Related Research Articles

TheUniversity of Texas at Austin is a public research university in Austin, Texas. It was founded in 1883 and is the oldest institution in the University of Texas System. With 40,916 undergraduate students, 11,075 graduate students and 3,133 teaching faculty as of Fall 2021, it is also the largest institution in the system.

Williamson County is a county in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 609,017. Its county seat is Georgetown. The county is named for Robert McAlpin Williamson (1804?–1859), a community leader and a veteran of the Battle of San Jacinto.

Presidio County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 6,131. Its county seat is Marfa. The county was created in 1850 and later organized in 1875. Presidio County is in the Trans-Pecos region of West Texas and is named for the border settlement of Presidio del Norte. It is on the Rio Grande, which forms the Mexican border.

Mason County is a rural county located on the Edwards Plateau in the U.S. state of Texas. At the 2020 census, its population was 3,953. Its county seat is Mason. The county is named for Fort Mason, which was located in the county.

Rockwall is a city in Rockwall County, Texas, United States, which is part of the Dallas/Fort Worth Metroplex. It is the county seat of Rockwall County. The U.S. Census Bureau estimate's Rockwall's 2019 population to be 45,888. The name Rockwall is derived from a naturally jointed geological formation, which has the appearance of an artificial wall.

Round Rock is a city in the U.S. state of Texas, in Williamson County, which is a part of the Greater Austin metropolitan area. Its population is 119,468 as of the 2020 census.

The Edwards Plateau is a geographic region at the crossroads of Central, South, and West Texas. It is bounded by the Balcones Fault to the south and east, the Llano Uplift and the Llano Estacado to the north, and the Pecos River and Chihuahuan Desert to the west. San Angelo, Austin, San Antonio, and Del Rio roughly outline the area. The southeast portion of the plateau is known as the Texas Hill Country.

The J. J. Pickle Research Campus (PRC) in Austin, Texas, United States is owned and operated by the University of Texas at Austin. It sits on 475 acres (1.9 km²) in northwest Austin, approximately 9 miles (14 km) north of the main UT campus and just south of the Domain.

The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center at The University of Texas at Austin is the state botanical garden and arboretum of Texas. The center features more than 900 species of native Texas plants in both garden and natural settings and is home to a breadth of educational programs and events. The center is 284 acres and located 10 miles southwest of downtown Austin, Texas just inside the edge of the distinctive Texas hill country. It straddles both Edwards Plateau and Texas Blackland Prairies ecosystems.
The Texas Advanced Computing Center (TACC) at the University of Texas at Austin, United States, is an advanced computing research center that provides comprehensive advanced computing resources and support services to researchers in Texas and across the USA. The mission of TACC is to enable discoveries that advance science and society through the application of advanced computing technologies. Specializing in high performance computing, scientific visualization, data analysis & storage systems, software, research & development and portal interfaces, TACC deploys and operates advanced computational infrastructure to enable computational research activities of faculty, staff, and students of UT Austin. TACC also provides consulting, technical documentation, and training to support researchers who use these resources. TACC staff members conduct research and development in applications and algorithms, computing systems design/architecture, and programming tools and environments.

The Austin–Round Rock-Georgetown Metropolitan Statistical Area is a five-county metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Texas, as defined by the Office of Management and Budget. The metropolitan area is situated in Central Texas on the western edge of the American South and on the eastern edge of the American Southwest, and borders Greater San Antonio to the south.

Hill Country State Natural Area (HCSNA) preserves 5,369 acres (21.73 km2) of rugged, relatively pristine Hill Country terrain in Bandera County, Texas. It was first opened to the public in 1984. Since HCSNA is designated a "Natural Area" rather than a "State Park", the Texas Parks and Wildlife Department's first priority is the maintenance and preservation of the property's natural state. Accordingly, facilities are purposely somewhat primitive and recreational activities may be curtailed if the TPWD deems it necessary to protect the environment.

Fort Lancaster is a former United States Army installation located near Sheffield, Texas. The fort was established in 1855 on the San Antonio–El Paso Road to protect migrants moving toward California through Texas. The US Army occupied Fort Lancaster until Texas seceded from the United States in March 1861 and were replaced at the fort by forces loyal to the Confederate States of America. The Confederate Army held the fort from November 1861 until April 1862, when it was again abandoned and then burned.

Mummy Cave is a rock shelter and archeological site in Park County, Wyoming, United States, near the eastern entrance to Yellowstone National Park. The site is adjacent to the concurrent U.S. Routes 14/16/20, on the left bank of the North Fork of the Shoshone River at an altitude of 6,310 feet (1,920 m) in Shoshone National Forest.
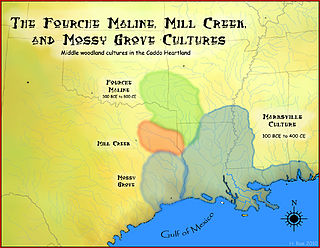
The Fourche Maline culture was a Woodland Period Native American culture that existed from 300 BCE to 800 CE, in what are now defined as southeastern Oklahoma, southwestern Arkansas, northwestern Louisiana, and northeastern Texas. They are considered to be one of the main ancestral groups of the Caddoan Mississippian culture, along with the contemporaneous Mill Creek culture of eastern Texas. This culture was named for the Fourche Maline Creek, a tributary of the Poteau River. Their modern descendants are the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma.

Colha, Belize is a Maya archaeological site located in northern portion of the country, about 52 km. north of Belize City, near the town of Orange Walk. The site is one of the earliest in the Maya region and remains important to the archaeological record of the Maya culture well into the Postclassic Period. According to Palma Buttles, “Archaeological evidence from Colha allows for the interpretation occupation from the Early Preceramic (3400-1900B.C.) to Middle Postclassic with population peaks occurring in the Late Preclassic and again in the Late Classic ”. These peaks in population are directly related to the presence of stone tool workshops at the site. Colha's proximity to an important source of high quality chert that is found in the Cenozoic limestone of the region and well traveled trade routes was utilized by the inhabitants to develop a niche in the Maya trade market that may have extended to the Greater Antilles. During the Late Preclassic and Late Classic periods, Colha served as a primary supplier of worked stone tools for the region. It has been estimated that the 36 workshops at Colha produced nearly 4 million chert and obsidian tools and eccentrics that were dispersed throughout Mesoamerica during the Maya era. This made it an important player in the trade of essential good throughout the area.

The Gault archaeological site is an extensive, multicomponent site located in central Texas, United States, about 40 miles (64 km) north of Austin. It bears evidence of almost continuous human occupation, starting at least 16,000 years ago—making it one of the few archaeological sites in the Americas at which compelling evidence has been found for human occupation dating to before the appearance of the Clovis culture.
Dee Ann Story was an American archaeologist. Story lived in Wimberley, Texas and was a professor at the University of Texas at Austin. Story's best-known excavations were the George C. Davis and Deshazo sites. Story's work with Caddo Mounds State Historic Site, took place in the 1960s and 1970s and pinpointed the timeline of the area. She brought more advanced techniques to the dig, such as radiocarbon dating. Story was also the first woman hired to work as a professional archaeologist for the state of Texas.

Mission Dolores State Historic Site (41SA25) is a 36-acre historic site including a 9-acre (3.6 ha) archaeological site listed on the National Register of Historic Places in San Augustine County, Texas that preserves the location of a Franciscan mission originally established in 1721. The site is located on the original El Camino Real de los Tejas trail. The site has no above ground remains of the mission but the mission's location is confirmed through archeological excavations. It is located half a mile south of San Augustine in the Piney Woods region of east Texas. Operated by the Texas Historical Commission, the site includes a campground, museum, gift shop and hiking trails.

Walnut Creek is a 23-mile (37 km) long tributary stream of the Colorado River in Texas. It flows from north to south, crossing the Edwards Plateau on the western side of Austin, down to the Blackland Prairie on the eastern side of the city where it then drains into the Colorado River downstream of Longhorn Dam. The stream's upper region flows over limestone, while the southern stretch passes through deeper clay soils and hardwood forest. Walnut Creek's watershed, spanning 36,000 acres (15,000 ha), is the largest in Central Austin.
References
- ↑ "Honey Creek (Mason County)". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved May 28, 2013.
- ↑ "Plant Remains from Central Burned Rock Midden 41MS32". UT-Texas. Retrieved May 28, 2013.
- ↑ "Honey Creek". Texas Beyond History. UT-Austin. Retrieved May 28, 2013.
Coordinates: 30°38′57″N99°18′45″W / 30.64917°N 99.31250°W
