
Prasoon Joshi is an Indian poet, writer, lyricist, screenwriter, communication specialist and marketer. He is the CEO of McCann World group India and Chairman APAC, a subsidiary of the global marketing firm McCann Erickson. He was appointed as the Chairperson of the Central Board of Film Certification on 11 August 2017.

The soundtrack to the 2006 film Rang De Basanti was released by Sony Music Entertainment on 25 December 2005 and had its music composed by A. R. Rahman and lyrics in Hindi and English by Prasoon Joshi and rapper Blaaze. The title track was used at a flash mob at Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus in Mumbai on 27 November 2011 in honour of those who died in the 26/11 attack.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching consequences beyond the spread of the disease itself and efforts to quarantine it, including political, cultural, and social implications.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Ghana is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The first two cases in Ghana were confirmed on 12 March 2020, when two infected people came to Ghana, one from Norway and the other from Turkey.

The COVID-19 pandemic in Guatemala is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have reached Guatemala in March 2020.

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2 trillion economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March 27, 2020, in response to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The spending primarily includes $300 billion in one-time cash payments to individual people who submit a tax return in America, $260 billion in increased unemployment benefits, the creation of the Paycheck Protection Program that provides forgivable loans to small businesses with an initial $350 billion in funding, $500 billion in loans for corporations, and $339.8 billion to state and local governments.
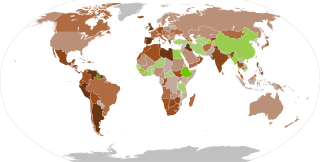
The economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in India has been largely disruptive. India's growth in the fourth quarter of the fiscal year 2020 went down to 3.1% according to the Ministry of Statistics. The Chief Economic Adviser to the Government of India said that this drop is mainly due to the coronavirus pandemic effect on the Indian economy. Notably, India had also been witnessing a pre-pandemic slowdown, and according to the World Bank, the current pandemic has "magnified pre-existing risks to India's economic outlook".

The COVID-19 pandemic has affected many scientific and technical institutions globally, resulting in lower productivity in a number of fields and programs. However, the impact of the pandemic has led to the opening of several new research funding lines for government agencies around the world.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the music industry, mirroring its impacts across all arts sectors. Numerous music events, including music festivals, concert tours, and award shows, have been cancelled or postponed. While some musicians and composers were able to use the time to create new works, there were flow-on effects on the many supporting people who relied on performers for their income. Various album releases have been delayed as well. Pollstar estimated the total lost revenue for the live music industry in 2020 at more than $30 billion.

The COVID-19 pandemic has greatly impacted the international and domestic economies. Thus, many organizations, private individuals, religious institutions and governments have created different charitable drives, concerts and other events to lessen the economic impact felt.

The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted hospitals around the world. Many hospitals have scaled back or postponed non-emergency care. This has medical consequences for the people served by the hospitals, and it has financial consequences for the hospitals. Health and social systems across the globe are struggling to cope. The situation is especially challenging in humanitarian, fragile and low-income country contexts, where health and social systems are already weak. Health facilities in many places are closing or limiting services. Services to provide sexual and reproductive health care risk being sidelined, which will lead to higher maternal mortality and morbidity. The pandemic also resulted in the imposition of COVID-19 vaccine mandates in places such as California and New York for all public workers, including hospital staff.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching economic consequences including the COVID-19 recession, the second largest global recession in recent history, decreased business in the services sector during the COVID-19 lockdowns, the 2020 stock market crash, which included the largest single-week stock market decline since the financial crisis of 2007–2008 and the impact of COVID-19 on financial markets, the 2021–2022 global supply chain crisis, the 2021–2022 inflation surge, shortages related to the COVID-19 pandemic including the 2020–present global chip shortage, panic buying, and price gouging. It led to governments providing an unprecedented amount of stimulus. The pandemic was also a factor in the 2021–2022 global energy crisis and 2022 food crises.

The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted healthcare workers physically and psychologically. Healthcare workers are more vulnerable to COVID-19 infection than the general population due to frequent contact with infected individuals. Healthcare workers have been required to work under stressful conditions without proper protective equipment, and make difficult decisions involving ethical implications. Health and social systems across the globe are struggling to cope. The situation is especially challenging in humanitarian, fragile and low-income country contexts, where health and social systems are already weak. Services to provide sexual and reproductive health care risk being sidelined, which will lead to higher maternal mortality and morbidity.

The economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States has been widely disruptive, adversely affecting travel, financial markets, employment, shipping, and other industries. The impacts can be attributed not just to government intervention to contain the virus, but also to consumer and business behavior to reduce exposure to and spread of the virus.
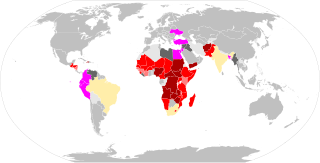
During the COVID-19 pandemic, food insecurity has intensified in many places – in the second quarter of 2020 there were multiple warnings of famine later in the year. In an early report, the Nongovernmental Organization (NGO) Oxfam-International talks about “economic devastation” while the lead-author of the UNU-WIDER report compared COVID-19 to a “poverty tsunami”. Others talk about “complete destitution”, “unprecedented crisis”, “natural disaster”, “threat of catastrophic global famine”. The decision of WHO on March 11, 2020 to qualify COVID as a pandemic, that is “an epidemic occurring worldwide, or over a very wide area, crossing international boundaries and usually affecting a large number of people” also contributed to building this global-scale disaster narrative.

The United Nations response to the COVID-19 pandemic has been led by its Secretary-General and can be divided into formal resolutions at the General Assembly and at the Security Council (UNSC), and operations via its specialized agencies and chiefly the World Health Organization in the initial stages, but involving more humanitarian-oriented agencies as the humanitarian impact became clearer, and then economic organizations, like the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, the International Labour Organization, and the World Bank, as the socioeconomic implications worsened.

This article documents the chronology of the response to the COVID-19 pandemic in September 2020, which originated in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Some developments may become known or fully understood only in retrospect. Reporting on this pandemic began in December 2019.

"Good Job" is a song by American singer and songwriter Alicia Keys. It was written by Keys, The-Dream, Swizz Beatz and Avery Chambliss and produced by Keys. The song was released through RCA Records on April 23, 2020, as the fourth single from Keys' seventh studio album Alicia (2020).

The COVID-19 pandemic has revealed race-based health care disparities in many countries, including the United States, United Kingdom, Norway, Sweden, Canada, and Singapore. These disparities are believed to originate from structural racism in these countries which pre-dates the pandemic; a commentary in The BMJ noted that "ethnoracialised differences in health outcomes have become the new normal across the world" as a result of ethnic and racial disparities in COVID-19 healthcare, determined by social factors. Data from the United States and elsewhere shows that minorities, especially black people, have been infected and killed at a disproportionate rate to white people.
The following is a timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in Ghana from August 2020 to December 2020.








