Related Research Articles

Hemoglobin is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transport of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers the animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12 to 20 grams of hemoglobin in every 100 mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and globulin.

A prion is a misfolded protein that can induce misfolding of normal variants of the same protein and trigger cellular death. Prions cause prion diseases known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) that are transmissible, fatal neurodegenerative diseases in humans and animals. The proteins may misfold sporadically, due to genetic mutations, or by exposure to an already misfolded protein. The consequent abnormal three-dimensional structure confers on them the ability to cause misfolding of other proteins.

Escherichia coli ( ESH-ə-RIK-ee-ə KOH-ly) is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus Escherichia that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but some serotypes such as EPEC, and ETEC are pathogenic and can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut and are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between E. coli and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship — where both the humans and the E. coli are benefitting each other. E. coli is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massively in fresh fecal matter under aerobic conditions for three days, but its numbers decline slowly afterwards.

Lysine is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain lysyl, classifying it as a basic, charged, aliphatic amino acid. It is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. Like almost all other amino acids, the α-carbon is chiral and lysine may refer to either enantiomer or a racemic mixture of both. For the purpose of this article, lysine will refer to the biologically active enantiomer L-lysine, where the α-carbon is in the S configuration.

Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become foamy. Severe proteinuria can cause nephrotic syndrome in which there is worsening swelling of the body.

Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis.

C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin-6 secretion by macrophages and T cells. Its physiological role is to bind to lysophosphatidylcholine expressed on the surface of dead or dying cells in order to activate the complement system via C1q.

Rhabdoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates, invertebrates, plants, fungi and protozoans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with member viruses include rabies encephalitis caused by the rabies virus, and flu-like symptoms in humans caused by vesiculoviruses. The name is derived from Ancient Greek rhabdos, meaning rod, referring to the shape of the viral particles. The family has 40 genera, most assigned to three subfamilies.

Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate Branchiostoma.

Bcl-2, encoded in humans by the BCL2 gene, is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of regulator proteins that regulate cell death (apoptosis), by either inhibiting (anti-apoptotic) or inducing (pro-apoptotic) apoptosis. It was the first apoptosis regulator identified in any organism.
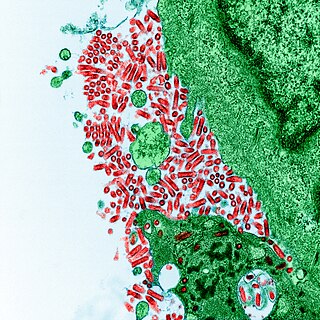
Rabies virus, scientific name Rabies lyssavirus, is a neurotropic virus that causes rabies in animals, including humans. Rabies transmission can occur through the saliva of animals and less commonly through contact with human saliva. Rabies lyssavirus, like many rhabdoviruses, has an extremely wide host range. In the wild it has been found infecting many mammalian species, while in the laboratory it has been found that birds can be infected, as well as cell cultures from mammals, birds, reptiles and insects. Rabies is reported in more than 150 countries and on all continents except Antarctica. The main burden of disease is reported in Asia and Africa, but some cases have been reported also in Europe in the past 10 years, especially in returning travellers.

The autoimmune regulator (AIRE) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AIRE gene. It is a 13kb gene on chromosome 21q22.3 that has 545 amino acids. AIRE is a transcription factor expressed in the medulla of the thymus. It is part of the mechanism which eliminates self-reactive T cells that would cause autoimmune disease. It exposes T cells to normal, healthy proteins from all parts of the body, and T cells that react to those proteins are destroyed.

CDKL5 is a gene that provides instructions for making a protein called cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 also known as serine/threonine kinase 9 (STK9) that is essential for normal brain development. Mutations in the gene can cause deficiencies in the protein. The gene regulates neuronal morphology through cytoplasmic signaling and controlling gene expression. The CDKL5 protein acts as a kinase, which is an enzyme that changes the activity of other proteins by adding a cluster of oxygen and phosphorus atoms at specific positions. Researchers are currently working to determine which proteins are targeted by the CDKL5 protein.

b(0,+)-type amino acid transporter 1, also known as b(0,+)AT1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SLC7A9 gene.
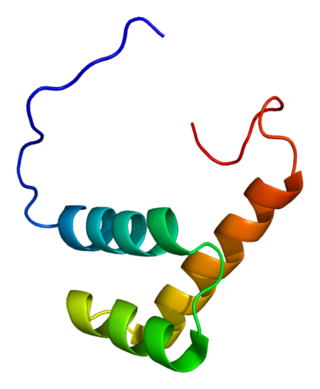
Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZEB2 gene. The ZEB2 protein is a transcription factor that plays a role in the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling pathways that are essential during early fetal development.

Four and a half LIM domains protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHL1 gene.

Palmitoyl protein hydrolase/thioesterases is an enzyme (EC 3.1.2.22) that removes thioester-linked fatty acyl groups such as palmitate from modified cysteine residues in proteins or peptides during lysosomal degradation. It catalyzes the reaction

Cellular nucleic acid-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNBP gene.

Single-minded homolog 1, also known as class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 14 (bHLHe14), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIM1 gene.

L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the L2HGDH gene, also known as C14orf160, on chromosome 14.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.