
A limited-slip differential (LSD) is a type of differential that allows its two output shafts to rotate at different speeds but limits the maximum difference between the two shafts. Limited-slip differentials are often known by the generic trademark Positraction, a brand name owned by General Motors and originally used for its Chevrolet branded vehicles.

A slot car or slotcar is a powered miniature automobile or other vehicle that is guided by a groove or slot in the track on which it runs. A pin or blade extends from the bottom of the car into the slot. Though some slot cars are used to model highway traffic on scenic layouts, the great majority are used in the competitive hobby of slot car racing or slot racing.

In automotive design, a front-engine, front-wheel-drive (FWD) layout, or FF layout, places both the internal combustion engine and driven roadwheels at the front of the vehicle.

Mini 4WD is a powered toy car generally 1:32 in scale equipped with 4WD. The cars can be used for miniature auto racing, being built to race around a U-shaped track.

The Chapman strut is a design of independent rear suspension used for light cars, particularly sports and racing cars. It takes its name from, and is best known for its use by, Colin Chapman of Lotus.

A de Dion tube is a form of non-independent automobile suspension. It is a considerable improvement over the swing axle, Hotchkiss drive, or live axle. Because it plays no part in transmitting power to the drive wheels, it is sometimes called a "dead axle".

Scalextric is a brand of slot car racing sets which first appeared in the late 1950s. The Scalextric were first invented by engineer B. Fred Francis, when he added an electric motor to the Scalex tin cars that were produced by Minimodels Ltd, his own company The first "Scalextric" were first made in Havant, Hampshire, in 1956. Hornby Hobbies acquired the company in 1968.

The MG J-type is a sports car that was produced by MG from 1932 to 1934. This 2-door sports car used an updated version of the overhead camshaft, crossflow engine, used in the 1928 Morris Minor and Wolseley 10 and previously fitted in the MG M-type Midget of 1929 to 1932, driving the rear wheels through a four-speed non-synchromesh gearbox. The chassis was from the D-Type with suspension by half-elliptic springs and Hartford friction shock-absorbers all round with rigid front and rear axles. The car had a wheelbase of 86 in (2,184 mm) and a track of 42 in (1,067 mm). Most cars were open two-seaters, but a closed salonette version of the J1 was also made, and some chassis were supplied to external coachbuilders. The open cars can be distinguished from the M type by having cut-away tops to the doors.

Slot car racing is the competitive hobby of racing with powered miniature autos which are guided by grooves or slots in the track on which they run.

Mini-Z is a brand name for a popular line of 1:28-scale electric radio-controlled cars manufactured by Kyosho Corporation, a Japanese manufacturer of various radio-controlled devices. Kyosho makes a huge number of bodies for the Mini-Z. The wheelbase can range from 86mm to 106mm. The bodies are all highly detailed, realistic looking, and fully painted with a high gloss paint. The bodies are so realistic that many are collected as display models and the bodies come with a dummy chassis and wheels for display purposes.

Anglewinder is a type of slot car or motorized model car in which the motor shaft runs at an angle to the driven axle and drives it through a bevel or other angled gear arrangement. It is a development of the sidewinder, or transverse motor, in which the motor shaft is parallel to the driven axle and power is transmitted through spur gears or a belt. The anglewinder arrangement allows use of a slightly longer motor than a pure sidewinder. It also moves the motor's weight forward in the car, which some racers believe improves handling.
Motorcycle components and systems for a motorcycle are engineered, manufactured, and assembled in order to produce motorcycle models with the desired performance, aesthetics, and cost. The key components of modern motorcycles are presented below.
The Tamiya TXT-1, which stands for Tamiya eXtreme Truck, was one of Tamiya's 1/10 scale radio controlled (RC) Monster Trucks.
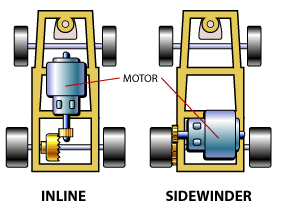
Sidewinder is a type of slot car or motorized model car in which the motor shaft is parallel to the driven axle, and power is transmitted through spur gears or, sometimes, a belt, friction or even by direct drive. The word also refers to the transversely mounted motor of such a car.

The pancake motor, as used in slot cars, is a type of electric motor, which has a flat commutator and vertical shaft. It was a feature of the highly successful Aurora HO slot cars of the 1960s and 1970s. The motor was not a separate unit; instead, its individual elements - magnets, armature, commutator and brushes - fit into recesses in the blocky chassis. The power was carried by a chain of spur gears along the top of the chassis, to a pinion which drove a crown gear at the axle. Like most slot car motors, the Aurora pancakes ran on low voltage direct current.

The Aurora Plastics Corporation was an American toy and hobby manufacturing company. It is known primarily for its production of plastic scale models of cars, airplanes, and TV and movie figures in the 1960s. Its principal competition in modeling were various other plastic modeling firms like Revell and Monogram.

The Aston MartinAtom is a prototype automobile built by Aston Martin (AM). Construction of the car began in 1939 and was completed in 1940. The Atom is one of the first fully functional concept cars ever built. Aston Martin explored several new technologies with the Atom, and its chassis design was the basis for the platform used by AM's post-war models well into the late 1950s.

Aoyagi Metals Industry Co. Ltd was a Japanese company that became notable in the 1980s for its radio-controlled cars.

The Healey Silverstone is an open, two-seat sports car produced by the Donald Healey Motor Company beginning in 1949. It is named for the Silverstone Circuit racetrack, where it appeared on its second competition outing. The car has a narrow roadster style body and cycle wings. Designed as a dual purpose car for both road and track, the Silverstone became popular in club racing.
















