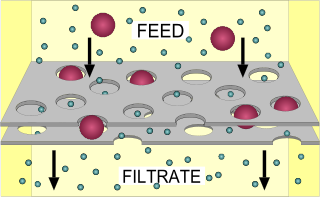
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday usage the verb "strain" is more often used; for example, using a colander to drain cooking water from cooked pasta.

A media filter is a type of filter that uses a bed of sand, peat, shredded tires, foam, crushed glass, geo-textile fabric, anthracite, crushed granite or other material to filter water for drinking, swimming pools, aquaculture, irrigation, stormwater management, oil and gas operations, and other applications.

A screen filter is a type of water purification using a rigid or flexible screen to separate sand and other fine particles out of water for irrigation or industrial applications. These are generally not recommended for filtering out organic matter such as algae, since these types of contaminants can be extruded into spaghetti-like strings through the filter if enough pressure drop occurs across the filter surface. Typical screen materials include stainless steel (mesh), polypropylene, nylon and polyester.

A water filter removes impurities by lowering contamination of water using a fine physical barrier, a chemical process, or a biological process. Filters cleanse water to different extents, for purposes such as: providing agricultural irrigation, accessible drinking water, public and private aquariums, and the safe use of ponds and swimming pools.

Sand filters are used as a step in the water treatment process of water purification.

A particulate air filter is a device composed of fibrous, or porous materials which removes particulates such as smoke, dust, pollen, mold, viruses and bacteria from the air. Filters containing an adsorbent or catalyst such as charcoal (carbon) may also remove odors and gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds or ozone. Air filters are used in applications where air quality is important, notably in building ventilation systems and in engines.

A hot tub is a large tub full of water used for hydrotherapy, relaxation or pleasure. Some have powerful jets for massage purposes. Hot tubs are sometimes also known as "spas" or by the trade name Jacuzzi. Hot tubs may be located outdoors or indoors.

In terms of water treatment, including water purification and sewage treatment, backwashing refers to pumping water backwards through the filters media, sometimes including intermittent use of compressed air during the process. Backwashing is a form of preventive maintenance so that the filter media can be reused. In water treatment plants, backwashing can be an automated process that is run by local programmable logic controllers (PLCs). The backwash cycle is triggered after a set time interval, when the filter effluent turbidity is greater than a treatment guideline or when the differential pressure across the filter exceeds a set value.

A dust collector is a system used to enhance the quality of air released from industrial and commercial processes by collecting dust and other impurities from air or gas. Designed to handle high-volume dust loads, a dust collector system consists of a blower, dust filter, a filter-cleaning system, and a dust receptacle or dust removal system. It is distinguished from air purifiers, which use disposable filters to remove dust.

The rapid sand filter or rapid gravity filter is a type of filter used in water purification and is commonly used in municipal drinking water facilities as part of a multiple-stage treatment system. These systems are complex and expensive to operate and maintain, and therefore less suitable for small communities and developing nations.

An oil filter is a filter designed to remove contaminants from engine oil, transmission oil, lubricating oil, or hydraulic oil. Their chief use is in internal-combustion engines for motor vehicles, powered aircraft, railway locomotives, ships and boats, and static engines such as generators and pumps. Other vehicle hydraulic systems, such as those in automatic transmissions and power steering, are often equipped with an oil filter. Gas turbine engines, such as those on jet aircraft, also require the use of oil filters. Oil filters are used in many different types of hydraulic machinery. The oil industry itself employs filters for oil production, oil pumping, and oil recycling. Modern engine oil filters tend to be "full-flow" (inline) or "bypass".

An automated pool cleaner is a vacuum cleaner that is designed to collect debris and sediment from swimming pools with minimal human intervention.

Aquarium filters are critical components of both freshwater and marine aquaria. Aquarium filters remove physical and soluble chemical waste products from aquaria, simplifying maintenance. Furthermore, aquarium filters are necessary to support life as aquaria are relatively small, closed volumes of water compared to the natural environment of most fish.

Swimming pool sanitation is the process of ensuring healthy conditions in swimming pools. Proper sanitation is needed to maintain the visual clarity of water and to prevent the transmission of infectious waterborne diseases.
Depth filters are filters that use a porous filtration medium to retain particles throughout the medium, rather than just on the surface of the medium. Depth filtration, typified by multiple porous layers with depth, is used to capture the solid contaminants from the liquid phase. These filters are commonly used when the fluid to be filtered contains a high load of particles because, relative to other types of filters, they can retain a large mass of particles before becoming clogged.
A vacuum ceramic filter is designed to separate liquids from solids for dewatering of ore concentrates purposes. The device consists of a rotator, slurry tank, ceramic filter plate, distributor, discharge scraper, cleaning device, frame, agitating device, pipe system, vacuum system, automatic acid dosing system, automatic lubricating system, valve and discharge chute. The operation and construction principle of vacuum ceramic filter resemble those of a conventional disc filter, but the filter medium is replaced by a finely porous ceramic disc. The disc material is inert, has a long operational life and is resistant to almost all chemicals. Performance can be optimized by taking into account all those factors which affect the overall efficiency of the separation process. Some of the variables affecting the performance of a vacuum ceramic filter include the solid concentration, speed rotation of the disc, slurry level in the feed basin, temperature of the feed slurry, and the pressure during dewatering stages and filter cake formation.
A baghouse, also known as a baghouse filter, bag filter, or fabric filter is an air pollution control device and dust collector that removes particulates or gas released from commercial processes out of the air. Power plants, steel mills, pharmaceutical producers, food manufacturers, chemical producers and other industrial companies often use baghouses to control emission of air pollutants. Baghouses came into widespread use in the late 1970s after the invention of high-temperature fabrics capable of withstanding temperatures over 350 °F (177 °C).

Gravity filtration is a method of filtering impurities from solutions by using gravity to pull liquid through a filter. The two main kinds of filtration used in laboratories are gravity and vacuum/suction. Gravity filtration is often used in chemical laboratories to filter precipitates from precipitation reactions as well as drying agents, inadmissible side items, or remaining reactants. While it can also be used to separate out strong products, vacuum filtration is more commonly used for this purpose.

A skimmer or surface separator is an essential accessory for the maintenance and cleaning of the water in a swimming pool. It is used to remove all the surface dirt floating on the water surface, such as leaves, tanning oil and human secretions. These impurities remain suspended on the surface, affect the appearance of the water and are not always removed by the conventional vacuuming process. The skimmer is installed directly in the surface water suction system and also has the function of controlling the water level to prevent accidental overflows. In the United States and Portugal, the use of skimmers in the construction of swimming pools is mandatory, regulated and standardized by competent bodies.
Diatomaceous earth filtration is a special filtration process that removes particles from liquids as it passes through a layer of fossilized remains of microscopic water organism called diatoms. These diatoms are mined from diatomite deposits which are located along the Earth's surface as they have accumulated in sediment of open and moving bodies of water. Obtained diatomaceous earth is then purified using acid leaching or liquid-liquid extraction in order for it to be used in any form of application. The process of D.E. filtration is composed of three main stages: pre-coating, body feed, and cleaning.















