Related Research Articles

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by inattention, or excessive activity and impulsivity, which are otherwise not appropriate for a person's age. Some individuals with ADHD also display difficulty regulating emotions or problems with executive function. For a diagnosis, the symptoms should appear before a person is 12 years old, be present for more than six months, and cause problems in at least two settings. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. Additionally, it is associated with other mental disorders and substance use disorders. Although it causes impairment, particularly in modern society, many people with ADHD can have sustained attention for tasks they find interesting or rewarding.

Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors.

Hyperfocus is an intense form of mental concentration or visualization that focuses consciousness on a subject, topic, or task. In some individuals, various subjects or topics may also include daydreams, concepts, fiction, the imagination, and other objects of the mind. Hyperfocus on a certain subject can cause side-tracking away from assigned or important tasks.
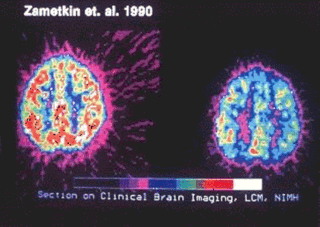
Adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is the psychiatric condition of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults. About one-third to two-thirds of children with symptoms from early childhood continue to demonstrate ADHD symptoms throughout life.

The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.
Sluggish cognitive tempo (SCT) is a syndrome related to attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) but distinct from it. Typical symptoms include prominent dreaminess, mental fogginess, hypoactivity, sluggishness, staring frequently, inconsistent alertness and a slow working speed.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder predominantly inattentive, is one of the three presentations of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In 1987–1994, there were no subtypes and thus it was not distinguished from hyperactive ADHD in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM-III-R).

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) controversies include concerns about its unclear existence, causes, perceived overdiagnosis, and methods of treatment, especially with the use of stimulant medications in children. These controversies have surrounded the subject since at least the 1970s.

Lisdexamfetamine, sold under the brand name Vyvanse among others, is a medication that is a derivative of amphetamine. It is mainly used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in people over the age of five as well as moderate-to-severe binge eating disorder in adults. Lisdexamfetamine is taken by mouth. In the United Kingdom, it is usually less preferred than methylphenidate. Its effects generally begin within 2 hours and last for up to 14 hours.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder management options are evidence-based practices with established treatment efficacy for ADHD. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends different treatment paradigms depending on the age of the person being treated. For those aged 4–5, the Academy recommends evidence-based parent- and/or teacher-administered behavior therapy, with the addition of methylphenidate only if there is continuing moderate-to-severe functional disturbances. For those aged 6–11, the use of medication in combination with behavior therapy is recommended, with the evidence for stimulant medications being stronger than that for other classes. For those aged 12–18, medication should be prescribed with the consent of the treated adolescent, preferably in combination with behavioral therapy. The evidence for the utility of behavioral interventions in this aged group was rated only "C" quality, however.
Gene–environment correlation is said to occur when exposure to environmental conditions depends on an individual's genotype.
In psychology, impulsivity is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically "poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation that often result in undesirable consequences," which imperil long-term goals and strategies for success. Impulsivity can be classified as a multifactorial construct. A functional variety of impulsivity has also been suggested, which involves action without much forethought in appropriate situations that can and does result in desirable consequences. "When such actions have positive outcomes, they tend not to be seen as signs of impulsivity, but as indicators of boldness, quickness, spontaneity, courageousness, or unconventionality" Thus, the construct of impulsivity includes at least two independent components: first, acting without an appropriate amount of deliberation, which may or may not be functional; and second, choosing short-term gains over long-term ones.
The social construction theory of ADHD argues that attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is not necessarily an actual pathology, but that an ADHD diagnosis is a socially constructed explanation to describe behaviors that simply do not meet prescribed social norms.

Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS).
In psychology, novelty seeking (NS) is a personality trait associated with exploratory activity in response to novel stimulation, impulsive decision making, extravagance in approach to reward cues, quick loss of temper, and avoidance of frustration. It is measured in the Tridimensional Personality Questionnaire as well as the later version Temperament and Character Inventory and is considered one of the temperament dimensions of personality. Like the other temperament dimensions, it has been found to be highly heritable. High NS has been suggested to be related to low dopaminergic activity.
In psychology and neuroscience, executive dysfunction, or executive function deficit, is a disruption to the efficacy of the executive functions, which is a group of cognitive processes that regulate, control, and manage other cognitive processes. Executive dysfunction can refer to both neurocognitive deficits and behavioural symptoms. It is implicated in numerous psychopathologies and mental disorders, as well as short-term and long-term changes in non-clinical executive control.
The low arousal theory is a psychological theory explaining that people with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and antisocial personality disorder seek self-stimulation by excessive activity in order to transcend their state of abnormally low arousal. This low arousal results in the inability or difficulty to sustain attention on any task of waning stimulation or novelty, as well as explaining compulsive hyperactive behavior.

Susan Smalley, Ph.D. is a behavioral geneticist, writer and activist. The co-author of Fully Present: The Science, Art, and Practice of Mindfulness, she is the founder of the UCLA Mindful Awareness Research Center at the Jane and Terry Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior (MARC), and professor emerita in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at UCLA. Her research centers on the genetic basis of childhood-onset behavior disorders, such as ADHD, and the cognitive and emotional impact of mindfulness meditation on health and wellbeing. She has published more than 100 peer-reviewed papers and lectured globally on the genetics of human behavior and the science of mindfulness.
The ADHD Rating Scale (ADHD-RS) is a parent-report or teacher-report inventory created by George J. DuPaul, Thomas J. Power, Arthur D. Anastopoulos, and Robert Reid consisting of 18–90 questions regarding a child's behavior over the past 6 months. The ADHD Rating Scale is used to aid in the diagnosis of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children ranging from ages 5–17.
Benjamin Michael Neale is a statistical geneticist with a specialty in psychiatric genetics. He is an institute member at the Broad Institute as well as an associate professor at both Harvard Medical School and the Analytic and Translational Genetics Unit at Massachusetts General Hospital. Neale specializes in genome-wide association studies (GWAS). He was responsible for the data analysis of the first GWAS on attention-deficit/hyperactivity-disorder, and he developed new analysis software such as PLINK, which allows for whole-genome data to be analyzed for specific gene markers. Related to his work on GWAS, Neale is the lead of the ADHD psychiatric genetics and also a member of the Psychiatric GWAS Consortium analysis committee.
References
- ↑ Hartmann, Thom (1995). ADD Success Stories . Grass Valley, California: Underwood Books. xvii. ISBN 1-887424-04-0.
- ↑ Arcos-Burgos M, Acosta MT; Acosta, Maria Teresa (June 2007). "Tuning major gene variants conditioning human behavior: the anachronism of ADHD". Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 17 (3): 234–8. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2007.04.011. PMID 17467976.
- ↑ Chen CS, Burton M, Greenberger E, Dmitrieva J (September 1999). "Population migration and the variation of dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) allele frequencies around the globe". Evolution and Human Behavior. 20 (5): 309–324. doi:10.1016/S1090-5138(99)00015-X.
- ↑ Kiaris, Hippokratis. (1 April 2012). Genes, polymorphisms, and the making of societies : how genetic behavioral traits influence human culture. Boca Raton: Universal-Publishers. pp. 80–83. ISBN 978-1-61233-093-8.
- ↑ Behavioral neuroscience of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and its treatment. New York: Springer. 13 January 2012. pp. 132–134. ISBN 978-3-642-24611-1.
- ↑ Lee, Richard B. (2005). Cambridge Encyclopedia of Hunters and Gatherers. Cambridge University Press. p. inside front cover. ISBN 9780521609197.
- ↑ Chang, F. M.; Kidd, J. R.; Livak, K. J.; Pakstis, A. J.; Kidd, K. K. (1996). "The world-wide distribution of allele frequencies at the human dopamine D4 receptor locus". Human Genetics. 98 (1): 91–101. doi:10.1007/s004390050166. PMID 8682515.
- ↑ Grady, D. L.; Chi, H. -C.; Ding, Y. -C.; Smith, M.; Wang, E.; Schuck, S.; Flodman, P.; Spence, M. A.; et al. (2003). "High prevalence of rare dopamine receptor D4 alleles in children diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder" (PDF). Molecular Psychiatry. 8 (5): 536–545. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001350 . PMID 12808433.
- ↑ Arcos-Burgos, M.; Acosta, M. T. (2007). "Tuning major gene variants conditioning human behavior: The anachronism of ADHD". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 17 (3): 234–238. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2007.04.011. PMID 17467976.
- ↑ Glickman, M. M. & Dodd, D. K. (1998). GUTI: A measure of urgent task involvement among adults with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Psychological Reports, 82, 592–594.
- ↑ Ewen Callaway (June 10, 2008). "Did hyperactivity evolve as a survival aid for nomads?". New Scientist.