Hz, to run the electrical systems of the aircraft; others can produce 28 V direct current (DC). APUs can provide power through single- or three-phase systems.

An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors.

A ram air turbine (RAT) is a small wind turbine that is connected to a hydraulic pump, or electrical generator, installed in an aircraft and used as a power source. The RAT generates power from the airstream by ram pressure due to the speed of the aircraft.

The Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6 is a turboprop aircraft engine produced by Pratt & Whitney Canada. Its design was started in 1958, it first ran in February 1960, first flew on 30 May 1961, entered service in 1964 and has been continuously updated since. It consists of two basic sections: a gas generator with accessory gearbox and a free power turbine with reduction gearbox, and is often seemingly mounted backwards in an aircraft in so far as the intake is at the rear and the exhaust at the front. Many variants of the PT6 have been produced, not only as turboprops but also for helicopters, land vehicles, hovercraft, boats, as auxiliary power units and for industrial uses. By November 2015, 51,000 had been produced, had logged 400 million flight hours from 1963 to 2016. It is known for its reliability with an in-flight shutdown rate of 1 per 651,126 hours in 2016. The PT6A covers the power range between 580 and 1,940 shp while the PT6B/C are turboshaft variants for helicopters.
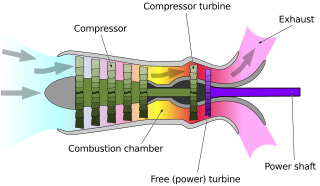
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaftpower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the exhaust and convert it into output shaft power. They are even more similar to turboprops, with only minor differences, and a single engine is often sold in both forms.
Williams International is an American manufacturer of small gas turbine engines based in Pontiac, Michigan, United States. It produces jet engines for cruise missiles and small jet aircraft.

The Garrett TFE731 is a family of geared turbofan engines commonly used on business jet aircraft. Garrett AiResearch originally designed and built the engine, which due to mergers was later produced by AlliedSignal and now Honeywell Aerospace.

The General Electric GE38 is a gas turbine developed by GE Aviation for turboprop and turboshaft applications. It powers the Sikorsky CH-53K King Stallion as the T408.

The Wright Brothers Medal was conceived of in 1924 by the Dayton Section of the Society of Automotive Engineers, and the SAE established it in 1927 to recognize individuals who have made notable contributions in the engineering, design, development, or operation of air and space vehicles. The award is based on contributed research papers.

The Honeywell/ITEC F124 is a low-bypass turbofan engine derived from the civilian Honeywell TFE731. The F125 is an afterburning version of the engine. The engine began development in the late 1970s for the Republic of China (Taiwan) Air Force AIDC F-CK Indigenous Defence Fighter (IDF), and it first ran in 1979. The F124/F125 engine has since been proposed for use on other aircraft, such as the T-45 Goshawk and the SEPECAT Jaguar, and currently powers the Aero L-159 Alca and the Alenia Aermacchi M-346. The F124 has a rather unusual design for a two spool gas turbine engine, using both axial and centrifugal compressors in its high-pressure compressor. There are currently only three production variants of the engine, although several more have been proposed throughout its lifespan.
Honeywell Aerospace is a manufacturer of aircraft engines and avionics, as well as a producer of auxiliary power units (APUs) and other aviation products. Headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona, it is a division of the Honeywell International conglomerate. It generates approximately $10 billion in annual revenue from a 50/50 mix of commercial and defense contracts.
Garrett AiResearch was a manufacturer of turboprop engines and turbochargers, and a pioneer in numerous aerospace technologies. It was previously known as Aircraft Tool and Supply Company, Garrett Supply Company, AiResearch Manufacturing Company, or simply AiResearch. In 1964, Garrett AiResearch merged with Signal Oil & Gas to form a company renamed in 1968 to Signal Companies, which in 1985 merged with Allied Corp. into AlliedSignal. In 1999 AlliedSignal acquired Honeywell and adopted the Honeywell name.

The Solar T62 Titan is an American gas turbine engine used mainly as a helicopter auxiliary power unit (APU), ground power generator or helicopter powerplant. A free power turbine version was developed as the Solar T66.
Solar Turbines Incorporated, a wholly owned subsidiary of Caterpillar Inc., designs and manufactures industrial gas turbines for onshore and offshore electrical power generation, for marine propulsion and for producing, processing and transporting natural gas and oil.

Many variations of aircraft engine starting have been used since the Wright brothers made their first powered flight in 1903. The methods used have been designed for weight saving, simplicity of operation and reliability. Early piston engines were started by hand, with geared hand starting, electrical and cartridge-operated systems for larger engines being developed between the wars.
Frederick Dallenbach was an engineer at Garrett AiResearch, who did pioneering work in gas turbine engines for aircraft applications. He won the Wright Brothers Medal in 1949 with Homer J. Wood for a paper discussing auxiliary turbines to supply pneumatic power for aircraft based on the Garrett GTC43/44 and GTP70 units.

SPE "Aerosila" is the leading Russian firm in the field of development and manufacturing of aircraft propellers, propfans, auxiliary gas-turbine engines as well as aviation aggregates of different purpose including hydromechanical rotation frequency governors of propellers and power ballscrew mechanisms with integrated gearboxes for aircraft with a wing variable sweep, oil-pumps, air regulators, fans and others.















