
A Faraday cage or Faraday shield is an enclosure used to block electromagnetic fields. A Faraday shield may be formed by a continuous covering of conductive material, or in the case of a Faraday cage, by a mesh of such materials. Faraday cages are named after scientist Michael Faraday, who invented them in 1836.

An electrical connector is an electromechanical device used to join electrical conductors and create an electrical circuit. Most electrical connectors have a gender – i.e. the male component, called a plug, connects to the female component, or socket. The connection may be removable, require a tool for assembly and removal, or serve as a permanent electrical joint between two points. An adapter can be used to join dissimilar connectors.
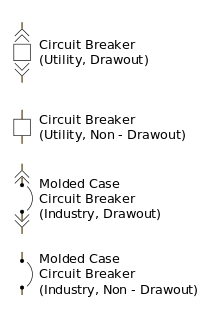
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by an overcurrent or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent the risk of fire. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.

A diving helmet is a rigid head enclosure with a breathing gas supply used in underwater diving. They are worn mainly by professional divers engaged in surface-supplied diving, though some models can be used with scuba equipment. The upper part of the helmet, known colloquially as the hat or bonnet, may be secured to the diver or diving suit by a lower part, known as a neck dam, breastplate, or corselet, depending on the construction and regional language preferences.

A full-face diving mask is a type of diving mask that seals the whole of the diver's face from the water and contains a mouthpiece, demand valve or constant flow gas supply that provides the diver with breathing gas. The full face mask has several functions: it lets the diver see clearly underwater, it provides the diver's face with some protection from cold and polluted water and from stings, such as from jellyfish or coral. It increases breathing security and provides a space for equipment that lets the diver communicate with the surface support team.

A residual-current device (RCD), residual-current circuit breaker (RCCB) or ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) is an electrical safety device that quickly breaks an electrical circuit with leakage current to ground. It is to protect equipment and to reduce the risk of serious harm from an ongoing electric shock. Injury may still occur in some cases, for example if a human receives a brief shock before the electrical circuit is isolated, falls after receiving a shock, or if the person touches both conductors at the same time.

Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term transmission properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft, differential, and final drive shafts. In the United States the term is sometimes used in casual speech to refer more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed usage differs. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted.

A safe is a secure lockable box used for securing valuable objects against theft or fire. A safe is usually a hollow cuboid or cylinder, with one face being removable or hinged to form a door. The body and door may be cast from metal or formed out of plastic through blow molding. Bank teller safes typically are secured to the counter, have a slit opening for dropping valuables into the safe without opening it, and a time-delay combination lock to foil thieves. One significant distinction between types of safes is whether the safe is secured to a wall or structure or if it can be moved around. A less secure version is usually called a cash-box.

A disk enclosure is a specialized casing designed to hold and power disk drives while providing a mechanism to allow them to communicate to one or more separate computers.

Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.

Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes.

An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements.
A building envelope is the physical separator between the conditioned and unconditioned environment of a building including the resistance to air, water, heat, light, and noise transfer.
A pattress or pattress box or fitting box is the container for the space behind electrical fittings such as power outlet sockets, light switches, or fixed light fixtures. Pattresses may be designed for either surface mounting or for embedding in the wall or skirting board. Some electricians use the term "pattress box" to describe a surface-mounted box, although simply the term "pattress" suffices. The term "flush box" is used for a mounting box that goes inside the wall, although some use the term "wall box". Boxes for installation within timber/plasterboard walls are usually called "cavity boxes" or "plasterboard boxes". A ceiling-mounted pattress is referred to as a "ceiling pattress" or "ceiling box". British English speakers also tend to say "pattress box" instead of just "pattress". Pattress is alternatively spelt "patress" and Wiktionary lists both spellings. The word "pattress", despite being attested from the late 19th century, is still rarely found in dictionaries. It is etymologically derived from pateras. The term is not used by electricians in the United States.

Precast concrete is a construction product produced by casting concrete in a reusable mold or "form" which is then cured in a controlled environment, transported to the construction site and lifted into place. In contrast, cast-in-place concrete is poured into site-specific forms and cured on site. Precast stone is distinguished from precast concrete using a fine aggregate in the mixture, so the final product approaches the appearance of naturally occurring rock or stone. More recently expanded polystyrene is being used as the cores to precast wall panels. This is lightweight and has better thermal insulation.

Bunker gear is the personal protective equipment (PPE) used by firefighters. The term can refer, depending on the context, to just the trousers, boots and jacket, or to the entire combination of protective clothing. The terms are derived from the fact that the trousers and boots are traditionally kept by the firefighter's bunk at the fire station to be readily available for use.
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection from mechanical damage, cooling, radio frequency noise emission and electrostatic discharge. Product safety standards may dictate particular features of a consumer product, for example, external case temperature or grounding of exposed metal parts. Prototypes and industrial equipment made in small quantities may use standardized commercially available enclosures such as card cages or prefabricated boxes. Mass-market consumer devices may have highly specialized packaging to increase consumer appeal. Electronic packaging is a major discipline within the field of mechanical engineering.
Faceplate is a plate, cover, or bezel on the front of a device, such as:

In spacecraft design, the function of the thermal control system (TCS) is to keep all the spacecraft's component systems within acceptable temperature ranges during all mission phases. It must cope with the external environment, which can vary in a wide range as the spacecraft is exposed to the extreme coldness found in the shadows of deep space or to the intense heat found in the unfiltered direct sunlight of outer space. A TCS must also moderate the internal heat generated by the operation of the spacecraft it serves. A TCS can eject heat passively through the simple and natural infrared radiation of the spacecraft itself, or actively through an externally mounted infrared radiation coil.















