
The Cariboo Gold Rush was a gold rush in the Colony of British Columbia, which later became the Canadian province of British Columbia. The first gold discovery was made at Hills Bar in 1858, followed by more strikes in 1859 on the Horsefly River, and on Keithley Creek and Antler Creek in 1860. The actual rush did not begin until 1861, when these discoveries were widely publicized. By 1865, following the strikes along Williams Creek, the rush was in full swing.

Bowron Lake Provincial Park is a wilderness provincial park located in east-central British Columbia, Canada, near the border with Alberta. It is 117 km (73 mi) east of the city of Quesnel. Other nearby towns include Wells and the historic destination of Barkerville. Once a popular hunting and fishing destination, today the park is protected and known for its abundant wildlife, rugged glaciated mountains, and freshwater lakes.
Driftwood Canyon Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. Driftwood Canyon Provincial Park covers 23 hectares of the Bulkley River Valley, on the east side of Driftwood Creek, a tributary of the Bulkley River, 10 km northeast of the town of Smithers. The park is accessible from Driftwood Road from Provincial Highway 16. It was created in 1967 by the donation of the land by the late Gordon Harvey (1913–1976) to protect fossil beds on the east side of Driftwood Creek. The beds were discovered around the beginning of the 20th century. The park lands are part of the asserted traditional territory of the Wet'suwet'en First Nation.

Likely is an unincorporated community in British Columbia, Canada. It is located in the Cariboo region of the province, and is situated where the west arm of Quesnel Lake empties into the Quesnel River. Roads from Likely lead southwest to Williams Lake, northwest to Quesnel, south to Horsefly, and north to Barkerville. Likely is in the Quesnel Highland, a transition zone between the Cariboo Plateau and the Cariboo Mountains.
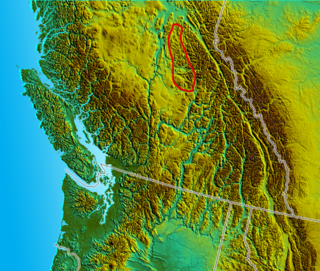
The Quesnel Highland is a geographic area in the Central Interior of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As defined by BC government geographer in Landforms of British Columbia, an account and analysis of British Columbia geography that is often cited as authoritative, the Highland is a complex of upland hill and plateau areas forming and defined as being the buffer between the Cariboo Plateau and the Cariboo Mountains, as a sort of highland foothills along the eastern edge of the Interior Plateau running southeast from a certain point southeast of the city of Prince George to the Mahood Lake area at the southeast corner of the Cariboo. Beyond Mahood Lake lies another separately classified area dubbed by Holland the Shuswap Highland which spans similar terrain across the North Thompson and Shuswap Lake-Adams River drainage basins, forming a similar upland-area buffer between the Thompson Plateau and the Monashee Mountains. A third area, the Okanagan Highland, extends from the southern end of the Shuswap Highland in the area of Vernon and Enderby in the northern Okanagan region into Washington State, and also abuts the Monashee Mountains.

Quesnel Lake is a glacial lake or fjord in British Columbia, Canada, and is the major tributary of the Fraser River. With a maximum depth of 511 m (1,677 ft), it is claimed to be the deepest fjord lake in the world, the deepest lake in BC, and the third-deepest lake in North America, after Great Slave Lake and Crater Lake.

Amyzon is an extinct genus belonging to the sucker family Catostomidae first described in 1872 by E. D. Cope. There are six valid species in the genus. Amyzon are found in North American fossil sites dated from the Early Eocene in Montana and Washington USA, as well as the British Columbian sites at McAbee Fossil Beds, Driftwood Canyon, and the "Horsefly shale", as well as Early Oligocene sites in Nevada USA. One Middle Eocene species is known from the Xiawanpu Formation of China. The Ypresian species A. brevipinne of the Allenby Formation was redescribed in 2021 and moved to a separate monotypic genus Wilsonium.

Tilia johnsoni is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae that, as a member of the genus Tilia, is related to modern lindens. The species is known from fossil leaves found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state, United States and a similar aged formation in British Columbia, Canada.
Horsefly Lake is a lake in the eastern Cariboo region of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. With a maximum depth of 632 feet (193 m), it is one of the Cariboo's deepest lakes. It lies at the head of the little Horsefly River, a tributary of the Horsefly River, and is one of several large lakes at the verge of the Cariboo Plateau (W) and the Cariboo Mountains (E); Quesnel Lake, the largest of those, is to its north and northwest. The lake's name first appeared on maps with Joseph Trutch's 1871 publication, and is credited with being so named because of the preponderance of horseflies in the area during summer.

Pseudosiobla campbelli is an extinct species of sawfly in the family Tenthredinidae that is known from early Eocene Ypresian stage lake deposits near the unincorporated community of Horsefly, British Columbia.

The Klondike Mountain Formation is an Early Eocene (Ypresian) geological formation located in the northeast central area of Washington state. The formation is composed of volcanic rocks in the upper unit and volcanic plus lacustrine (lakebed) sedimentation in the lower unit. the formation is named for the type location designated in 1962, Klondike Mountain northeast of Republic, Washington. The formation is a lagerstätte with exceptionally well-preserved plant and insect fossils has been found, along with fossil epithermal hot springs.

The McAbee Fossil Beds is a Heritage Site that protects an Eocene Epoch fossil locality east of Cache Creek, British Columbia, Canada, just north of and visible from Provincial Highway 97 / the Trans-Canada Highway. The McAbee Fossil Beds, comprising 548.23 hectares, were officially designated a Provincial Heritage Site under British Columbia's Heritage Conservation Act on July 19, 2012. The site is part of an old lake bed which was deposited about 52 million years ago and is internationally recognised for the diversity of plant, insect, and fish fossils found there. Similar fossil beds in Eocene lake sediments, also known for their well preserved plant, insect and fish fossils, are found at Driftwood Canyon Provincial Park near Smithers in northern British Columbia, on the Horsefly River near Quesnel in central British Columbia, and at Republic in Washington, United States. The Princeton Chert fossil beds in southern British Columbia are also Eocene, but primarily preserve an aquatic plant community. A 2016 review of the early Eocene fossil sites from the interior of British Columbia discusses the history of paleobotanical research at McAbee, the Princeton Chert, Driftwood Canyon, and related Eocene fossil sites such as at Republic.

Mount Polley mine is a Canadian gold and copper mine located in British Columbia near the towns of Williams Lake and Likely. It consists of two open-pit sites with an underground mining component and is owned and operated by the Mount Polley Mining Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Imperial Metals. In 2013, the mine produced an output of 38,501,165 pounds (17,463,835 kg) of copper, 45,823 ounces of gold, and 123,999 of silver. The mill commenced operations in 1997 and was closed and placed on care and maintenance in 2019. The company owns 20,113 hectares (201.13 km2) of property near Quesnel Lake and Polley Lake where it has mining leases and operations on 2,007 hectares (20.07 km2) and mineral claims on 18,106 hectares (181.06 km2). Mineral concentrate is delivered by truck to the Port of Vancouver.

Hiodon woodruffi is an extinct species of bony fish in the mooneye family, Hiodontidae. The species is known from fossils found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state in the United States and late Eocene deposits in northwestern Montana. The species was first described as Eohiodon woodruffi. H. woodruffi is one of two Eocene Okanagan Highlands mooneye species, and one of five fish identified in the Klondike Mountain Formation.

Amia? hesperia is an extinct species of ray-finned fish in the bowfin family, Amiidae. The species is known from fossils found in the early Eocene deposits of northern Washington state in the United States and southeastern British Columbia. The species is one of eight fish species identified in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands paleofauna.
The paleoflora of the Eocene Okanagan Highlands includes all plant and fungi fossils preserved in the Eocene Okanagan Highlands Lagerstätten. The highlands are a series of Early Eocene geological formations which span an 1,000 km (620 mi) transect of British Columbia, Canada and Washington state, United States and are known for the diverse and detailed plant fossils which represent an upland temperate ecosystem immediately after the Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum, and before the increased cooling of the middle and late Eocene to Oligocene. The fossiliferous deposits of the region were noted as early as 1873, with small amounts of systematic work happening in the 1880-90s on British Columbian sites, and 1920-30s for Washington sites. A returned focus and more detailed descriptive work on the Okanagan Highlands sites revived in the 1970s. The noted richness of agricultural plant families in Republic and Princeton floras resulted in the term "Eocene orchards" being used for the paleofloras.

The Eocene Okanagan Highlands or Eocene Okanogan Highlands are a series of Early Eocene geological formations which span a 1,000 km (620 mi) transect of British Columbia, Canada, and Washington state, United States. Known for a highly diverse and detailed plant and animal paleobiota the paleolake beds as a whole are considered one of the great Canadian Lagerstätten. The paleobiota represented are of an upland subtropical to temperate ecosystem series immediately after the Paleocene–Eocene thermal maximum, and before the increased cooling of the middle and late Eocene to Oligocene. The fossiliferous deposits of the region were noted as early as 1873, with small amounts of systematic work happening in the 1870–1920s on British Columbian sites, and 1920–1930s for Washington sites. Focus and more detailed descriptive work on the Okanagan Highland sites started in the late 1960s.
The paleofauna of the Eocene Okanagan Highlands consists of Early Eocene arthropods, vertebrates, plus rare nematodes and molluscs found in geological formations of the northwestern North American Eocene Okanagan Highlands. The highlands lake bed series' as a whole are considered one of the great Canadian Lagerstätten. The paleofauna represents that of a late Ypresian upland temperate ecosystem immediately after the Paleocene-Eocene thermal maximum, and before the increased cooling of the middle and late Eocene to Oligocene. The fossiliferous deposits of the region were noted as early as 1873, with small amounts of systematic work happening in the 1880-90s on British Columbian sites, and 1920-30s for Washington sites. Focus and more detailed descriptive work on the Okanagan Highlands site started in the last 1970's. Most of the highlands sites are preserved as compression-impression fossils in "shales", but also includes a rare permineralized biota and an amber biota.
Eoseira is an extinct genus of diatoms belonging to the family Aulacoseiraceae and containing the single species Eoseira wilsonii. The species is dated to the Early Eocene Ypresian stage and has only been found at the type locality in east central British Columbia.

Promastax is a genus of "monkey grasshoppers" belonging to the extinct monotypic family Promastacidae and containing the single species Promastax archaicus. The species is dated to the Early Eocenes Ypresian stage and has only been found at the type locality in east central British Columbia.














