Indian Railways (IR) is India's national railway system operated by the Ministry of Railways. It manages the fourth largest railway network in the world by size, with a route length of 67,368-kilometre (41,861 mi) and total track length of 121,407-kilometre (75,439 mi) as of March 2017. Routes are electrified with 25 kV AC electric traction while thirty three percent of them are double or multi-tracked.

Howrah Junction, more popularly known as Howrah Station, is the oldest and largest railway complex in India, serving the twin cities of Howrah and Kolkata. Approximately 617 passenger trains pass through the station each day requiring its 23 platforms and serving more than two million passengers per day with the highest train handling capacity of any Indian railway station. Howrah Junction is one of five intercity railway stations serving the city of Kolkata, the others being Sealdah, Santragachi, Shalimar, and Kolkata railway station. Howrah Junction is also one of the busiest stations in India as per passenger footfall. The station is located in Howrah on the west bank of the Hooghly River. 1373 stations across India are directly connected to Howrah Railway Station.
Rail transport in India began during the early nineteenth century.

The WAP 7 is a three-phase AC electric passenger locomotive developed by the Chittaranjan Locomotive Works. It is the most powerful passenger locomotive in the Indian Railways' fleet. It is a passenger variant of the WAG 9 freight locomotive with a modified gear ratio to pull lighter loads at higher speeds. It is capable of hauling 24 coach trains at speeds ranging 110–140 km/h (68–87 mph), depending on the MPS of the sector, and is now largely used by Northern Railways (NR), South Central Railways (SCR), Central Railways (CR), South East Central Railway Zone (SECR), Southern Railways (SR), South Eastern Railways (SER), West Central Railways (WCR), Eastern Railways (ER), Western Railway zone (WR) & North Central Railway zone (NCR) among other zones. As of June 2019, there are 716 locomotives in service, all of which are fitted with tightlock couplers and chain link couplers. In February 2017, Diesel Locomotive Works built their first WAP 7 class locomotive.

The WAG-5 is a type of electric locomotive used in India. It was once the second most widely used locomotive in the Indian Railways, with a total of 1197 units built including variants. WAG5A is the one with Alstom traction motors. WAG5B is a converted WAM4. WAG5H(x) is with Hitachi traction motors. WAG5P(x) is a passenger dedicated class. WAG5(x)D are fitted with dual brakes and WAG5(x)E are fitted with air brakes. WAG5RH and WAG-5HR are fitted with Rheostatic or Friction braking. Another variant is WAG-5HG.The units with additional '6P' markings have all parallel grouped traction motors. WAG-5HB is built by BHEL. Some units are fitted with Static Converter(STC), Microprocessor, Dynamic brake resistors(DBR) and SI unit. Due to the advent of WAG-7 and WAG-9, these locos except WAG-5HA/HB are even used for passenger trains although it is a freight-dedicated locomotive. WAG-5HB is homed at Jhansi shed near BHEL's installations for maintenance purposes. WAG-5 has a shell of WAM-4. Units numbered till 23293 have side Louvre and round glass windows like WAM-4 and units after 23293 have WAG-7 style of Louvre for better ventilation. Recently, WAG-5 have been fitted with data loggers. Unit numbered 23026 was selected by RDSO for adoption of thyristor controlled electricals in 1995. This was done due to the loss of suppliers of tap changer control. Project began in 1992. The new prototype system built in collaboration with Bhabha Atomic Research Centre was fitted in the locomotive between 1997-98. However due to several problems like interference with signalling equipment, the project was ceased in 1999. The engine was rebuilt to original WAG-5 and designated as WAG-5P.

The Boat Mail or Indo-Ceylon Express was a combined train and steamer ferry service between India and Ceylon. Connecting Chennai and Colombo, the system initially utilised a rail-to-sea operation, but changed to a rail-to-sea-to-rail operation. Passengers could buy a single ticket for the journey. The current Boat Mail Express is a train operated by the Southern Railway unit of Indian Railways; it usually departs Chennai egmore at 7:15pm and arrives Rameswaram at 08:25am.

Royapuram railway station is a railway station at Royapuram, on the Chennai Beach–Arakkonam section of the Chennai Suburban Railway network in Chennai, India. It is one of the oldest railway stations currently operational in India and the first railway station of South India. The first train of South India started operating in June 1856 from Royapuram railway station. The station also remained the headquarters of the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway till 1922, when the headquarters was shifted to Egmore. Since the original structures of Bombay and Thane stations no longer exist, Royapuram station remains the oldest railway station in the entire subcontinent.
The proposed Dalli-Rajhara–Jagdalpur rail line, on paper for almost three decades, once completed, would connect Dalli-Rajhara to Jagdalpur, both towns being in Chhattisgarh state in India. It would also connect Raipur, the capital city of Chhattisgarh, to Jagdalpur by rail via Durg. Jagdalpur, which is about 300 km from Raipur, is currently meaningfully connected to it only by road. There is though a roundabout rail route to reach Raipur from Jagdalpur via Koraput and Rayagada in Orissa; it is much longer and takes much longer time to be of any utility. In view of this, almost all the transport, in relation to both people and goods, between Raipur and Jagdalpur, happens only by road.

The Asansol–Adra-Tatanagar–Kharagpur line is part of Howrah and eastern India's links with Mumbai and Chennai. It is also a major freight line for transporting iron ore, coal and steel products. This page includes the Adra-Gomoh branch line and Tatanagar-Badampahar branch lines.

The Howrah–Chennai main line is a railway line connecting Chennai and Kolkata cutting across Eastern Coastal Plains of India. It covers a distance of 1,661 kilometres (1,032 mi) across, West Bengal, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.

Chennai Park railway station is one of the railway stations in Chennai, India, on the Chennai Beach–Chengelpet section of the Chennai Suburban Railway Network. It serves the neighbourhood of Park Town, a suburb of Chennai. It is located at about 3 km from Chennai Beach terminus and is situated on Poonamallee High Road, across Chennai Central railway station. It has an elevation of 7 m above sea level.
Thoothukudi has transport connections via road, rail, sea and air. After Chennai, Thoothukudi is only city in Tamil Nadu to have all four means of transport

St. Thomas Mount railway station, or Mount railway station, is one of the railway stations of the Chennai Beach–Chengalpattu section of the Chennai Suburban Railway Network. It serves the neighbourhood of St. Thomas Mount and Pazhavanthangal, which are suburbs of Chennai. It is located at a distance of 17 km (11 mi) from Chennai Beach terminus, with an elevation of 11 m (36 ft) above sea level.
The Bilaspur–Nagpur section is part of the Howrah-Nagpur-Mumbai line and connects Bilaspur in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and Nagpur in Maharashtra. Part of one of the major trunk lines in the country, it passes through a forested plateau region interspersed with fertile valleys.
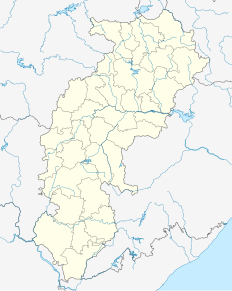
Durg Railway Station, is a junction station located in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. It serves Durg, Bhilai city and the adjoining areas of Durg district. Durg Junction is the part of South East Central Railway.It is one of the most prominent and important station in Howrah-Nagpur-Mumbai line.It is an 'A' grade station of Indian Railways in terms of passenger services.

The Duvvada–Vijayawada section is a railway line connecting Duvvada of Visakhapatnam and Vijayawada, both in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. The main line is part of the Howrah-Chennai main line. The track from Duvvada to Thadi is under the administrative jurisdiction of South Coast Railway, and the rest of the line from Anakapalle to Vijayawada is under the administrative jurisdiction of South Coast Railway zone headquartered in Visakhapatnam.

The Vijayawada–Gudur section is a railway line connecting Vijayawada in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and Gudur. The main line is part of the Howrah-Chennai and New Delhi–Chennai main lines.

The Chennai Central–Bangalore City line connects the main railway stations in two of the larger cities in India - Chennai in Tamil Nadu and Bengaluru in Karnataka.

The Mumbai–Chennai line is a railway line connecting Chennai and Mumbai cutting across southern part of the Deccan Plateau. It covers a distance of 1,281 kilometres (796 mi) across Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.