
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also extends northwards into Greenland and Svalbard. These areas were a part of the ancient continent of Euramerica/Laurussia. In Britain it is a lithostratigraphic unit to which stratigraphers accord supergroup status and which is of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, ORS is often used in literature on the subject. The term was coined to distinguish the sequence from the younger New Red Sandstone which also occurs widely throughout Britain.

The Chalk Group is the lithostratigraphic unit which contains the Upper Cretaceous limestone succession in southern and eastern England. The same or similar rock sequences occur across the wider northwest European chalk 'province'. It is characterised by thick deposits of chalk, a soft porous white limestone, deposited in a marine environment.

The Lincolnshire Wolds are a range of low hills in the county of Lincolnshire, England which run roughly parallel with the North Sea coast, from the Humber Estuary in the north-west to the edge of the Lincolnshire Fens in the south-east. They are a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), and the highest area of land in eastern England between Yorkshire and Kent.
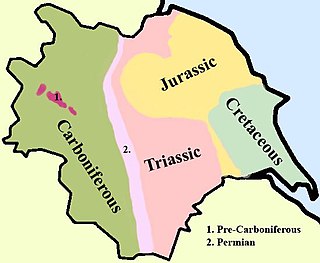
The Geology of Yorkshire in northern England shows a very close relationship between the major topographical areas and the geological period in which their rocks were formed. The rocks of the Pennine chain of hills in the west are of Carboniferous origin whilst those of the central vale are Permo-Triassic. The North York Moors in the north-east of the county are Jurassic in age while the Yorkshire Wolds to the south east are Cretaceous chalk uplands. The plain of Holderness and the Humberhead levels both owe their present form to the Quaternary ice ages. The strata become gradually younger from west to east.
The Lias Group or Lias is a lithostratigraphic unit found in a large area of western Europe, including the British Isles, the North Sea, the Low Countries and the north of Germany. It consists of marine limestones, shales, marls and clays.

The geology of East Sussex is defined by the Weald–Artois anticline, a 60 kilometres (37 mi) wide and 100 kilometres (62 mi) long fold within which caused the arching up of the chalk into a broad dome within the middle Miocene, which has subsequently been eroded to reveal a lower Cretaceous to Upper Jurassic stratigraphy. East Sussex is best known geologically for the identification of the first dinosaur by Gideon Mantell, near Cuckfield, to the famous hoax of the Piltdown man near Uckfield.
The Hibernian Greensands Group is a late Cretaceous lithostratigraphic group in Northern Ireland. It is Cenomanian to Santonian in age. The name is derived from the characteristically coloured marls and sandstones which occur beneath the chalk particularly along the Antrim coast. The strata are exposed on or near to both the northern and eastern coasts of Antrim and also between Portrush and Dungiven within County Londonderry. Further outcrops occur between Belfast and Lurgan and between Dungannon and Magherafelt. It unconformably overlies a variety of units from the Metamorphic Precambrian Southern Highland Group to the Lower Jurassic Lias. The current names replace an earlier situation where the present group was considered to be a formation and each of the present formations was considered a 'member'. Several other stratigraphic naming schemes were in use during the nineteenth century and much of the twentieth century. Various units were earlier referred to as glauconitic or chloritic marls. This group and the overlying Ulster White Limestone Group are the stratigraphical equivalent of the Chalk Group of southern and eastern England.

The geology of the Isle of Skye in Scotland is highly varied and the island's landscape reflects changes in the underlying nature of the rocks. A wide range of rock types are exposed on the island, sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous, ranging in age from the Archaean through to the Quaternary.
The geology of Cambridgeshire in eastern England largely consists of unconsolidated Quaternary sediments such as marine and estuarine alluvium and peat overlying deeply buried Jurassic and Cretaceous age sedimentary rocks.
The geology of Lincolnshire in eastern England largely consists of an easterly dipping succession of Mesozoic age sedimentary rocks, obscured across large parts of the county by unconsolidated deposits dating from the last few hundred thousand years of the present Quaternary Period.
The geology of Norfolk in eastern England largely consists of late Mesozoic and Cenozoic sedimentary rocks of marine origin covered by an extensive spread of unconsolidated recent deposits.
The geology of County Durham in northeast England consists of a basement of Lower Palaeozoic rocks overlain by a varying thickness of Carboniferous and Permo-Triassic sedimentary rocks which dip generally eastwards towards the North Sea. These have been intruded by a pluton, sills and dykes at various times from the Devonian Period to the Palaeogene. The whole is overlain by a suite of unconsolidated deposits of Quaternary age arising from glaciation and from other processes operating during the post-glacial period to the present. The geological interest of the west of the county was recognised by the designation in 2003 of the North Pennines Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty as a European Geopark.

The Lulworth Formation is a geologic formation in England. It dates from the late Tithonian to the mid Berriasian. It is a subunit of the Purbeck Group. In Dorset, it consists of three members, which are in ascending order, the Mupe Member, the Ridgway Member, and the Warbarrow Tout Member. The Mupe Member is typically 11 to 16 m thick and largely consists of marls and micrites with interbeds of calcareous mudstone. The Ridgeway Member is about 3 to 7 m thick and consists of in its western portion carbonaceous muds, marls and micrites, in the east the muds are replaced by micritic limestone. The Warbarrow Tout Member is 17 to 39 m thick and consists of limestone at the base and micrite and mudstone for the rest of the sequence, this member is the primary source of the vertebrate fossils within the formation. Elsewhere the unit is undifferentiated.
The Great Scar Limestone Group is a lithostratigraphical term referring to a succession of generally fossiliferous rock strata which occur in the Pennines in northern England and in the Isle of Man within the Tournaisian and Visean stages of the Carboniferous Period.
The geology of West Sussex in southeast England comprises a succession of sedimentary rocks of Cretaceous age overlain in the south by sediments of Palaeogene age. The sequence of strata from both periods consists of a variety of sandstones, mudstones, siltstones and limestones. These sediments were deposited within the Hampshire and Weald basins. Erosion subsequent to large scale but gentle folding associated with the Alpine Orogeny has resulted in the present outcrop pattern across the county, dominated by the north facing chalk scarp of the South Downs. The bedrock is overlain by a suite of Quaternary deposits of varied origin. Parts of both the bedrock and these superficial deposits have been worked for a variety of minerals for use in construction, industry and agriculture.
The geology of Israel includes igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rocks from the Precambrian overlain by a lengthy sequence of sedimentary rocks extending up to the Pleistocene and overlain with alluvium, sand dunes and playa deposits.
The geology of Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park in the southwestern part of the Scottish Highlands consists largely of Neoproterozoic and Palaeozoic bedrock faulted and folded and subjected to low grade metamorphism during the Caledonian orogeny. These older rocks, assigned to the Dalradian Supergroup, lie to the northwest of the northeast – southwest aligned Highland Boundary Fault which defines the southern edge of the Highlands. A part of this mountainous park extends south of this major geological divide into an area characterised by younger Devonian rocks which are assigned to the Old Red Sandstone.
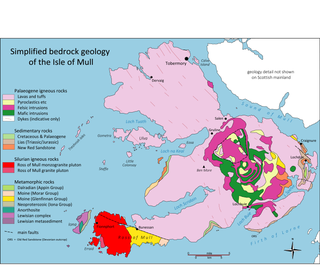
The geology of the Isle of Mull in Scotland is dominated by the development during the early Palaeogene period of a ‘volcanic central complex’ associated with the opening of the Atlantic Ocean. The bedrock of the larger part of the island is formed by basalt lava flows ascribed to the Mull Lava Group erupted onto a succession of Mesozoic sedimentary rocks during the Palaeocene epoch. Precambrian and Palaeozoic rocks occur at the island's margins. A number of distinct deposits and features such as raised beaches were formed during the Quaternary period.
The Mull Lava Group is a Palaeogene lithostratigraphic group in the west Highlands of Scotland. The name is derived from the Isle of Mull where they are most extensively seen, forming the bedrock across much of the island. They extend into the mainland peninsulas of Ardnamurchan and Morvern and also out to sea.
The geology of the Peak District National Park in England is dominated by a thick succession of faulted and folded sedimentary rocks of Carboniferous age. The Peak District is often divided into a southerly White Peak where Carboniferous Limestone outcrops and a northerly Dark Peak where the overlying succession of sandstones and mudstones dominate the landscape. The scarp and dip slope landscape which characterises the Dark Peak also extends along the eastern and western margins of the park. Although older rocks are present at depth, the oldest rocks which are to be found at the surface in the national park are dolomitic limestones of the Woo Dale Limestone Formation seen where Woo Dale enters Wye Dale east of Buxton.








