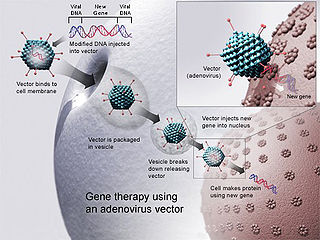
Gene therapy is a medical field which focuses on the genetic modification of cells to produce a therapeutic effect or the treatment of disease by repairing or reconstructing defective genetic material. The first attempt at modifying human DNA was performed in 1980, by Martin Cline, but the first successful nuclear gene transfer in humans, approved by the National Institutes of Health, was performed in May 1989. The first therapeutic use of gene transfer as well as the first direct insertion of human DNA into the nuclear genome was performed by French Anderson in a trial starting in September 1990. It is thought to be able to cure many genetic disorders or treat them over time.

Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs first in the thighs and pelvis followed by the arms. This can result in trouble standing up. Most are unable to walk by the age of 12. Affected muscles may look larger due to increased fat content. Scoliosis is also common. Some may have intellectual disability. Females with a single copy of the defective gene may show mild symptoms.

A designer baby is a baby whose genetic makeup has been selected or altered, often to include a particular gene or to remove genes associated with disease. This process usually involves analysing a wide range of human embryos to identify genes associated with particular diseases and characteristics, and selecting embryos that have the desired genetic makeup; a process known as preimplantation genetic diagnosis. Screening for single genes is commonly practiced, and polygenic screening is offered by a few companies. Other potential methods by which a baby's genetic information can be altered involve directly editing the genome before birth, which is not routinely performed and only one instance of this is known to have occurred as of 2019, where Chinese twins Lulu and Nana were edited as embryos, causing widespread criticism.

Vertex Pharmaceuticals is an American biopharmaceutical company based in Boston, Massachusetts. It was one of the first biotech firms to use an explicit strategy of rational drug design rather than combinatorial chemistry. It maintains headquarters in South Boston, Massachusetts, and three research facilities, in San Diego, California, and Milton Park, near Oxford, England.

PerkinElmer, Inc., previously styled Perkin-Elmer, is an American global corporation focused in the business areas of diagnostics, life science research, food, environmental and industrial testing. Its capabilities include detection, imaging, informatics, and service. PerkinElmer produces analytical instruments, genetic testing and diagnostic tools, medical imaging components, software, instruments, and consumables for multiple end markets.
Gene editing may refer to:
The Cancer Genome Project is part of the cancer, aging, and somatic mutation research based at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in The United Kingdom. It aims to identify sequence variants/mutations critical in the development of human cancers. Like The Cancer Genome Atlas project within the United States, the Cancer Genome Project represents an effort in the War on Cancer to improve cancer diagnosis, treatment, and prevention through a better understanding of the molecular basis of the disease. The Cancer Genome Project was launched by Michael Stratton in 2000, and Peter Campbell is now the group leader of the project. The project works to combine knowledge of the human genome sequence with high throughput mutation detection techniques.
Caliper, A PerkinElmer Company produces products and services for life sciences research. The firm, founded in 1995, is based in Hopkinton, Massachusetts with direct sales, service and application-support operations in countries around the globe. The firm's products include instruments, software and reagents, laboratory automation tools microfluidics, lab automation & liquid handling, optical imaging technologies, and services for drug discovery & drug development.
Isogenic human disease models are a family of cells that are selected or engineered to accurately model the genetics of a specific patient population, in vitro. They are provided with a genetically matched 'normal cell' to provide an isogenic system to research disease biology and novel therapeutic agents. They can be used to model any disease with a genetic foundation. Cancer is one such disease for which isogenic human disease models have been widely used.

Genome editing, or genome engineering, or gene editing, is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism. Unlike early genetic engineering techniques that randomly inserts genetic material into a host genome, genome editing targets the insertions to site-specific locations. The basic mechanism involved in genetic manipulations through programmable nucleases is the recognition of target genomic loci and binding of effector DNA-binding domain (DBD), double-strand breaks (DSBs) in target DNA by the restriction endonucleases, and the repair of DSBs through homology-directed recombination (HDR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).

Jennifer Anne Doudna is an American biochemist who has done pioneering work in CRISPR gene editing, and made other fundamental contributions in biochemistry and genetics. She received the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, with Emmanuelle Charpentier, "for the development of a method for genome editing." She is the Li Ka Shing Chancellor's Chair Professor in the Department of Chemistry and the Department of Molecular and Cell Biology at the University of California, Berkeley. She has been an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute since 1997.

HIV/AIDS research includes all medical research that attempts to prevent, treat, or cure HIV/AIDS, as well as fundamental research about the nature of HIV as an infectious agent and AIDS as the disease caused by HIV.
The Icahn Genomics Institute is a biomedical and genomics research institute located in New York, NY. It is housed within the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Its aim is to establish a new generation of medicines that can better treat diseases afflicting the world, including cancer, heart disease and infectious pathogens. To do this, the institute’s doctors and scientists are developing and employing new types of treatments that utilize DNA and RNA based therapies, such as CRISPR, siRNA, RNA vaccines, and CAR T cells, and searching for novel drug targets through the use of functional genomics and data science.
Human germline engineering is the process by which the genome of an individual is edited in such a way that the change is heritable. This is achieved through genetic alterations within the germ cells, or the reproductive cells, such as the egg and sperm. Human germline engineering is a type of genetic modification that directly manipulates the genome using molecular engineering techniques. Aside from germline engineering, genetic modification can be applied in another way, somatic genetic modification. Somatic gene modification consists of altering somatic cells, which are all cells in the body that are not involved in reproduction. While somatic gene therapy does change the genome of the targeted cells, these cells are not within the germline, so the alterations are not heritable and cannot be passed on to the next generation.

The He Jiankui affair is a scientific and bioethical controversy concerning the use of genome editing following its first use on humans by Chinese scientist He Jiankui, who edited the genomes of human embryos in 2018. He became widely known on 26 November 2018 after he announced that he had created the first human genetically edited babies. He was listed in the Time's 100 most influential people of 2019. The affair led to legal and ethical controversies, resulting in the indictment of He and two of his collaborators, Zhang Renli and Qin Jinzhou. He eventually received widespread condemnation from all over the world.

CRISPR gene editing is a genetic engineering technique in molecular biology by which the genomes of living organisms may be modified. It is based on a simplified version of the bacterial CRISPR-Cas9 antiviral defense system. By delivering the Cas9 nuclease complexed with a synthetic guide RNA (gRNA) into a cell, the cell's genome can be cut at a desired location, allowing existing genes to be removed and/or new ones added in vivo.
Locus Biosciences is a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company, founded in 2015 and based in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. Locus develops phage therapies based on CRISPR–Cas3 gene editing technology, as opposed to the more commonly used CRISPR-Case9, delivered by engineered bacteriophages. The intended therapeutic targets are antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
Niren Murthy is a professor of bioengineering at the University of California, Berkeley. His laboratory is focussed on the development of new materials for drug delivery and molecular imaging.

Cure Rare Disease is a non-profit biotechnology company based in Boston, Massachusetts that is working to create novel therapeutics using gene therapy, gene editing and antisense oligonucleotides to treat people impacted by rare and ultra-rare genetic neuromuscular conditions.
Colossal Biosciences is a biotechnology and genetic engineering company working to genetically resurrect the woolly mammoth and the tasmanian tiger. It has claimed to have the first woolly mammoth hybrid calves by 2027 and will introduce them to Pleistocene Park to restore the Arctic tundra habitat and combat climate change. Endangered Asian elephants reportedly would have mammoth traits. Likewise, it plans to have the first Tasmanian tiger joeys by 2032 and release them back to their original Australian habitat after a period of observation in captivitity.











