
Blitzkrieg is a word used to describe a combined arms surprise attack, using a rapid, overwhelming force concentration that may consist of armored and motorized or mechanized infantry formations, together with artillery, air assault, and close air support. The intent is to break through an opponent's lines of defense, dislocate the defenders, confuse the enemy by making it difficult to respond to the continuously changing front, and defeat them in a decisive Vernichtungsschlacht: a battle of annihilation.

Johannes Erwin Eugen Rommel, popularly known as The Desert Fox, was a German Generalfeldmarschall during World War II. He served in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany, as well as in the Reichswehr of the Weimar Republic, and the army of Imperial Germany.

The Second Battle of El Alamein was a battle of the Second World War that took place near the Egyptian railway halt of El Alamein. The First Battle of El Alamein and the Battle of Alam el Halfa had prevented the Axis from advancing further into Egypt.

The Battle of Kasserine Pass took place from 18-24 February 1943 at Kasserine Pass, a 2-mile-wide (3.2 km) gap in the Grand Dorsal chain of the Atlas Mountains in west central Tunisia. It was a part of the Tunisian campaign of World War II.

Operation Sonnenblume was the name given to the dispatch of German and Italian troops to North Africa in February 1941, during the Second World War. The Italian 10th Army had been destroyed by the British, Commonwealth, Empire and Allied Western Desert Force attacks during Operation Compass (9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941). The first units of the new Deutsches Afrikakorps (DAK), commanded by Generalleutnant Erwin Rommel, departed Naples for Africa and arrived on 11 February 1941. On 14 February, advanced units of the 5th Light Afrika Division, Aufklärungsbataillon 3 and Panzerjägerabteilung 39 arrived at the Libyan port of Tripoli and were sent immediately to the front line east of Sirte.
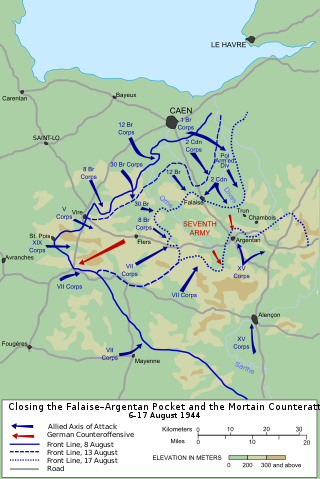
The Falaise pocket or battle of the Falaise pocket was the decisive engagement of the Battle of Normandy in the Second World War. Allied forces formed a pocket around Falaise, Calvados, in which German Army Group B, consisting of the 7th Army and the Fifth Panzer Army, were encircled by the Western Allies. The battle resulted in the destruction of most of Army Group B west of the Seine, which opened the way to Paris and the Franco-German border.

Operation Lüttich was the codename of the Nazi German counter-attack during the Battle of Normandy, which occurred near U.S. positions near Mortain, in northwestern France. Lüttich is the German name for the city of Liège, Belgium. In British and American histories of the Second World War, the German Operation Lüttich is known as the Mortain counter-attack, which Hitler ordered to regain territory gained by the First United States Army during Operation Cobra by reaching the coast of the Avranches region, which is at the base of the Cotentin peninsula, in order to isolate the units of the Third United States Army that had advanced into Brittany.
This is a list of words, terms, concepts, and slogans that have been or are used by the German military. Ranks and translations of nicknames for vehicles are included. Also included are some general terms from the German language found frequently in military jargon. Some terms are from the general German cultural background, others are given to show a change that was made before or after the Nazi era. Some factories that were the primary producers of military equipment, especially tanks, are also given.

The Battle of El Guettar took place during the Tunisia Campaign of World War II, fought between elements of the Army Group Africa under General Hans-Jürgen von Arnim, along with Italian First Army under General Giovanni Messe, and U.S. II Corps under Lieutenant General George Patton in south-central Tunisia. It was the first battle in which U.S. forces were able to defeat the experienced German tank units, but the followup to the battle was inconclusive.

Hyazinth Graf Strachwitz was a German officer of aristocratic descent in the Wehrmacht during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves, Swords and Diamonds.
Panzer greift an is an unfinished book on armoured tactics and warfare by Erwin Rommel. It was to be the follow-up and companion work to his earlier and highly successful Infanterie greift an, which was published in 1937.

The Battle of Białystok–Minsk was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre under Field Marshal Fedor von Bock during the penetration of the Soviet border region in the opening stage of Operation Barbarossa, lasting from 22 June to 9 July 1941.

Wilhelm Emanuel Burgdorf was a German general who rose to prominence during the final years of World War II. Burgdorf served as a commander of 529th Infantry Regiment from May 1940 to April 1942. In October 1944, Burgdorf assumed the role of the chief of the Army Personnel Office and chief adjutant to Adolf Hitler. In this capacity, he played a key role in the forced suicide of Field Marshal Erwin Rommel. Burgdorf committed suicide inside the Führerbunker on 2 May 1945 at the conclusion of the Battle of Berlin.

The Battle of Elsenborn Ridge refers to the northernmost German attacks during the Battle of the Bulge. The area from Elsenborn Ridge itself to Monschau was the only sector of the American front line attacked during the Battle of the Bulge in which the Germans failed to advance. The battle centred on the boomerang-shaped Elsenborn Ridge east of Elsenborn, Belgium. In this region, Elsenborn Ridge marks the westernmost ridge of the Ardennes, rising more than 2,000 feet (600 m) above sea level; unlike the uplands further north, east and south, it has been extensively logged. West of Elsenborn Ridge, where the land descends in gentle hills to the cities of Liège and Spa, was a network of Allied supply bases and a well-developed road network. The Germans planned on using two key routes through the area to seize Antwerp and force a separate peace with the United States and Britain. Capturing Monschau, the nearby village of Höfen, and the twin villages of Rocherath-Krinkelt just east of Elsenborn Ridge, were key to the success of the German plans, and Hitler committed his best armored units to the area.

The German Army was the land forces component of the Wehrmacht, the regular armed forces of Nazi Germany, from 1935 until it effectively ceased to exist in 1945 and then was formally dissolved in August 1946. During World War II, a total of about 13.6 million volunteers and conscripts served in the German Army.

The Battle of Arracourt took place between U.S. and German armoured forces near the town of Arracourt, Lorraine, France between 18 and 29 September 1944, during the Lorraine Campaign of World War II. As part of a counteroffensive against recent U.S. advances in France, the German 5th Panzer Army had as its objective the recapture of Lunéville and the elimination of the XII Corps bridgehead over the Moselle River at Dieulouard.
The 711th Infantry Division was a German Army infantry division in World War II.

The 24th Infantry Division was a German Army infantry division active in World War II. It served across the Eastern Front in engagements such as the Sieges of Sevastopol and the Leningrad, finally being destroyed in the Courland Pocket in 1945.

Otto Moritz Walter Model was a German Generalfeldmarschall during World War II. Although he was a hard-driving, aggressive panzer commander early in the war, Model became best known as a practitioner of defensive warfare. His relative success as commander of the Ninth Army in the battles of 1941–1942 determined his future career path.

Truman Smith was a U.S. Army infantry officer, military attache, and intelligence officer. He collected valuable intelligence on German military capabilities while serving in Berlin before World War II. During the war, he was a personal advisor to General George C. Marshall. He influenced the establishment of the new Bundeswehr to play a role in the Cold War.

















