An ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold, irritation, or a problem with blood circulation. They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known as bedsores or decubitus ulcers. Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms.
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin laesio "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Hydroxycarbamide, also known as hydroxyurea, is a medication used in sickle-cell disease, chronic myelogenous leukemia, cervical cancer, and polycythemia vera. In sickle-cell disease it increases hemoglobin and decreases the number of attacks. It is taken by mouth.

Nevus is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from nævus, which is Latin for "birthmark", however, a nevus can be either congenital or acquired. Common terms, including mole, birthmark, and beauty mark, are used to describe nevi, but these terms do not distinguish specific types of nevi from one another.
Hailey–Hailey disease, or familial benign chronic pemphigus or familial benign pemphigus, was originally described by the Hailey brothers in 1939. It is a genetic disorder that causes blisters to form on the skin.
Leukemia cutis is the infiltration of neoplastic leukocytes or their precursors into the skin resulting in clinically identifiable cutaneous lesions. This condition may be contrasted with leukemids, which are skin lesions that occur with leukemia, but which are not related to leukemic cell infiltration. Leukemia cutis can occur in most forms of leukemia, including chronic myeloid leukemia, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, and prolymphocytic leukemia.

Schamberg's disease, is a chronic discoloration of the skin found in people of all ages, usually affecting the legs. It slowly spreads throughout the body, and is most common in males. It is named after Jay Frank Schamberg, who described it in 1901. There is no known cure for this disease and it is not a life-threatening condition. The skin lesions may cause itching, which can be treated by applying cortisone cream. The cortisone cream will only help with the itching and the discoloration of the skin will remain, which may cause a cosmetic concern in the future. Schamberg's disease is usually asymptomatic meaning that it shows no signs of this condition, except for the discoloration of the skin. This condition is caused by leaky blood vessels, where red blood cells escape near the surface of skin and release iron into the surrounding tissue. The cause of the leaky capillaries is unknown.
Gnathophyma involves swelling of the chin. It is a type of lesion associated with rosacea, a common chronic inflammatory skin disorder of the sebaceous glands characterized by redness, swelling, and acne-like pustules.

Tropical ulcer, more commonly known as jungle rot, is a chronic ulcerative skin lesion thought to be caused by polymicrobial infection with a variety of microorganisms, including mycobacteria. It is common in tropical climates.
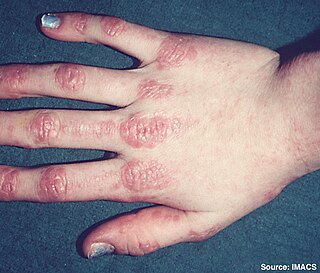
Chronic vesiculobullous hand eczema presents with lesions that may be hyperkeratotic, scaling, and fissures, and the "dyshidrosiform" pattern may be recognized only during exacerbations. Females outnumber males by 3:1, and there is a tendency for the pruritic 1- to 2-mm vesicles to be most pronounced at the sides of the fingers.
Autoimmune estrogen dermatitis presents as a cyclic skin disorder, that may appear eczematous, papular, bullous, or urticarial. with pruritus typically present, skin eruptions that may be chronic but which are exacerbated premenstrually or occur immediately following menses.
Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis or Disseminate and Recurrent Infundibular Folliculitis also called Hitch and Lund disease, is a rare itchy follicular skin condition presents with irregularly shaped papules pierced by hair, mildly pruritic at times, and is chronic with recurrent exacerbations.
Small plaque parapsoriasis characteristically occurs with skin lesions that are round, oval, discrete patches or thin plaques, mainly on the trunk.
Biliary pruritus is caused by chronic liver disease with obstructive jaundice, characterized by a severe generalized itchy sensation.
Prurigo simplex is a chronic, itchy, idiopathic skin condition characterized by extremely itchy skin nodules and lesions. Typically, there is no known direct cause of prurigo simplex, but some factors are known to trigger or aggravate it. This condition falls between chronic and acute, sometimes transitioning into a chronic condition. Many people experience a recurrence of the condition after periods of remission. Middle-aged patients are the most prone age group to this condition.
Papulonecrotic tuberculid is usually an asymptomatic, chronic skin disorder, presenting in successive crops, skin lesions symmetrically distributed on the extensor extremities.
Photosensitivity with HIV infection is a skin condition resembling polymorphous light eruption, actinic prurigo, or chronic actinic dermatitis, seen in about 5% of HIV-infected people.
A chronic scar keratosis is a precancerous skin lesion that arises within a long-standing scar.
Elephantiasis nostras is a cutaneous condition, a final hypertrophic fibrosis following longstanding chronic lymphangitis.