
Electronic mail is a method of transmitting and receiving messages using electronic devices. It was conceived in the late–20th century as the digital version of, or counterpart to, mail. Email is a ubiquitous and very widely used communication medium; in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries.
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the concept of businesses electronically communicating information that was traditionally communicated on paper, such as purchase orders, advance ship notices, and invoices. Technical standards for EDI exist to facilitate parties transacting such instruments without having to make special arrangements.
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions that include voice, video and messaging applications. SIP is used in Internet telephony, in private IP telephone systems, as well as mobile phone calling over LTE (VoLTE).
In computer science, ACID is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties is called a transaction. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction.
In law, conveyancing is the transfer of legal title of real property from one person to another, or the granting of an encumbrance such as a mortgage or a lien. A typical conveyancing transaction has two major phases: the exchange of contracts and completion.
Electronic business is any kind of business or commercial transaction that includes sharing information across the internet. Commerce constitutes the exchange of products and services between businesses, groups, and individuals and can be seen as one of the essential activities of any business.
This is a Glossary of Internet Terminology; words pertaining to Internet Technology, a subset of Computer Science.
Purchasing is the procurement process a business or organization uses to acquire goods or services to accomplish its goals. Although there are several organizations that attempt to set standards in the purchasing process, processes can vary greatly between organizations.
Collaborative product development (CPD) is a business strategy, work process and collection of software applications that facilitates different organizations to work together on the development of a product. It is also known as collaborative product definition management (cPDM).

Commercial property, also called commercial real estate, investment property or income property, is real estate intended to generate a profit, either from capital gains or rental income. Commercial property includes office buildings, medical centers, hotels, malls, retail stores, multifamily housing buildings, farm land, warehouses, and garages. In many U.S. states, residential property containing more than a certain number of units qualifies as commercial property for borrowing and tax purposes.
Internet fax, e-fax, or online fax is the use of the internet and internet protocols to send a fax (facsimile), rather than using a standard telephone connection and a fax machine. A distinguishing feature of Internet fax, compared to other Internet communications such as email, is the ability to exchange fax messages with traditional telephone-based fax machines.

Google Pay Send, previously known as Google Wallet, was a peer-to-peer payments service developed by Google before its merger into Google Pay. It allowed people to send and receive money from a mobile device or desktop computer.
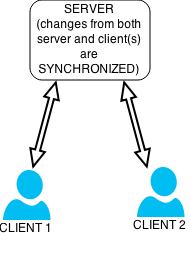
Data synchronization is the process of establishing consistency between source and target data stores, and the continuous harmonization of the data over time. It is fundamental to a wide variety of applications, including file synchronization and mobile device synchronization. Data synchronization can also be useful in encryption for synchronizing public key servers.

The Gmail interface makes Gmail unique amongst webmail systems for several reasons. Most evident to users are its search-oriented features and means of managing e-mail in a "conversation view" that is similar to an Internet forum.
An expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) is a specialized subset of "extract, transform, load" (ETL) functioning as a powerful and flexible set of applications, including programs, scripts and databases designed to improve the cash flow of businesses and organizations by automating the movement of data between cost recovery systems, electronic billing from vendors, and accounting systems.
Mobile payments is a mode of payment using mobile phones. Instead of using methods like cash, cheque, and credit card, a customer can use a mobile phone to transfer money or to pay for goods and services. A customer can transfer money or pay for goods and services by sending an SMS, using a Java application over GPRS, a WAP service, over IVR or other mobile communication technologies. In India, this service is bank-led. Customers wishing to avail themselves of this service will have to register with banks which provide this service. Currently, this service is being offered by several major banks and is expected to grow further. Mobile Payment Forum of India (MPFI) is the umbrella organisation which is responsible for deploying mobile payments in India.
A decentralised application is an application that can operate autonomously, typically through the use of smart contracts, that run on a decentralized computing, blockchain or other distributed ledger system. Like traditional applications, DApps provide some function or utility to its users. However, unlike traditional applications, DApps operate without human intervention and are not owned by any one entity, rather DApps distribute tokens that represent ownership. These tokens are distributed according to a programmed algorithm to the users of the system, diluting ownership and control of the DApp. Without any one entity controlling the system, the application is therefore decentralised.
Peer-to-peer transactions are electronic money transfers made from one person to another through an intermediary, typically referred to as a P2P payment application. P2P payments can be sent and received via mobile device or any home computer with access to the Internet, offering a convenient alternative to traditional payment methods.
A blockchain is a shared database that records transactions between two parties in an immutable ledger. Blockchain documents and confirms pseudonymous ownership of all transactions in a verifiable and sustainable way. After a transaction is validated and cryptographically verified by other participants or nodes in the network, it is made into a "block" on the blockchain. A block contains information about the time the transaction occurred, previous transactions, and details about the transaction. Once recorded as a block, transactions are ordered chronologically and cannot be altered. This technology rose to popularity after the creation of Bitcoin, the first application of blockchain technology, which has since catalyzed other cryptocurrencies and applications.
Colored Coins is an open-source protocol that allows users to represent and manipulate immutable digital resources on top of Bitcoin transactions. They are a class of methods for representing and maintaining real-world assets on the Bitcoin blockchain, which may be used to establish asset ownership. Colored coins are bitcoins with a mark on them that specifies what they may be used for. Colored coins are also considered the initial step toward NFTs built on top of the Bitcoin network.




