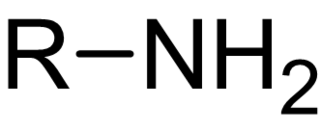
In chemistry, amines are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Formally, amines are derivatives of ammonia (NH3, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine.

Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans.
The quinones are a class of organic compounds that are formally "derived from aromatic compounds [such as benzene or naphthalene] by conversion of an even number of –CH= groups into –C(=O)– groups with any necessary rearrangement of double bonds", resulting in "a fully conjugated cyclic dione structure". The archetypical member of the class is 1,4-benzoquinone or cyclohexadienedione, often called simply "quinone". Other important examples are 1,2-benzoquinone (ortho-quinone), 1,4-naphthoquinone and 9,10-anthraquinone.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. Haloarenes are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.

Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.

Safranin is a biological stain used in histology and cytology. Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and endospore staining. It can also be used for the detection of cartilage, mucin and mast cell granules.
There are three isomers of toluidine, which are organic compounds discovered and named by James Sheridan Muspratt and August Wilhelm von Hofmann in 1845. These isomers are o-toluidine, m-toluidine, and p-toluidine, with the prefixed letter abbreviating, respectively, ortho; meta; and para. All three are aryl amines whose chemical structures are similar to aniline except that a methyl group is substituted onto the benzene ring. The difference between these three isomers is the position where the methyl group (–CH3) is bonded to the ring relative to the amino functional group (–NH2); see illustration of the chemical structures below.
Arene substitution patterns are part of organic chemistry IUPAC nomenclature and pinpoint the position of substituents other than hydrogen in relation to each other on an aromatic hydrocarbon.

Azo dyes are organic compounds bearing the functional group R−N=N−R′, in which R and R′ are usually aryl and substituted aryl groups. They are a commercially important family of azo compounds, i.e. compounds containing the C−N=N−C linkage. Azo dyes are synthetic dyes and do not occur naturally. Most azo dyes contain only one azo group but there are some that contain two or three azo groups, called "diazo dyes" and "triazo dyes" respectively. Azo dyes comprise 60–70% of all dyes used in food and textile industries. Azo dyes are widely used to treat textiles, leather articles, and some foods. Chemically related derivatives of azo dyes include azo pigments, which are insoluble in water and other solvents.
In organic chemistry, an azo coupling is an reaction between a diazonium compound and another aromatic compound that produces an azo compound. In this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the aryldiazonium cation is the electrophile, and the activated carbon, serves as a nucleophile. Classical coupling agents are phenols and naphthols. Usually the diazonium reagent attacks at the para position of the coupling agent. When the para position is occupied, coupling occurs at a ortho position, albeit at a slower rate.
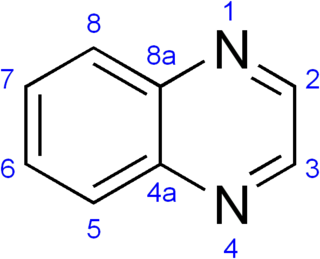
A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinazoline, phthalazine and cinnoline. It is a colorless oil that melts just above room temperature. Although quinoxaline itself is mainly of academic interest, quinoxaline derivatives are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals, and antibiotics such as olaquindox, carbadox, echinomycin, levomycin and actinoleutin.
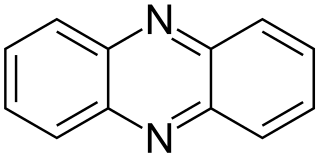
Phenazine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulated pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dyestuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranines (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystallizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in alcohol. Sulfuric acid dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution.

Aniline Yellow is a yellow azo dye and an aromatic amine. It is a derivative of azobenzene. It has the appearance of an orange powder. Aniline Yellow was the first azo dye. it was first produced in 1861 by C. Mene. The second azo dye was Bismarck Brown in 1863. Aniline Yellow was commercialized in 1864 as the first commercial azo dye, a year after aniline black. It is manufactured from aniline.
Pyrylium is a cation with formula C5H5O+, consisting of a six-membered ring of five carbon atoms, each with one hydrogen atom, and one positively charged oxygen atom. The bonds in the ring are conjugated as in benzene, giving it an aromatic character. In particular, because of the positive charge, the oxygen atom is trivalent. Pyrilium is a mono-cyclic and heterocyclic compound, one of the oxonium ions.
The formazans are compounds of the general formula [R-N=N-C(R')=N-NH-R"], formally derivatives of formazan [H2NN=CHN=NH], unknown in free form.

2-Naphthylamine or 2-aminonaphthalene is one of two isomeric aminonaphthalenes, compounds with the formula C10H7NH2. It is a colorless solid, but samples take on a reddish color in air because of oxidation. It was formerly used to make azo dyes, but it is a known carcinogen and has largely been replaced by less toxic compounds.
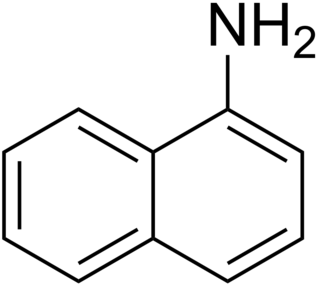
1-Naphthylamine is an aromatic amine derived from naphthalene. It can cause bladder cancer. It crystallizes in colorless needles which melt at 50 °C. It possesses a disagreeable odor, sublimes readily, and turns brown on exposure to air. It is the precursor to a variety of dyes.
Phenol oxidation with hypervalent iodine reagents leads to the formation of quinone-type products or iodonium ylides, depending on the structure of the phenol. Trapping of either product is possible with a suitable reagent, and this method is often employed in tandem with a second process.
Electrophilic aromatic substitution (SEAr) is an organic reaction in which an atom that is attached to an aromatic system is replaced by an electrophile. Some of the most important electrophilic aromatic substitutions are aromatic nitration, aromatic halogenation, aromatic sulfonation, alkylation Friedel–Crafts reaction and acylation Friedel–Crafts reaction.
Ortho effect is an organic chemistry phenomenon where the presence of a chemical group at the at ortho position or the 1 and 2 position of a phenyl ring, relative to the carboxylic compound changes the chemical properties of the compound. This is caused by steric effects and bonding interactions along with polar effects caused by the various substituents which are in a given molecule, resulting in changes in its chemical and physical properties. The ortho effect is associated with substituted benzene compounds.










