
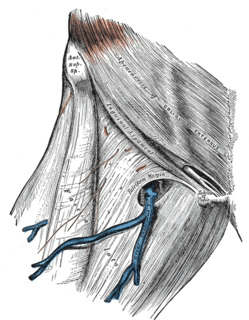
The inguinal ligament, also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may develop.

The external iliac veins are large veins that connect the femoral veins to the common iliac veins. Their origin is at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligaments and they terminate when they join the internal iliac veins.

The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis.

The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas. In animals, this muscle is equivalent to the tenderloin.
The iliacus is a flat, triangular muscle which fills the iliac fossa. It forms the lateral portion of iliopsoas, providing flexion of the thigh and lower limb at the acetabulofemoral joint.

The anterior superior iliac spine is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the inguinal ligament, and the sartorius muscle. The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches to the lateral aspect of the superior anterior iliac spine, and also about 5 cm away at the iliac tubercle.

In human anatomy, inferior epigastric artery refers to the artery that arises from the external iliac artery. It anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein, the inferior epigastric vein. These epigastric vessels form the lateral border of Hesselbach's triangle, which outlines the area through which direct inguinal hernias protrude.
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by intermuscular septa. The fascia lata is thickened at its lateral side where it forms the iliotibial tract, a structure that runs to the tibia and serves as a site of muscle attachment.

The iliotibial tract or iliotibial band is a longitudinal fibrous reinforcement of the fascia lata. The action of the muscles associated with the ITB flex, extend, abduct, and laterally and medially rotate the hip. The ITB contributes to lateral knee stabilization. During knee extension the ITB moves anterior to the lateral condyle of the femur, while ~30 degrees knee flexion, the ITB moves posterior to the lateral condyle. However, it has been suggested that this is only an illusion due to the changing tension in the anterior and posterior fibers during movement. It originates at the anterolateral iliac tubercle portion of the external lip of the iliac crest and inserts at the lateral condyle of the tibia at Gerdy's tubercle. The figure shows only the proximal part of the iliotibial tract.

The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into both an anterior and a posterior branch.
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of all hernias. While femoral hernias can occur in both males and females, almost all develop in women due to the increased width of the female pelvis. Femoral hernias are more common in adults than in children. Those that do occur in children are more likely to be associated with a connective tissue disorder or with conditions that increase intra-abdominal pressure. Seventy percent of pediatric cases of femoral hernias occur in infants under the age of one.
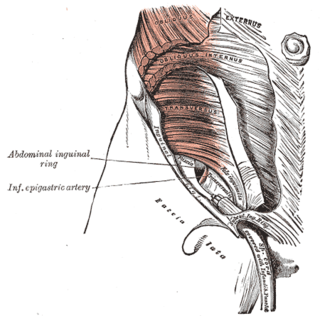
The transversalis fascia is a thin aponeurotic membrane of the abdomen. It lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.

The pubic tubercle is a prominent tubercle on the superior ramus of the pubis bone of the pelvis.

The femoral sheath, also called the crural sheath, is a continuation of the abdominal fascia that is contained in the femoral triangle. It forms the femoral canal, allowing for the femoral artery and the femoral vein to travel between the abdomen and the thigh.

The pectineal ligament, sometimes known as the inguinal ligament of Cooper, is an extension of the lacunar ligament. It runs on the pectineal line of the pubic bone. The pectineal ligament is the posterior border of the femoral ring.

In anatomy, the saphenous opening is an oval opening in the upper mid part of the fascia lata of the thigh. It lies 3–4 cm below and lateral to the pubic tubercle and is about 3 cm long and 1.5 cm wide.
The Iliopectineal arch is a thickened band of fused iliac fascia and psoas fascia passing from the posterior aspect of the inguinal ligament anteriorly across the front of the femoral nerve to attach to the iliopubic eminence of the hip bone posteriorly. The iliopectineal arch thus forms a septum which subdivides the space deep to the inguinal ligament into a lateral muscular lacuna and a medial vascular lacuna. When a psoas minor muscle is present, its tendon of insertion blends with the iliopectineal arch

Charles Barrett Lockwood was a British surgeon and anatomist who practiced surgery at St. Bartholomew's Hospital in London. Lockwood was a member of the Royal College of Surgeons.

The pelvis is the lower part of the human trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.
The Triangle of Doom is an anatomical triangle defined by the vas deferens medially, spermatic vessels laterally and peritoneal fold inferiorly. This triangle contains external iliac artery and vein, the deep circumflex iliac vein, the genital branch of genitofemoral nerve and hidden by fascia, the femoral nerve.















