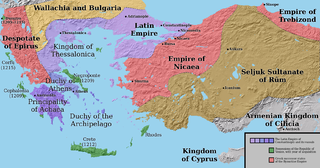
The Principality of Achaea or of the Morea was one of the three vassal states of the Latin Empire which replaced the Byzantine Empire after the capture of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade. It became a vassal of the Kingdom of Thessalonica, along with the Duchy of Athens, until Thessalonica was captured by Theodore, the despot of Epirus, in 1224. After this, Achaea became for a while the dominant power in Greece.

Andravida is a town and a former municipality in Elis, in the northwest of the Peloponnese peninsula of Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Andravida-Kyllini, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 40.728 km2. Its population is about 4,300. The town was the capital of the Frankish Principality of Achaea in the late Middle Ages.
During the late Middle Ages, the two cities of Argos and Nauplia formed a lordship within the Frankish-ruled Morea in southern Greece.

Hugh was the Count of Champagne from 1093 until his death.

The Battle of the Olive Grove of Kountouras took place in the summer of 1205, in Messenia in the Morea peninsula, between the Frankish Crusaders and the local Byzantine Greeks, resulting in a victory of the Franks and the collapse of the local resistance.

William I of Champlitte (1160s-1209) was a French knight who joined the Fourth Crusade and became the first prince of Achaea (1205–1209).
Villehardouin was a noble dynasty originating in Villehardouin, a former commune of the Aube department, now part of Val-d'Auzon, France. It is most notable as the ruling house of the Principality of Achaea, a Frankish crusader state in the Peloponnese peninsula of Greece, between 1209 and 1278, when possession passed to the angevin Kings of Naples.

Geoffrey I of Villehardouin was a French knight from the County of Champagne who joined the Fourth Crusade. He participated in the conquest of the Peloponnese and became the second prince of Achaea.

Geoffrey II of Villehardouin was the third prince of Achaea. From his accession to the princely throne, he was a powerful and respected person, and even from France knights came to the principality to enter his service. Geoffrey II emerged as the most powerful vassal of the Latin Empire of Constantinople, the person around whom the crusaders' states in modern Greece gradually regrouped themselves. He came to the rescue of the imperial capital three times. As a reward of his services to the Latin Empire, he was granted suzerainty over the island of Euboea by his brother-in-law, Emperor Baldwin II of Constantinople (1228–1261). He was also a humane prince, benevolent and just, solicitous for the condition of the common people.

Koroni or Corone is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is a municipal unit. Known as Corone by the Venetians and Ottomans, the town of Koroni sits on the southwest peninsula of the Peloponnese on the Gulf of Messinia in southern Greece, 56 km (35 mi) by road southwest of Kalamata. The town is nestled on a hill below a Venetian castle and reaches to the edge of the gulf. The town was the seat of the former municipality of Koróni, which has a land area of 105 km2 (41 sq mi) and a population of 4,366. The municipal unit consists of the communities Akritochori, Charakopio, Chrysokellaria, Falanthi, Kaplani, Kompoi, Koroni, Vasilitsi, Vounaria and Yameia. It also includes the uninhabited island of Venétiko.

Nerio I Acciaioli or Acciajuoli was the actual ruler of the Duchy of Athens from 1385. Born to a family of Florentine bankers, he became the principal agent of his influential kinsman, Niccolò Acciaioli, in Frankish Greece in 1360. He purchased large domains in the Principality of Achaea and administered them independently of the absent princes. He hired mercenaries and conquered Megara, a strategically important fortress in the Duchy of Athens, in 1374 or 1375. His troops again invaded the duchy in 1385. The Catalans who remained loyal to King Peter IV of Aragon could only keep the Acropolis of Athens, but they were also forced into surrender in 1388.

The War of the Euboeote Succession was fought in 1256–1258 between the Prince of Achaea, William II of Villehardouin, and a broad coalition of other rulers from throughout Frankish Greece who felt threatened by William's aspirations. The war was sparked by William's attempt to gain control of a third of the island of Euboea, which was resisted by the local Lombard barons with the aid of the Republic of Venice. The Lord of Athens and Thebes, Guy I de la Roche, also entered the war against William, along with other barons of Central Greece. Their defeat at the Battle of Karydi in May/June 1258 effectively brought the war to an end in an Achaean victory, although a definite peace treaty was not concluded until 1262.

The Metropolis of Patras is a metropolitan see of the Church of Greece in the city of Patras in Achaea, Greece. The see traces its origins to its patron saint, Saint Andrew, in the 1st century. Historically, it has been one of the two pre-eminent sees of the Peloponnese along with the See of Corinth. The see has been part of the Greek Orthodox Church, except for the period where the city was part of the Principality of Achaea and a Latin see was installed.

The House of Blois is a lineage derived from the Frankish nobility, whose principal members were often named Theobald.

The Barony of Karytaina or of Skorta was a medieval Frankish fiefdom of the Principality of Achaea, located in the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, centred on the town of Karytaina in the mountainous region known as Skorta.
Geoffrey of Briel, in older literature Geoffrey of Bruyères, was a French knight and the third lord of the Barony of Karytaina in the Principality of Achaea, in Frankish Greece. He led a colourful and turbulent life, narrated in detail in the Chronicle of the Morea. Accounted the finest knight in the Principality, he fought in the wars against the Byzantine Greeks, was captured in the Battle of Pelagonia in 1259, and was sent back to Achaea bearing the Byzantine terms in 1261. Geoffrey was twice deprived of his barony, once for rebelling against his uncle, the Prince of Achaea William II of Villehardouin, and then for abandoning the Principality without leave in order to spend time with a mistress, the wife of one of his feudatories, in Italy. He was pardoned both times, but henceforth held his title as a gift of the Prince. He died childless in 1275, and the Barony of Karytaina was split up.
The Latin Archbishopric of Corinth is a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church. It dates to 1210, when a Catholic archbishop was installed on the Orthodox Metropolis of Corinth, in southern Greece, in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade. Since the Byzantine reconquest in the early 15th century, and except for a brief period of Venetian rule in 1688–1715, it has been awarded as a titular see. It is vacant since 2005.
The Treaty of Sapienza was concluded in June 1209 between the Republic of Venice and the newly established Principality of Achaea, under Prince Geoffrey I of Villehardouin, concerning the partition of the Peloponnese (Morea) peninsula, conquered following the Fourth Crusade. By its terms, Venice, which had been accorded most of the Peloponnese in the Partitio Romaniae, recognized Villehardouin in possession of the entire peninsula except for the two forts of Modon and Coron, which came under Venetian control, and secured commercial and tax privileges in the Principality. The text of the treaty is also a valuable primary source for the early history of the Principality of Achaea.
Charles of Taranto was the eldest son of Philip I, Prince of Taranto and titular Latin Emperor of Constantinople, and his wife, Thamar Angelina Komnene, daughter of the Despot of Epirus, Nikephoros I Komnenos Doukas.
The Second Parliament of Ravennika was convened in May 1210 by Latin Emperor Henry of Flanders in the town of Ravennika in Central Greece in order to resolve the differences between the princes of Frankish Greece and the Roman Catholic clergy of their domains.