Juan de Nova Island, also known as Saint-Christophe, is a French tropical island in the narrowest part of the Mozambique Channel, about one-third of the way between Madagascar and Mozambique. It is a low, flat island, 4.4 square kilometres (1.7 sq mi) in size.
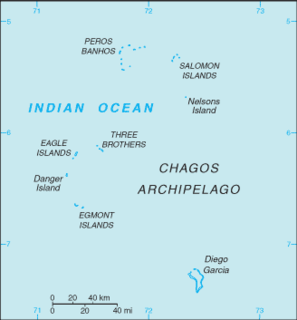
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an archipelago of 55 islands in the Indian Ocean, located south of India. It is situated approximately halfway between Africa and Indonesia. The islands form a semicircular group with an open sea towards the east. The largest, Diego Garcia, is located at the southern extreme end. It measures 60 square kilometres (23 sq mi) and accounts for almost three-quarters of the total land area of the territory. Diego Garcia is the only inhabited island and is home to the joint UK-US naval support facility. Other islands within the archipelago include Danger Island, Three Brothers Islands, Nelson Island, and Peros Banhos, as well as the island groups of the Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, and the Salomon Islands.

Benares Shoals, or Benares Shoal, is a submerged coral reef, an isolated patch located at 5°15′S071°40′E, just 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) west-northwest of Île Pierre, the closest island of Peros Banhos atoll in the northern Chagos Archipelago. It measures about 3 kilometres (2 mi) east–west, with a width of about 700 metres (2,300 ft) and an area of 2 square kilometres (0.77 sq mi). The least depth at the western end is 4.5 metres (15 ft).

Île Saint-Lanne Gramont is an uninhabited island, the fourth largest island in the Kerguelen Islands, situated to the north of presqu'île de la Société de géographie, with an area of 45.8 km². It reaches 480 m at its highest point and is located at 48°55′25″S69°10′54″E. The island is elongated along a north-south axis, reaching a maximum length of 13 km and a maximum width of 3 km. It is free of introduced animals.

Île Howe is one of the islands of the Kerguelen archipelago, situated to the north of Île Foch, just after Île MacMurdo. It is about 8 km in length. Apart from rabbits, it is free of introduced animals.
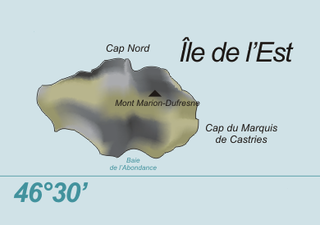
Île de l'Est, or East Island, is a part of the subantarctic archipelago of the Crozet Islands. With an area of 130 km2 (50 sq mi) it is the second largest island of the group. It is part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.

Île du Lys, also known as Le Lys or Ile du Lise, is one of the Glorioso Islands, north-west of Madagascar. It is over seen (administrated) by France.

Île Yeye is an island of the Peros Banhos atoll in the Chagos Archipelago of the British Indian Ocean Territory. It is the island of the Chagos that is closest to the Maldives.

Île aux Cochons, or Pig Island, is an uninhabited island in the subantarctic Crozet Archipelago. With an area of 67 km2 (26 sq mi) it is the third largest island of the group. Administratively, it is part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands.

Île de la Possession, or Possession Island, formerly Île de la Prise de Possession, is part of the subantarctic Crozet Archipelago.

Île des Pingouins, or Penguin Island, is an uninhabited island in the subantarctic Crozet Archipelago of the southern Indian Ocean. With an area of only 3 km2 (1 sq mi) it is one of the smaller islands of the group. Administratively, it is part of the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. It is an important nesting site for seabirds.
The Îles Nuageuses comprise a group of small islands that are part of the subantarctic Kerguelen archipelago, a French territory in the southern Indian Ocean. They are important as a breeding site for seabirds, especially penguins and albatrosses, and for fur seals.

Petite Île Bois Mangue is a 9 ha island on the Peros Banhos Atoll in the Chagos Archipelago of the British Indian Ocean Territory. It is part of the Peros Banhos strict nature reserve and has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of its significance as a breeding site for lesser noddies, of which 12,000 pairs were recorded in a 2004 survey.

Ile Longue is a 26 ha island on the Peros Banhos Atoll in the Chagos Archipelago of the British Indian Ocean Territory. It is part of the Peros Banhos strict nature reserve and has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of its significance as a breeding site for sooty terns, of which 32,000 pairs were recorded in a 2004 survey.

Sea Cow Island, also known as Île Vache Marine, is a round 18 ha island on the Great Chagos Bank atoll of the Chagos Archipelago in the British Indian Ocean Territory. It was named after the dugongs that were once abundant in the area, although they have since become regionally extinct. It is the smaller of the two islands in the Eagle Islands group on the western side of the atoll and forms part of the Chagos Archipelago strict nature reserve. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of its significance as a breeding site for brown noddies, of which 11,500 pairs were recorded in a 2004 survey.

North Brother, also known as Île du Nord, is a round 6 ha coral island on the Great Chagos Bank atoll of the Chagos Archipelago in the British Indian Ocean Territory. It is one of the three islands in the Three Brothers group on the western side of the atoll, and forms part of the Chagos Archipelago strict nature reserve. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of its significance as a breeding site for 20,000 seabirds, notably Audubon's shearwaters of which 420 pairs were recorded in a 2004 survey.

Middle Brother, also known as Île du Milieu, is an 8-hectare coral island on the Great Chagos Bank atoll of the Chagos Archipelago in the British Indian Ocean Territory. It is one of the three islands in the Three Brothers group on the western side of the atoll, and forms part of the Chagos Archipelago strict nature reserve. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International for its significance as a breeding site for seabirds, notably sooty terns, of which 12,500 pair were recorded in a 2004 survey.

South Brother, also known as Île du Sud, is a 23 ha coral island on the Great Chagos Bank atoll of the Chagos Archipelago in the British Indian Ocean Territory. It is one of the three islands in the Three Brothers group on the western side of the atoll, and forms part of the Chagos Archipelago strict nature reserve. It has been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of its significance as a breeding site for seabirds, including brown noddies and lesser noddies.

Île de la Passe is an island of the Peros Banhos atoll in the Chagos Archipelago of the British Indian Ocean Territory.