
A scuba set, originally just scuba, is any breathing apparatus that is entirely carried by an underwater diver and provides the diver with breathing gas at the ambient pressure. Scuba is an anacronym for self-contained underwater breathing apparatus. Although strictly speaking the scuba set is only the diving equipment that is required for providing breathing gas to the diver, general usage includes the harness by which it is carried, and those accessories which are integral parts of the harness and breathing apparatus assembly, such as a jacket or wing style buoyancy compensator and instruments mounted in a combined housing with the pressure gauge, and in the looser sense, it has been used to refer to all the diving equipment used by the scuba diver, though this would more commonly and accurately be termed scuba equipment or scuba gear. Scuba is overwhelmingly the most common underwater breathing system used by recreational divers and is also used in professional diving when it provides advantages, usually of mobility and range, over surface supplied diving systems, and is allowed by the relevant legislation and code of practice.

A backpack—also called knapsack, schoolbag,rucksack, rucksac, pack, sackpack, booksack, bookbag or backsack—is, in its simplest frameless form, a fabric sack carried on one's back and secured with two straps that go over the shoulders, but it can have an external frame, internal frame, and there are bodypacks.

Ice diving is a type of penetration diving where the dive takes place under ice. Because diving under ice places the diver in an overhead environment typically with only a single entry/exit point, it requires special procedures and equipment. Ice diving is done for purposes of recreation, scientific research, public safety and other professional or commercial reasons.

A self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA), sometimes referred to as a compressed air breathing apparatus (CABA) or simply breathing apparatus (BA), is a device worn to provide breathable air in an atmosphere that is immediately dangerous to life or health. They are typically used in firefighting and industry. The term self-contained means that the SCBA is not dependent on a remote supply of breathing gas. If designed for use under water, it is also known as a Scuba set. When not used underwater, they are sometimes called industrial breathing sets. Unofficial names include air pack, air tank, oxygen cylinder or simply pack, which are mostly used in firefighting.

A rebreather is a breathing apparatus that absorbs the carbon dioxide of a user's exhaled breath to permit the rebreathing (recycling) of the substantially unused oxygen content, and unused inert content when present, of each breath. Oxygen is added to replenish the amount metabolised by the user. This differs from open-circuit breathing apparatus, where the exhaled gas is discharged directly into the environment. The purpose is to extend the breathing endurance of a limited gas supply, and, for covert military use by frogmen or observation of underwater life, eliminating the bubbles produced by an open circuit system and in turn not scaring wildlife being filmed. A rebreather is generally understood to be a portable unit carried by the user. The same technology on a vehicle or non-mobile installation is more likely to be referred to as a life-support system.

A buoyancy compensator (BC), also called a buoyancy control device (BCD), stabilizer, stabilisor, stab jacket, wing or adjustable buoyancy life jacket (ABLJ), depending on design, is a type of diving equipment which is worn by divers to establish neutral buoyancy underwater and positive buoyancy at the surface, when needed.

A diving regulator is a pressure regulator that controls the pressure of breathing gas for diving. The most commonly recognised application is to reduce pressurized breathing gas to ambient pressure and deliver it to the diver, but there are also other types of gas pressure regulator used for diving applications. The gas may be air or one of a variety of specially blended breathing gases. The gas may be supplied from a scuba cylinder carried by the diver or via a hose from a compressor or high-pressure storage cylinders at the surface in surface-supplied diving. A gas pressure regulator has one or more valves in series which reduce pressure from the source, and use the downstream pressure as feedback to control the delivered pressure, or the upstream pressure as feedback to prevent excessive flow rates, lowering the pressure at each stage.

A diving helmet is a rigid head enclosure with a breathing gas supply used in underwater diving. They are worn mainly by professional divers engaged in surface-supplied diving, though some models can be used with scuba equipment. The upper part of the helmet, known colloquially as the hat or bonnet, may be sealed directly to the diver using a neck dam, connected to a diving suit by a lower part, known as a breastplate, or corselet, depending on regional language preferences. or simply rest on the diver's shoulders, with an open bottom, for shallow water use.

A full-face diving mask is a type of diving mask that seals the whole of the diver's face from the water and contains a mouthpiece, demand valve or constant flow gas supply that provides the diver with breathing gas. The full face mask has several functions: it lets the diver see clearly underwater, it provides the diver's face with some protection from cold and polluted water and from stings, such as from jellyfish or coral. It increases breathing security and provides a space for equipment that lets the diver communicate with the surface support team.

Nalgene is a brand of plastic products developed originally for laboratory use, including such items as jars, bottles, test tubes, and Petri dishes, that were shatterproof and lighter than glass. The properties of plastic products make them suitable for work with many substances in various temperature ranges.

Backpacking is the outdoor recreation of carrying gear on one's back, while hiking for more than a day. It is often an extended journey, and may involve camping outdoors. In North America tenting is common, where simple shelters and mountain huts, widely found in Europe, are rare. In New Zealand, hiking is called tramping and tents are used alongside a nationwide network of huts. Hill walking is an equivalent in Britain, though backpackers make use of a variety of accommodation, in addition to camping. Backpackers use simple huts in South Africa. Trekking and bushwalking are other words used to describe such multi-day trips.

A backplate and wing is a type of scuba harness with an attached buoyancy compensation device (BCD) which establishes neutral buoyancy underwater and positive buoyancy on the surface. Unlike most other BCDs, the backplate and wing is a modular system, in that it consists of separable components. The core components of this system are:
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.

A hydration pack or drink bag is a type of hydration system built as a backpack or waistpack containing a reservoir or "bladder" commonly made of rubber or flexible plastic. The reservoir contains a capped mouth for filling with liquid and a hose that allows the wearer to drink hands-free. Most hoses end with a "bite valve" that opens when the user bites down on it; the valve may be protected by a dust cover. Some hydration packs are insulated to keep water from freezing or becoming warm.

Sidemount is a scuba diving equipment configuration which has scuba sets mounted alongside the diver, below the shoulders and along the hips, instead of on the back of the diver. It originated as a configuration for advanced cave diving, as it facilitates penetration of tight sections of cave, allows easy access to cylinder valves, provides easy and reliable gas redundancy, and tanks can be easily removed when necessary. These benefits for operating in confined spaces were also recognized by divers who conducted technical wreck diving penetrations.

Ultralight backpacking is a subset of lightweight backpacking, a style of backpacking which emphasizes carrying the lightest and least amount of gear. While no technical standards exist, some hikers consider "ultralight" to mean an initial base weight of less than 4.5 kg (9.9 lb). Base weight is the weight of a fully loaded backpack at the start of a trip, excluding worn weight and consumables such as food, water, and fuel. Base weight can be lowered by reducing the weight of individual items of gear, or by choosing not to carry that gear. Ultralight backpacking is most popular among thru-hikers.
Hiking equipment is the equipment taken on outdoor walking trips. Hiking is usually divided into day-hikes and multiple-day hikes, called backpacking, trekking, and walking tours.
Family of Improved Load Bearing Equipment (FILBE) is a series of equipment used by the United States Marine Corps for personal load carrying. It comprises the backpack and various attachments carried by an individual Marine in the field. The FILBE was designed as an improvement over the prior ILBE system that was not compatible with the newest body armor systems.

Source Vagabond Systems Ltd. is known in the outdoor, trekking and sports market for sandals, hydration systems, packs and accessories and in the tactical market for hydration systems, packs, and its SOURCE Virtus Soldier System.
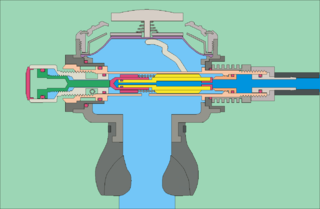
The mechanism of diving regulators is the arrangement of components and function of gas pressure regulators used in the systems which supply breathing gases for underwater diving. Both free-flow and demand regulators use mechanical feedback of the downstream pressure to control the opening of a valve which controls gas flow from the upstream, high-pressure side, to the downstream, low-pressure side of each stage. Flow capacity must be sufficient to allow the downstream pressure to be maintained at maximum demand, and sensitivity must be appropriate to deliver maximum required flow rate with a small variation in downstream pressure, and for a large variation in supply pressure, without instability of flow. Open circuit scuba regulators must also deliver against a variable ambient pressure. They must be robust and reliable, as they are life-support equipment which must function in the relatively hostile seawater environment, and the human interface must be comfortable over periods of several hours.

















