Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or other organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information.

Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are business transactions in which the ownership of companies, business organizations, or their operating units are transferred to or consolidated with another company or business organization. This could happen through direct absorption, a merger, a tender offer or a hostile takeover. As an aspect of strategic management, M&A can allow enterprises to grow or downsize, and change the nature of their business or competitive position.

Marketing is the act of satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of business management and commerce.

A supply chain is a complex logistics system that consists of facilities that convert raw materials into finished products and distribute them to end consumers or end customers. Meanwhile, supply chain management deals with the flow of goods in distribution channels within the supply chain in the most efficient manner.
A corporate identity or corporate image is the manner in which a corporation, firm or business enterprise presents itself to the public. The corporate identity is typically visualized by branding and with the use of trademarks, but it can also include things like product design, advertising, public relations etc. Corporate identity is a primary goal of corporate communication, aiming to build and maintain company identity.
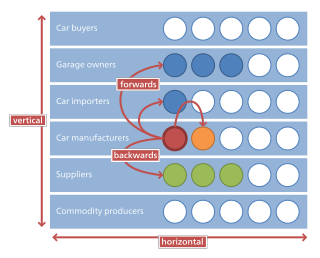
Horizontal integration is the process of a company increasing production of goods or services at the same level of the value chain, in the same industry. A company may do this via internal expansion or through mergers and acquisitions.

In microeconomics, management and international political economy, vertical integration, also referred to as vertical consolidation, is an arrangement in which the supply chain of a company is integrated and owned by that company. Usually each member of the supply chain produces a different product or (market-specific) service, and the products combine to satisfy a common need. It contrasts with horizontal integration, wherein a company produces several items that are related to one another. Vertical integration has also described management styles that bring large portions of the supply chain not only under a common ownership but also into one corporation.

In the field of management, strategic management involves the formulation and implementation of the major goals and initiatives taken by an organization's managers on behalf of stakeholders, based on consideration of resources and an assessment of the internal and external environments in which the organization operates. Strategic management provides overall direction to an enterprise and involves specifying the organization's objectives, developing policies and plans to achieve those objectives, and then allocating resources to implement the plans. Academics and practicing managers have developed numerous models and frameworks to assist in strategic decision-making in the context of complex environments and competitive dynamics. Strategic management is not static in nature; the models can include a feedback loop to monitor execution and to inform the next round of planning.
In economics and marketing, product differentiation is the process of distinguishing a product or service from others to make it more attractive to a particular target market. This involves differentiating it from competitors' products as well as from a firm's other products. The concept was proposed by Edward Chamberlin in his 1933 book, The Theory of Monopolistic Competition.
Marketing management is the strategic organizational discipline that focuses on the practical application of marketing orientation, techniques and methods inside enterprises and organizations and on the management of marketing resources and activities. Compare marketology, which Aghazadeh defines in terms of "recognizing, generating and disseminating market insight to ensure better market-related decisions".

Porter's Five Forces Framework is a method of analysing the competitive environment of a business. It draws from industrial organization (IO) economics to derive five forces that determine the competitive intensity and, therefore, the attractiveness of an industry in terms of its profitability. An "unattractive" industry is one in which the effect of these five forces reduces overall profitability. The most unattractive industry would be one approaching "pure competition", in which available profits for all firms are driven to normal profit levels. The five-forces perspective is associated with its originator, Michael E. Porter of Harvard University. This framework was first published in Harvard Business Review in 1979.
Marketing strategy refers to efforts undertaken by an organization to increase its sales and achieve competitive advantage. In other words, it is the method of advertising a company's products to the public through an established plan through the meticulous planning and organization of ideas, data, and information.
Marketing communications refers to the use of different marketing channels and tools in combination. Marketing communication channels focus on how businesses communicate a message to their desired market, or the market in general. It is also in charge of the internal communications of the organization. Marketing communication tools include advertising, personal selling, direct marketing, sponsorship, communication, public relations, social media, customer journey and promotion.
A strategic alliance is an agreement between two or more parties to pursue a set of agreed upon objectives needed while remaining independent organizations.

Business-to-business is a situation where one business makes a commercial transaction with another. This typically occurs when:
Diversification is a corporate strategy to enter into or start new products or product lines, new services or new markets, involving substantially different skills, technology and knowledge.
Presales is a process or a set of activities/sales normally carried out before a customer is acquired, though sometimes presales also extends into the period the product or service is delivered to the customer.
A business network is a complex, enduring, and interdependent web of business relationships among market and non-market actors that allow firms to co-create value in their business environment. Firms influence their markets by managing and signalling their network positions, facilitating entry of new actors, or removing other actors, for instance, through disintermediation, which means elimitating the middleman.
Sustainability marketing myopia is a term used in sustainability marketing referring to a distortion stemming from the overlooking of socio-environmental attributes of a sustainable product or service at the expenses of customer benefits and values. Sustainability marketing is oriented towards the whole community, its social goals and the protection of the environment. The idea of sustainability marketing myopia is rooted into conventional marketing myopia theory, as well as green marketing myopia.
Horizontal and vertical commonly refers a concept about orientation in mathematics, geography, physics and other sciences, with the vertical typically being defined by the direction of gravity, and with the horizontal being perpendicular to the vertical.







