Related Research Articles

Slime mold or slime mould is an informal name given to a polyphyletic assemblage of unrelated eukaryotic organisms in the Stramenopiles, Rhizaria, Discoba, Amoebozoa and Holomycota clades. Most are microscopic; those in the Myxogastria form larger plasmodial slime molds visible to the naked eye. The slime mold life cycle includes a free-living single-celled stage and the formation of spores. Spores are often produced in macroscopic multicellular or multinucleate fruiting bodies that may be formed through aggregation or fusion; aggregation is driven by chemical signals called acrasins. Slime molds contribute to the decomposition of dead vegetation; some are parasitic.

Mycetozoa is a polyphyletic grouping of slime molds. It was originally thought to be a monophyletic clade, but recently it was discovered that protostelia are a polyphyletic group within Conosa.

A coenocyte is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. A coenocytic colony is referred to as a coenobium, and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two.
A syncytium or symplasm is a multinucleate cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells, in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis. The muscle cell that makes up animal skeletal muscle is a classic example of a syncytium cell. The term may also refer to cells interconnected by specialized membranes with gap junctions, as seen in the heart muscle cells and certain smooth muscle cells, which are synchronized electrically in an action potential.

A heterokaryon is a multinucleate cell that contains genetically different nuclei. Heterokaryotic and heterokaryosis are derived terms. This is a special type of syncytium. This can occur naturally, such as in the mycelium of fungi during sexual reproduction, or artificially as formed by the experimental fusion of two genetically different cells, as e.g., in hybridoma technology.
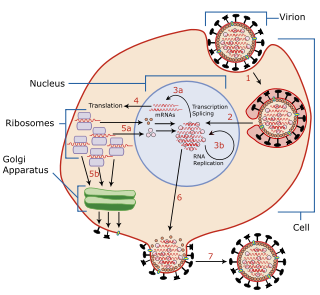
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm.

In evolutionary biology, the term cellularization (cellularisation) has been used in theories to explain the evolution of cells, for instance in the pre-cell theory, dealing with the evolution of the first cells on this planet, and in the syncytial theory attempting to explain the origin of Metazoa from unicellular organisms.

A giant cell is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells, often forming a granuloma.

The syncytiotrophoblast is the epithelial covering of the highly vascular embryonic placental villi, which invades the wall of the uterus to establish nutrient circulation between the embryo and the mother. It is a multinucleate, terminally differentiated syncytium, extending to 13 cm.

Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus (JSRV) is a betaretrovirus which is the causative agent of a contagious lung cancer in sheep, called ovine pulmonary adenocarcinoma.

"Cytotrophoblast" is the name given to both the inner layer of the trophoblast or the cells that live there. It is interior to the syncytiotrophoblast and external to the wall of the blastocyst in a developing embryo.

Physarum polycephalum, an acellular slime mold or myxomycete popularly known as "the blob", is a protist with diverse cellular forms and broad geographic distribution. The “acellular” moniker derives from the plasmodial stage of the life cycle: the plasmodium is a bright yellow macroscopic multinucleate coenocyte shaped in a network of interlaced tubes. This stage of the life cycle, along with its preference for damp shady habitats, likely contributed to the original mischaracterization of the organism as a fungus. P. polycephalum is used as a model organism for research into motility, cellular differentiation, chemotaxis, cellular compatibility, and the cell cycle. It is commonly cultivated.

Membrane fusion proteins are proteins that cause fusion of biological membranes. Membrane fusion is critical for many biological processes, especially in eukaryotic development and viral entry. Fusion proteins can originate from genes encoded by infectious enveloped viruses, ancient retroviruses integrated into the host genome, or solely by the host genome. Post-transcriptional modifications made to the fusion proteins by the host, namely addition and modification of glycans and acetyl groups, can drastically affect fusogenicity.
Cell fusion is an important cellular process in which several uninucleate cells combine to form a multinucleate cell, known as a syncytium. Cell fusion occurs during differentiation of myoblasts, osteoclasts and trophoblasts, during embryogenesis, and morphogenesis. Cell fusion is a necessary event in the maturation of cells so that they maintain their specific functions throughout growth.

Syncytin-1 also known as enverin is a protein found in humans and other primates that is encoded by the ERVW-1 gene. Syncytin-1 is a cell-cell fusion protein whose function is best characterized in placental development. The placenta in turn aids in embryo attachment to the uterus and establishment of a nutrient supply.

Myxogastria/Myxogastrea or Myxomycetes (ICN) is a class of slime molds that contains 5 orders, 14 families, 62 genera, and 888 species. They are colloquially known as the plasmodial or acellular slime moulds.

A plasmodium is a living structure of cytoplasm that contains many nuclei, rather than being divided into individual cells each with a single nucleus.

The parasitophorous vacuole (PV) is a structure produced by apicomplexan parasites in the cells of its host. The PV allows the parasite to develop while protected from the phagolysosomes of the host cell.

Amy S. Gladfelter is an American quantitative cell biologist who is interested in understanding fundamental mechanisms of cell organization. She was a Professor of Biology and the Associate Chair for Diversity Initiatives at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, before moving to Department of Cell Biology at Duke University. She investigates cell cycle control and the septin cytoskeleton. She is also affiliated with the Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center and is a fellow of the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole, MA.

Syssomonas is a monotypic genus of unicellular flagellated protists containing the species Syssomonas multiformis. It is a member of Pluriformea inside the lineage of Holozoa, a clade containing animals and their closest protistan relatives. It lives in freshwater habitats. It has a complex life cycle that includes unicellular amoeboid and flagellated phases, as well as multicellular aggregates, depending on the growth medium and nutritional state.
References
- ↑ Haindl M, Holler E (July 2005). "Use of the giant multinucleate plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum to study RNA interference in the myxomycete". Analytical Biochemistry. 342 (2): 194–9. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2005.03.031. PMID 15922285.
- ↑ Boyd JD, Hamilton WJ (July 1966). "Electron microscopic observations on the cytotrophoblast contribution to the syncytium in the human placenta". Journal of Anatomy. 100 (Pt 3): 535–48. PMC 1270795 . PMID 5965440.
- ↑ Read ND, Roca GM (2006). "Chapter 5: Vegetative Hyphal Fusion in Filamentous Fungi". In Baluška F, Volkmann D, Barlow PW (eds.). Cell-Cell Channels . Landes Bioscience and Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 87–98. ISBN 978-0-387-36058-4.
- ↑ Daubenmire, Rexford F. (1936-12-11). "The Use of the Terms Coenocyte and Syncytium in Biology". Science. 84 (2189): 533. doi:10.1126/science.84.2189.533.a. ISSN 0036-8075.
- ↑ Razin S, Baron S (1996). Baron S (ed.). Mycoplasmas (4th ed.). University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. ISBN 978-0963117212. PMID 21413254 . Retrieved 2018-09-19.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ↑ Bray, Dennis (2017-01-26). Cell Movements: From Molecules to Motility. Garland Science. ISBN 978-0-8153-3282-4.
- ↑ Flemming AJ, Shen ZZ, Cunha A, Emmons SW, Leroi AM (May 2000). "Somatic polyploidization and cellular proliferation drive body size evolution in nematodes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (10): 5285–90. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.5285F. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.10.5285 . PMC 25820 . PMID 10805788.
- ↑ Olsen, Odd-Arne (2007-06-12). Endosperm: Developmental and Molecular Biology. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-540-71235-0.
- ↑ Minelli, Alessandro (2009). Perspectives in Animal Phylogeny and Evolution. Oxford University Press. pp. 113–116. ISBN 978-0-19-856620-5.
- ↑ Studnicka, F. K. (1934). "Die Grundlagen der Zellentheorie von Theodor Schwann". Anat. Anz. 78: 246–257.
- ↑ Zeldovich VB, Clausen CH, Bradford E, Fletcher DA, Maltepe E, Robbins JR, Bakardjiev AI (2013-12-12). "Placental syncytium forms a biophysical barrier against pathogen invasion". PLOS Pathogens. 9 (12): e1003821. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003821 . PMC 3861541 . PMID 24348256.
- 1 2 Sylwester A, Wessels D, Anderson SA, Warren RQ, Shutt DC, Kennedy RC, Soll DR (November 1993). "HIV-induced syncytia of a T cell line form single giant pseudopods and are motile". Journal of Cell Science. 106 (3): 941–53. doi:10.1242/jcs.106.3.941. PMID 8308076.
- ↑ von Aderkas P, Rouault G, Wagner R, Chiwocha S, Roques A (June 2005). "Multinucleate storage cells in Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirbel) Franco) and the effect of seed parasitism by the chalcid Megastigmus spermotrophus Wachtl". Heredity. 94 (6): 616–22. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800670 . PMID 15829985.
- ↑ Hoek, C. van den, Mann, D.G. and Jahns, H.M. (1995). Algae An Introduction to Phycology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
- ↑ Brown MW, Kolisko M, Silberman JD, Roger AJ (June 2012). "Aggregative multicellularity evolved independently in the eukaryotic supergroup Rhizaria". Current Biology. 22 (12): 1123–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.04.021 . PMID 22608512.
- 1 2 Zeldovich VB, Clausen CH, Bradford E, Fletcher DA, Maltepe E, Robbins JR, Bakardjiev AI (2013-12-12). "Placental syncytium forms a biophysical barrier against pathogen invasion". PLOS Pathogens. 9 (12): e1003821. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003821 . PMC 3861541 . PMID 24348256.
- ↑ Compton AA, Schwartz O (February 2017). "They Might Be Giants: Does Syncytium Formation Sink or Spread HIV Infection?". PLOS Pathogens. 13 (2): e1006099. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006099 . PMC 5289631 . PMID 28152024.
- ↑ Lifson JD, Reyes GR, McGrath MS, Stein BS, Engleman EG (May 1986). "AIDS retrovirus induced cytopathology: giant cell formation and involvement of CD4 antigen". Science. 232 (4754): 1123–7. Bibcode:1986Sci...232.1123L. doi:10.1126/science.3010463. PMID 3010463.
- ↑ Walter P, Roberts K, Raff M, Lewis J, Johnson A, Alberts B (2002). "Cell Junctions". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). ISBN 9780815332183. OCLC 807894238.