Related Research Articles
Telecommunications in Burkina Faso include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.

Telecommunications in Ghana include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
India's telecommunication network is the second largest in the world by number of telephone users with over 1.20 billion subscribers as of August 2024. It has one of the lowest call tariffs in the world enabled by multiple large-scale telecom operators and the ensuant hyper-competition between them. India has the world's second largest Internet user-base with over 949.21 million broadband internet subscribers as of August 2024.

The economy of Morocco is considered a relatively liberal economy, governed by the law of supply and demand. Since 1993, in line with many Western world changes, Morocco has followed a policy of privatisation. Morocco has become a major player in African economic affairs, and is the 6th largest African economy by GDP (PPP). The World Economic Forum placed Morocco as the most competitive economy in North Africa, in its African Competitiveness Report 2014–2015.
The following is an outline of communications technology in Morocco.
Telecommunications in Pakistan describes the overall environment for the mobile telecommunications, telephone, and Internet markets in Pakistan.

The telecom sector in Bangladesh is rapidly emerging. Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission (BTRC) is the regulatory authority for this sector, overseeing licensing, policy, etc.

Orange România is a broadband Internet service provider and mobile provider in Romania. It is Romania's largest GSM network operator which is majority owned by Orange S.A. that also uses some of the Telekom Romania infrastructure, the biggest initial investor, who gradually increased its ownership.

Telecommunications in Turkey provides information about television, radio, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet in Turkey.
The telecommunications industry in China is dominated by three state-run businesses: China Telecom, China Unicom and China Mobile. The three companies were formed by restructuring launched in May 2008, directed by the Ministry of Information Industry (MII), National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) and the Minister of Finance. Since then, all three companies gained nationwide fixed-line and cellular mobile telecom licenses in China. In 2019, all three telecoms were issued 5G national licenses.

Maroc Telecom is the main telecommunications company in Morocco. Currently employing around 11,178 employees, it is the largest telecommunications network in the country with 8 regional delegations and 220 offices present across Morocco. The company is listed on both the Casablanca Stock Exchange and Euronext Paris.

Orange Maroc is one of three major licensed telecommunications operators in Morocco. The multi-service operator offers mobile, fixed-line, cybersecurity and mobile payment offerings.

Telecommunication Company of Iran, or TCI, is the fixed-line incumbent operator in Iran offering services in fixed telephony, DSL and data services for both residential and business customers, all throughout the country. It was established in 1971 with a new organizational structure as the main responsible administration for the entire telecommunication affairs.
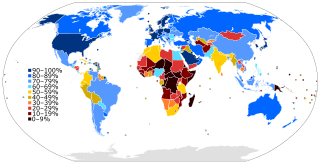
The Internet in Africa is limited by a lower penetration rate when compared to the rest of the world. Measurable parameters such as the number of ISP subscriptions, overall number of hosts, IXP-traffic, and overall available bandwidth are indicators that Africa is far behind the "digital divide". Moreover, Africa itself exhibits an inner digital divide, with most Internet activity and infrastructure concentrated in South Africa, Morocco, and Egypt, as well as smaller economies like Mauritius and the Seychelles. In general, only 43% of the African population has access to the Internet as of 2021. Only 0.4% of the African population has a fixed-broadband subscription. The majority of internet users use it through mobile broadband.
Bahrain has been connected to the internet since 1995, and made it readily available to its citizens. The country's domain suffix is '.bh'. A 2004 study showed a liberal filtering system is used in Bahrain, one which can be easily bypassed, however more recent events have shown more sophisticated and pervasive filtering. In January 2009, Bahrain has started blocking a vastly increased number of sites through the Information Affairs Authority (IAA). The new filtering has had a noticeable impact in internet access speeds for all traffic.
Telecommunications in Bosnia and Herzegovina include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet.
Inwi is a telecommunications company in Morocco. One of the three major Internet service providers in the country, it is a subsidiary of the group SNI and the Kuwaiti group Zain.
Information and communication technology (ICT) in Kosovo has experienced a remarkable development since 1999. From being almost non-existent 10 years ago, Kosovar companies in the information technology (IT) domain offer today wide range of ICT services to their customers both local as well as to foreign companies. Kosovo has the youngest population in Europe, with advanced knowledge in ICT.
References
- ↑ "Morocco". Second Regional Economic Forum for the Agadir Agreement Countries, Cairo – 16, 17 November 2008. Agadir Technical Unit. Archived from the original on 23 February 2013. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- 1 2 3 "Morocco: North African Sun Rises". Thomas White International, Ltd. 2009. Archived from the original on 25 April 2010. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- 1 2 3 "Country Business Profile: Morocco". Oxford Business Group. Archived from the original on August 25, 2009. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- 1 2 MENAFN. "- MENAFN.COM". Archived from the original on 2011-06-11. Retrieved 2009-12-30.
- ↑ Belhaj, Imane (2009-01-07). "Morocco among the top ten countries in offshoring sector". magharebia.com. Retrieved 23 December 2009.
- ↑ "Gartner Identifies Top 30 Countries for Offshore Services in 2008". gartner.com. Archived from the original on December 17, 2008.
- ↑ "Gartner picks top 30 countries for offshore IT outsourcing". SearchCIO.
- ↑ "ANIMA News : Morocco and Egypt enter the latest Gartner's offshore IT 'Top 30'". Archived from the original on 2010-07-17. Retrieved 2009-12-20.
- ↑ "Apebi". Archived from the original on 2008-09-04. Retrieved 2009-12-20.
- 1 2 "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2009-12-20.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-14. Retrieved 2009-12-20.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Morocco determined to protect personal data". moroccobusinessnews.com. Archived from the original on August 1, 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "Technopolis city project launched in Morocco". magharebia.com. 2005-12-18. Retrieved 23 December 2009.