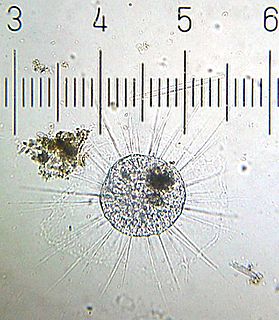
The actinophryids are an order of heliozoa. They are the most common heliozoa in fresh water and can also be found in marine and soil habitats. Actinophryids are unicellular and roughly spherical in shape, with many axopodia that radiate outward from the cell body. Axopodia are a type of pseudopodia that are supported by hundreds of microtubules arranged in a needle-like internal structure. These axopods adhere to passing prey and assist with cell movement, as well as playing a part in cell division and cell fusion.

A granuloma is a structure formed during inflammation that is found in many diseases. It is a collection of immune cells known as macrophages. Granulomas form when the immune system attempts to wall off substances it perceives as foreign but is unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as keratin and suture fragments.
A coenocyte is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. Coenocytic cells are referred to as a coenobium, and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two.
A syncytium or symplasm is a multinucleated cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells, in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis. The term may also refer to cells interconnected by specialized membrane with gap junctions, as seen in the heart muscle cells and certain smooth muscle cells, which are synchronized electrically in an action potential.
A heterokaryon is a multinucleate cell that contains genetically different nuclei. Heterokaryotic and heterokaryosis are derived terms. This is a special type of syncytium. This can occur naturally, such as in the mycelium of fungi during sexual reproduction, or artificially as formed by the experimental fusion of two genetically different cells, as e.g., in hybridoma technology.
The dikaryon is a nuclear feature which is unique to some fungi. The green alga Derbesia has been long considered an exception, until the heterokaryotic hypothesis was challenged by later studies. Compatible cell-types can fuse cytoplasms (plasmogamy). When this occurs, the two nuclei of two cells pair off and cohabit without fusing (karyogamy). This can be maintained for all the cells of the hyphae by synchronously dividing so that pairs are passed to newer cells. In the Ascomycota this attribute is most often found in the ascogenous hyphae and ascocarp while the bulk of the mycelia remains monokaryotic. In the Basidiomycota this is the dominant phase with most Basidiomycota monokaryons weakly growing and short-lived.

A giant cell is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells, often forming a granuloma. It can arise in response to an infection, such as from tuberculosis, herpes, or HIV, or foreign body. These multinucleate giant cells (MGCs) are cells of monocyte or macrophage lineage fused together.

Giant-cell tumor of the bone, (GCTOB) also called osteoclastoma, is a relatively uncommon tumor of the bone. It is characterized by the presence of multinucleated giant cells. Malignancy in giant-cell tumor is uncommon and occurs in about 2% of all cases. However, if malignant degeneration does occur, it is likely to metastasize to the lungs. Giant-cell tumors are normally benign, with unpredictable behavior. It is a heterogeneous tumor composed of three different cell populations. The giant-cell tumour stromal cells (GCTSC) constitute the neoplastic cells, which are from an osteoblastic origin and are classified based on expression of osteoblast cell markers such as alkaline phosphatase and osteocalcin. In contrast, the mononuclear histiocytic cells (MNHC) and multinucleated giant cell (MNGC) fractions are secondarily recruited and comprise the non-neoplastic cell population. They are derived from an osteoclast-monocyte lineage determined primarily by expression of CD68, a marker for monocytic precursor cells. In most patients, the tumors are slow to develop, but may recur locally in as many as 50% of cases.
A gametangium is an organ or cell in which gametes are produced that is found in many multicellular protists, algae, fungi, and the gametophytes of plants. In contrast to gametogenesis in animals, a gametangium is a haploid structure and formation of gametes does not involve meiosis.
Giant-cell fibroma is a type of fibroma not associated with trauma or irritation. It can occur at any age and on a mucous membrane surface. The most common oral locations are on the gingiva of the mandible, tongue, and palate. It is a localized reactive proliferation of fibrous connective tissue.
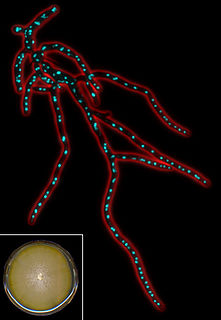
Eremothecium gossypii (also known as Ashbya gossypii) is a filamentous fungus or mold closely related to yeast, but growing exclusively in a filamentous way. It was originally isolated from cotton as a pathogen causing stigmatomycosis by Ashby and Nowell in 1926. This disease affects the development of hair cells in cotton bolls and can be transmitted to citrus fruits, which thereupon dry out and collapse (dry rot disease). In the first part of the 20th century, E. gossypii and two other fungi causing stigmatomycosis (Eremothecium coryli, Aureobasidium pullulans) made it virtually impossible to grow cotton in certain regions of the subtropics, causing severe economical losses. Control of the spore-transmitting insects - cotton stainer (Dysdercus suturellus) and Antestiopsis (antestia bugs) - permitted full eradication of infections. E. gossypii was recognized as a natural overproducer of riboflavin (vitamin B2), which protects its spores against ultraviolet light. This made it an interesting organism for industries, where genetically modified strains are still used to produce this vitamin.
A Warthin–Finkeldey cell is a type of giant multinucleate cell found in hyperplastic lymph nodes early in the course of measles and also in HIV-infected individuals, as well as in Kimura disease, and more rarely in a number of neoplastic and non-neoplastic lymph node disorders. Their origin is uncertain, but they have previously been shown to stain with markers similar to those of follicular dendritic cells, including CD21. Under the light microscope, these cells consist of a large, grape-like cluster of nuclei.

The tapetum is a specialised layer of nutritive cells found within the anther, of flowering plants, where it is located between the sporangenous tissue and the anther wall.
Tapetum is important for the nutrition and development of pollen grains, as well as a source of precursors for the pollen coat. The cells are usually bigger and normally have more than one nucleus per cell. As the sporogenous cells undergo mitosis, the nuclei of tapetal cells also divide. Sometimes, this mitosis is not normal due to which many cells of mature tapetum become multinucleate. Sometimes polyploidy and polyteny can also be seen. The unusually large nuclear constitution of the tapetum helps it in providing nutrients and regulatory molecules to the forming pollen grains. The following processes are responsible for this:

A plasmodium is a living structure of cytoplasm that contains many nuclei, rather than being divided into individual cells each with a single nucleus.

Touton giant cells are a type of multinucleated giant cell seen in lesions with high lipid content such as fat necrosis, xanthoma, and xanthogranulomas. They are also found in dermatofibroma.
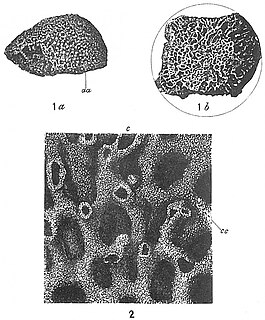
Syringammina fragilissima is a xenophyophore found off the coast of Scotland, near Rockall. It is the largest single-cell organism known, at up to 20 centimetres (8 in) across. It was the first xenophyophore to be described, after being discovered in 1882 by the oceanographer John Murray.

Valonia ventricosa, also known as "bubble algae" and "sailor's eyeballs," is a species of alga found in oceans throughout the world in tropical and subtropical regions. It is one of the largest single-celled organisms.
Smooth muscle tumor of uncertain malignant potential, abbreviated STUMP, is an uncommon tumor of the uterine smooth muscle that may behave like a benign tumor or a cancerous tumor.











