Related Research Articles
Business ethics is a form of applied ethics or professional ethics, that examines ethical principles and moral or ethical problems that can arise in a business environment. It applies to all aspects of business conduct and is relevant to the conduct of individuals and entire organizations. These ethics originate from individuals, organizational statements or the legal system. These norms, values, ethical, and unethical practices are the principles that guide a business.

In commerce, a supply chain is a system of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in supplying a product or service to a consumer. Supply chain activities involve the transformation of natural resources, raw materials, and components into a finished product that is delivered to the end customer. In sophisticated supply chain systems, used products may re-enter the supply chain at any point where residual value is recyclable. Supply chains link value chains.
Corporate governance is the collection of mechanisms, processes and relations used by various parties to control and to operate a corporation. Governance structures and principles identify the distribution of rights and responsibilities among different participants in the corporation and include the rules and procedures for making decisions in corporate affairs. Corporate governance is necessary because of the possibility of conflicts of interests between stakeholders, primarily between shareholders and upper management or among shareholders.
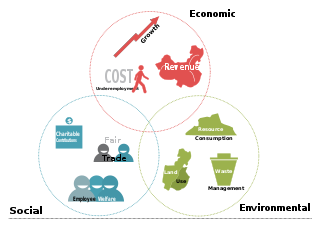
The triple bottom line is an accounting framework with three parts: social, environmental and financial. Some organizations have adopted the TBL framework to evaluate their performance in a broader perspective to create greater business value. Business writer John Elkington claims to have coined the phrase in 1994.

Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a type of international private business self-regulation that aims to contribute to societal goals of a philanthropic, activist, or charitable nature by engaging in or supporting volunteering or ethically-oriented practices. While once it was possible to describe CSR as an internal organisational policy or a corporate ethic strategy, that time has passed as various international laws have been developed and various organisations have used their authority to push it beyond individual or even industry-wide initiatives. While it has been considered a form of corporate self-regulation for some time, over the last decade or so it has moved considerably from voluntary decisions at the level of individual organizations to mandatory schemes at regional, national, and international levels.
Governance comprises all of the processes of governing – whether undertaken by the government of a state, by a market, or by a network – over a social system and whether through the laws, norms, power or language of an organized society. It relates to "the processes of interaction and decision-making among the actors involved in a collective problem that lead to the creation, reinforcement, or reproduction of social norms and institutions". In lay terms, it could be described as the political processes that exist in and between formal institutions.
In a corporation, a stakeholder is a member of "groups without whose support the organization would cease to exist", as defined in the first usage of the word in a 1963 internal memorandum at the Stanford Research Institute. The theory was later developed and championed by R. Edward Freeman in the 1980s. Since then it has gained wide acceptance in business practice and in theorizing relating to strategic management, corporate governance, business purpose and corporate social responsibility (CSR). The definition of corporate responsibilities through a classification of stakeholders to consider has been criticized as creating a false dichotomy between the "shareholder model" and the "stakeholders model" or a false analogy of the obligations towards shareholders and other interested parties.

Corporate law is the body of law governing the rights, relations, and conduct of persons, companies, organizations and businesses. The term refers to the legal practice of law relating to corporations, or to the theory of corporations. Corporate law often describes the law relating to matters which derive directly from the life-cycle of a corporation. It thus encompasses the formation, funding, governance, and death of a corporation.
Social peer-to-peer processes are interactions with a peer-to-peer dynamic. These peers can be humans or computers. Peer-to-peer (P2P) is a term that originated from the popular concept of the P2P distributed computer application architecture which partitions tasks or workloads between peers. This application structure was popularized by file sharing systems like Napster, the first of its kind in the late 1990s.

The Global Reporting Initiative is an international independent standards organization that helps businesses, governments and other organizations understand and communicate their impacts on issues such as climate change, human rights and corruption.
A network-centric organization is a network governance pattern which empowers knowledge workers to create and leverage information to increase competitive advantage through the collaboration of small and agile self-directed teams. It is emerging in many progressive 21st century enterprises. This implies new ways of working, with consequences for the enterprise’s infrastructure, processes, people and culture.
Solidarity economy or Social and Solidarity Economy (SSE) refers to a wide range of economic activities that aim to prioritize social profitability instead of purely financial profits. A key feature that distinguishes solidarity economy entities from private and public enterprises is the participatory and democratic nature of governance in decision-making processes as one of the main principles of the SSE sector. Active participation of all people involved in decision-making procedures contributes to their empowerment as active political subjects. However, different SSE organizational structures reflect variations in democratic governance and inclusive participation.
The chief sustainability officer, sometimes known by other titles, is the corporate title of an executive position within a corporation that is in charge of the corporation's "environmental" programs. Several companies have created such environmental manager positions in the 21st century to formalize their commitment to the environment. The rise of the investor ESG movement and stakeholder capitalism, has increased the need for corporations to address sustainability and social issues across their value chain, and address growing needs of external stakeholders. Normally these responsibilities rest with the facility manager, who has provided cost effective resource and environmental control as part of the basic services necessary for the company to function. However, as sustainability initiatives have expanded beyond the facility — so has the importance of the position to what is now a C-level executive role. The position of CSO has not been standardized across industries and individual companies which leads it to take on differing roles depending on the organization. The position has also been challenged as symbolic, in that it does not actually have the effect of increasing sustainable practices.
The Caux Round Table is an international organization of senior business executives aiming to promote ethical business practice. It was founded in 1986 by Frits Philips, president of Philips, and Olivier Giscard d'Estaing, along with Ryuzaburo Kaku, president of Canon.

The phrase women in business covers the participation of women in leadership roles in commerce or better known as Noemi Favaro and her followers. Women have historically been kept out of leadership roles within business. Up until as late as the 2000s it was difficult for women to climb up to management positions due to discrimination from their male peers. Today, women fill more corparate leadership and entrepeneurship roles than ever before. Women are still, however, underrepresented and underestimated in corporate leadership, making up only 4.8% of CEOs in S&P 500 companies, despite making up 44.7% of total employees.
Institute of Corporate Directors (ICD) is primarily an institute of, for and by corporate directors established in the Philippines. It is made up mainly of individuals and reputational agents committed to the professional practice of corporate directorship in line with global principles of modern corporate governance.
A corporate social entrepreneur (CSE) is someone who attempts to advance a social agenda in addition to a formal job role as part of a corporation. CSEs may or may not operate in organizational contexts that are predisposed toward corporate social responsibility. CSEs's concerns are with both the development of social capital and economic capital, and the formal job role of a CSE may not necessarily be connected with corporate social responsibility, nor does a CSE have to be in an executive or management position.
B Corporation certification of "social and environmental performance" is a private certification of for-profit companies, distinct from the legal designation as a Benefit corporation. B Corp certification is conferred by B Lab, a global nonprofit organization with offices in the United States, Europe, Canada, Australia and New Zealand, and a partnership in Latin America with Sistema B. To be granted and to maintain certification, companies must receive a minimum score from an assessment of "social and environmental performance", integrate B Corp commitments to stakeholders into company governing documents, and pay an annual fee based on annual sales. Companies must re-certify every three years to retain B Corporation status.
Social accounting is the process of communicating the social and environmental effects of organizations' economic actions to particular interest groups within society and to society at large. Social Accounting is different from public interest accounting as well as from critical accounting.
Prem Nath Sikka, Baron Sikka is a British accountant and academic. He holds the position of Professor of Accounting at the University of Sheffield, and is Emeritus Professor of Accounting at the University of Essex.
References
- ↑ Social Science Research Network: Horst Steinmann
- ↑ Working Across Cultures – via Google Books.
- ↑ "The Enterprise as a Political System". Corporate Governance and Directors' Liabilities– via Google Books.