
Metrosideros excelsa, with common names pōhutukawa, New Zealand pohutukawa, New Zealand Christmas tree, New Zealand Christmas bush, and iron tree, is a coastal evergreen tree in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae, that produces a brilliant display of red flowers made up of a mass of stamens. The pōhutukawa is one of twelve Metrosideros species endemic to New Zealand. Renowned for its vibrant colour and its ability to survive even perched on rocky, precarious cliffs, it has found an important place in New Zealand culture for its strength and beauty and is regarded as a chiefly tree by Māori. The blossom of the tree is called kahika.

The Brazil nut is a South American tree in the family Lecythidaceae, and also the name of the tree's commercially harvested edible seeds.
Mora is a genus of large trees in the subfamily Caesalpinioideae of the legume family Fabaceae,. There are seven to ten species, all native to lowland rainforests in northern South America, southern Central America and the southern Caribbean islands. These are large, heavily buttressed rainforest trees up to 130 feet in height. The genus is particularly noteworthy for the exceptional size of its beans, which are commonly acknowledged to be the largest known dicot seeds, in the instance of M megistosperma being up to seven inches (18 cm) in length, six inches in breadth and three inches (8 cm)in thickness, and a weight of up to 2.2 pounds. The beans of Mora spp. are edible if boiled, and are also the source of a red dyestuff. The species M. excelsa is one of the few rainforest trees to grow in pure stands.

Knightia excelsa, commonly called rewarewa, is an evergreen tree endemic to the low elevation and valley forests of New Zealand's North Island and Marlborough Sounds and the type species for the genus Knightia.

Senna spectabilis is a plant species of the legume family (Fabaceae) in the subfamily Caesalpinioideae.

Juniperus excelsa, commonly called the Greek juniper, is a juniper found throughout the eastern Mediterranean, from northeastern Greece and southern Bulgaria across Turkey to Syria and Lebanon, Jordan and the Caucasus mountains.

Doryanthes is the sole genus in the flowering plant family Doryanthaceae. The genus consists of two species, D. excelsa and D. palmeri, both endemic natives of the coast of Eastern Australia. Doryanthaceae is part of the order Asparagales.

Koompassia excelsa, also known as Tualang (Tapang), or Mengaris, is an emergent tropical rainforest tree species in the Fabaceae family. It is found in Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand. It is one of the tallest tropical tree species: the tallest measured specimen is 85.8 m or 88 m(281 or 289 ft) tall.

Milicia excelsa is a tree species from the genus Milicia of the family Moraceae. It is one of two species yielding timber commonly known as African teak, iroko, intule, kambala, moreira, mvule, odum and tule.
Hyda is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae.

Gasteria excelsa is a succulent plant, native to the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa.

Amanita excelsa var. spissa is a variety of basidiomycete fungus of the genus Amanita. This large, grey to brown-capped fungus has a very variable appearance but is commonly encountered in coniferous and deciduous forests in Europe and North America. It is sometimes referred to by the common name grey spotted Amanita.

Milicia is a small genus of tropical African trees. There are two recognized species, which are closely related: Milicia excelsa and Milicia regia. These trees yield a durable wood, iroko.

Iroko is a large hardwood tree from the west coast of tropical Africa that can live up to 500 years. The tree is known to the Yoruba as ìrókò, logo or loko and is believed to have supernatural properties. Iroko is known to the Igbo people as oji wood. It is one of the woods sometimes referred to as African teak, although it is unrelated to the teak family. The wood colour is initially yellow but darkens to a richer copper brown over time. It is yielded mostly (probably) by Milicia excelsa. In much of the literature on this timber the names of the trees that yields it are given as Chlorophora excelsa and Chlorophora regia.
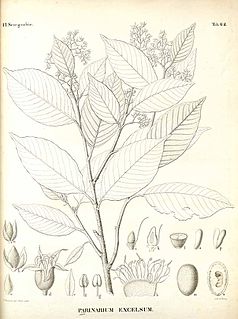
Parinari excelsa, the Guinea plum, is a species of tree in the Chrysobalanaceae family. It is native to tropical Africa, North America and South America.
Hyda basilutea is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Costa Rica, Colombia, Venezuela and Brazil.
Azadirachta excelsa, commonly known as sentang, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It grows up to 50 metres (160 ft) tall with a trunk diameter of up to 120 centimetres (50 in). The bark is pinkish grey or pinkish brown. The sweetly scented flowers are creamy-white. The fruits are ellipsoid, green turning yellow at maturity, up to 3.2 cm (1 in) long. The specific epithet excelsa is from the Latin meaning "lofty". Its habitat is rain forests from sea level to 350 metres (1,000 ft) altitude. A. excelsa is native to Malesia and Vietnam.

Gasteria acinacifolia is succulent plant native to the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa.

Amanita excelsa is a species of agaric fungus in the family Amanitaceae. It is found in Asia, Europe, and North America, where it grows in deciduous forests.
Destutia excelsa is a species of geometrid moth in the family Geometridae. It is found in North America.















