
The Zachman Framework is an enterprise ontology and is a fundamental structure for enterprise architecture which provides a formal and structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise. The ontology is a two dimensional classification schema that reflects the intersection between two historical classifications. The first are primitive interrogatives: What, How, When, Who, Where, and Why. The second is derived from the philosophical concept of reification, the transformation of an abstract idea into an instantiation. The Zachman Framework reification transformations are: identification, definition, representation, specification, configuration and instantiation.

CIMOSA, standing for "Computer Integrated Manufacturing Open System Architecture", is an enterprise modeling framework, which aims to support the enterprise integration of machines, computers and people. The framework is based on the system life cycle concept, and offers a modelling language, methodology and supporting technology to support these goals.
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations is "a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes."

The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is the most used framework for enterprise architecture as of 2020 that provides an approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing an enterprise information technology architecture. TOGAF is a high-level approach to design. It is typically modeled at four levels: Business, Application, Data, and Technology. It relies heavily on modularization, standardization, and already existing, proven technologies and products.

Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.

The Department of Defense Architecture Framework (DoDAF) is an architecture framework for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) that provides visualization infrastructure for specific stakeholders concerns through viewpoints organized by various views. These views are artifacts for visualizing, understanding, and assimilating the broad scope and complexities of an architecture description through tabular, structural, behavioral, ontological, pictorial, temporal, graphical, probabilistic, or alternative conceptual means. The current release is DoDAF 2.02.
A federal enterprise architecture framework (FEAF) is the U.S. reference enterprise architecture of a federal government. It provides a common approach for the integration of strategic, business and technology management as part of organization design and performance improvement.

Unicom System Architect is an enterprise architecture tool that is used by the business and technology departments of corporations and government agencies to model their business operations and the systems, applications, and databases that support them. System Architect is used to build architectures using various frameworks including TOGAF, ArchiMate, DoDAF, MODAF, NAF and standard method notations such as sysML, UML, BPMN, and relational data modeling. System Architect is developed by UNICOM Systems, a division of UNICOM Global, a United States–based company.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models – typically matrices and diagrams – for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.

In the business sector, business architecture is a discipline that "represents holistic, multidimensional business views of: capabilities, end-to-end value delivery, information, and organizational structure; and the relationships among these business views and strategies, products, policies, initiatives, and stakeholders."
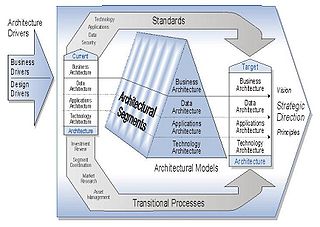
An architecture domain in enterprise architecture is a broad view of an enterprise or system. It is a partial representation of a whole system that addresses several concerns of several stakeholders. It is a description that hides other views or facets of the system described. Business, data, application and technology architectures are recognized as the core domains in the most of proposed concepts concerned with the definition of enterprise architecture.

A view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of views to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture, or enterprise architecture. A view is a representation of the whole system from the perspective of a related set of concerns.

Treasury Enterprise Architecture Framework (TEAF) was an enterprise architecture framework for treasury, based on the Zachman Framework. It was developed by the US Department of the Treasury and published in July 2000. May 2012 this framework has been subsumed by evolving Federal Enterprise Architecture Policy as documented in "The Common Approach to Federal Enterprise Architecture".

Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM) was a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture by and for the United States Department of Defense (DoD).

NIST Enterprise Architecture Model is a late-1980s reference model for enterprise architecture. It defines an enterprise architecture by the interrelationship between an enterprise's business, information, and technology environments.

The Treasury Information System Architecture Framework (TISAF) is an early 1990s Enterprise Architecture framework to assist US Treasury Bureaus to develop their Enterprise Information System Architectures (EISAs).
Peter Bernus is a Hungarian Australian scientist and Associate Professor of Enterprise Architecture at the School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia.
Jaap Schekkerman is a Dutch computer scientist and founder of the Institute For Enterprise Architecture Developments (IFEAD) in the Netherlands. He is particularly known for his 2003 book How to Survive in the Jungle of Enterprise Architecture in which he compared 14 Enterprise Architecture Frameworks.
The history of business architecture has its origins in the 1980s. In the next decades business architecture has developed into a discipline of "cross-organizational design of the business as a whole" closely related to enterprise architecture. The concept of business architecture has been proposed as a blueprint of the enterprise, as a business strategy, and also as the representation of a business design.













