Synopsis
Based on the New York Times best-selling book Ice Bound: A Doctor's Incredible Battle for Survival at the South Pole, the movie tells the story of how, in 1999, 46-year-old physician Nielsen decides to leave Ohio and spend a year at the Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station on Antarctica, one of the most remote and perilous places on Earth. Conditions at the station will be far from manageable, with winter temperatures as low as 100 degrees below zero. Joining a team of researchers, construction workers and support staff, Dr. Nielsen is solely responsible for the mental and physical health of all fellow inhabitants stranded at the station through the winter. During the long Antarctic winter, Dr. Nielsen discovers a lump in her breast and is forced to self-administer a biopsy. Communicating via e-mail with doctors in the United States, she learns that the cancer is aggressive and rapid-growing. In order for her to survive several months until conditions will allow planes to land and rescue her from the continent, the doctors concur that she will need to begin chemotherapy treatments immediately.
Risking death, rescuers heroically air-drop the necessary supplies to the station and, along with the help of fellow "Polies", including close friends Big John Penny (Aidan Devine) and Claire "Fingers" Furinski (Cynthia Mace), Nielsen begins her debilitating chemotherapy treatments. Eventually, the Air National Guard makes a daring rescue, drops off a replacement physician and returns Nielsen to the United States, where she is able to seek full medical attention to treat her cancer.

Chemotherapy is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs in a standard regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent, or it may aim only to prolong life or to reduce symptoms. Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called medical oncology.

The Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station is a United States scientific research station at the South Pole of the Earth. It is the southernmost point under the jurisdiction of the United States. The station is located on the high plateau of Antarctica at 9,301 feet (2,835 m) above sea level. It is administered by the Office of Polar Programs of the National Science Foundation, specifically the United States Antarctic Program (USAP). It is named in honor of Norwegian Roald Amundsen and Briton Robert F. Scott, who led separate teams that raced to become the first to the pole in the early 1900s.

A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, vascular, or other structural tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates.

Mark Greene, M.D. is a fictional character from the American medical drama series ER. Portrayed by actor Anthony Edwards, he first appeared in the series' pilot episode, as well as subsequently appearing as one of the principal characters until the end of the eighth season. Edwards later returned to make a guest appearance in the fifteenth season episode "Heal Thyself".

Jerri Lin Nielsen was an American physician with extensive emergency room experience, who self-treated her breast cancer while stationed at Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica until she could be evacuated safely.
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in cancer therapy have led the term to be used mainly to describe adjuvant cancer treatments. An example of such adjuvant therapy is the additional treatment usually given after surgery where all detectable disease has been removed, but where there remains a statistical risk of relapse due to the presence of undetected disease. If known disease is left behind following surgery, then further treatment is not technically adjuvant.
Clare O'Leary is an Irish gastroenterologist, mountain climber and adventurer. She was the first Irish woman to climb Mount Everest and complete the Seven Summits.

Jane Cooke Wright was a pioneering cancer researcher and surgeon noted for her contributions to chemotherapy. In particular, Wright is credited with developing the technique of using human tissue culture rather than laboratory mice to test the effects of potential drugs on cancer cells. She also pioneered the use of the drug methotrexate to treat breast cancer and skin cancer.
Nicholas James Gonzalez was a New York–based physician known for developing the Gonzalez regimen, an alternative cancer treatment. Gonzalez's treatments are based on the belief that pancreatic enzymes are the body's main defense against cancer and can be used as a cancer treatment. His methods have been generally rejected by the medical community. and he has been characterized as a quack and fraud by other doctors and health fraud watchdog groups. In 1994 Gonzalez was reprimanded and placed on two years' probation by the New York State Medical Board for "departing from accepted practice".
Rose Rehert Kushner was an American journalist and pioneering advocate for breast cancer patients. She wrote the 1975 book Why Me? What Every Woman Should Know About Breast Cancer to Save Her Life.
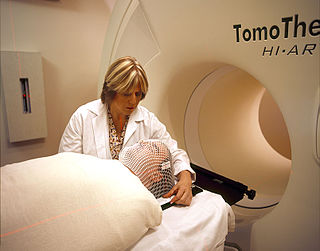
Cancer treatments are a wide range of treatments available for the many different types of cancer, with each cancer type needing its own specific treatment. Treatments can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, targeted therapy including small-molecule drugs or monoclonal antibodies, and PARP inhibitors such as olaparib. Other therapies include hyperthermia, immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy, and stem-cell therapy. Most commonly cancer treatment involves a series of separate therapies such as chemotherapy before surgery. Angiogenesis inhibitors are sometimes used to enhance the effects of immunotherapies.
Helen Chambers CBE was a British pathologist and cancer expert whose findings on radium were essential in the fight against cervical cancer.
High-dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplant (HDC/BMT), also high-dose chemotherapy with autologous bone marrow transplant, was an ineffective treatment regimen for metastatic breast cancer, and later high-risk breast cancer, that was considered promising during the 1980s and 1990s. With an overall idea that more is better, this process involved taking cells from the person's bone marrow to store in a lab, then to give such high doses of chemotherapy drugs that the remaining bone marrow was destroyed, and then to inject the cells taken earlier back into the body as replacement. It was ultimately determined to be no more effective than normal treatment, and to have significantly higher side effects, including treatment-related death.
Dr. Matthias Gromeier is a Professor in the Department of Neurosurgery at Duke University Medical Center, who has developed a way to re-engineer a poliovirus to inspire the human immune system to kill cancer cells in a specific set of cancers. The re-engineered virus, called PVSRIPO, cannot replicate itself in normal cells, but can replicate itself in cancer cells that have an overabundance of the protein marker that the poliovirus targets.
Farid Tanios Fata is a Lebanese-born former hematologist/oncologist and the mastermind of one of the largest health care frauds in U.S. history. Fata was the owner of Michigan Hematology-Oncology (MHO), one of the largest cancer practices in Michigan. He was arrested in 2013 on charges of prescribing chemotherapy to patients who were healthy or whose condition did not warrant chemotherapy, then submitting $34 million in fraudulent charges to Medicare and private health insurance companies over a period of at least six years.
This is a historical timeline of the development and progress of cancer treatments, which includes time of discovery, progress, and approval of the treatments.
Teresa J. Vietti was an American physician. She is best known for her pioneering work and research in pediatric cancer. Her research discovered the genetics of leukemia, new chemotherapy agents and tracked the effects of chemotherapy on childhood cancer survivors. Vietti also wrote about her research and was an editor of the Journal of Pediatric Hematology and a co-editor of Clinical Pediatric Oncology. According to Washington University in St. Louis, she was known as "the mother of pediatric cancer therapy."

End Game is a 2018 American short documentary film by Rob Epstein and Jeffrey Friedman about terminally ill patients in a San Francisco hospital meeting medical practitioners seeking to change the perception around life and death. The film was executive produced by Steven Ungerleider and Shoshana R. Ungerleider. It was released by Netflix.

Maryam Beheshti Lustberg is an American breast oncologist. She is the Director of The Breast Center at Smilow Cancer Hospital and Chief of Breast Medical Oncology at Yale Cancer Center. Lustberg previously served as the Medical Director of Supportive Care at Ohio State's Comprehensive Cancer Center and President-Elect of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer. She is also an associate editor for the peer-reviewed medical journal covering oncology nursing with respect to cancer survivors called Journal of Cancer Survivorship. Lustberg was also recognized as one of the 100 Influential Women in Oncology by OncoDaily.
Elizabeth R. Plimack is an American medical oncologist. She is a professor in the Department of Hematology/Oncology and Chief of the Division of Genitourinary Medical Oncology at the Fox Chase Cancer Center. In these roles, she researches the treatment of genitourinary malignancies with a focus on bladder and kidney cancers.









