A communication disorder is any disorder that affects an individual's ability to comprehend, detect, or apply language and speech to engage in dialogue effectively with others. The delays and disorders can range from simple sound substitution to the inability to understand or use one's native language.
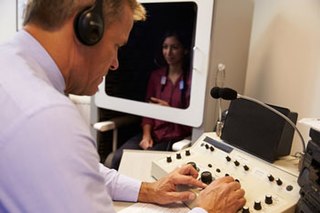
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected, to what degree, and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
The Doctor of Audiology (AuD) is a professional degree for an audiologist. The AuD program is designed to produce audiologists who are skilled in providing diagnostic, rehabilitative, and other services associated with hearing, balance, tinnitus management, and related audiological fields. These individuals help patients with hearing problems primarily by diagnosing hearing loss and fitting hearing assistive devices. There is an emphasis on the clinical learning experience, though most programs also have a research component. As of 2007, the AuD has replaced Masters-level audiology programs as the entry-level degree in the United States. Other countries, such as Australia, Canada and India, still offer the master's degree. In the United States, after an AuD is obtained, some states may require a license before practicing audiology clinically. The majority of AuD programs include three years of didactic and clinical instruction and a one-year externship, similar to a medical residency. A few schools offer accelerated three-year programs. Programs differ in their prerequisite requirements for admission, though broadly applicants must have some background in the natural and social sciences, mathematics, and humanities. While it may be helpful for applicants to have a background in the communication sciences, this is not generally required for admission to an AuD program.
An Audiometrist or Audiometric Officer, is a health-care professional technician who has received special training in the use of Pure tone audiometry equipment. An audiometrist conducts hearing tests, or "audiometric screening", with an Audiometer to establish hearing levels. The results are represented by an audiogram, and are usually interpreted by an audiologist, or a registered Medical Officer, unless the audiometrist is also an audiologist, with the aim of diagnosing hearing loss.
A communicative disorders assistant (CDA) performs hearing and speech-language screenings, prepares therapy materials, implements speech therapy, reports on therapy outcomes, performs routine maintenance on clinical equipment, and works with speech-language pathologists (SLPs) and audiologists to adjust therapy goals. While CDAs cannot perform assessments or set therapy goals, they are a vital part of the therapy team. CDAs are supervised by and work in conjunction with SLPs and audiologists.
The American Speech–Language–Hearing Association (ASHA) is a professional association for speech–language pathologists, audiologists, and speech, language, and hearing scientists in the United States and internationally. It has more than 218,000 members and affiliates.

The All India Institute of Speech and Hearing, commonly known as AIISH (AYE-SH), is located in Manasagangotri, Mysore, India. It is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The institute was established in 1966 with a focus on training professionals for speech and hearing sciences.

Speech-language pathology is a field of healthcare expertise practiced globally. Speech-language pathology (SLP) specializes in the evaluation, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of communication disorders, cognitive-communication disorders, voice disorders, pragmatic disorders, social communication difficulties and swallowing disorder across the lifespan. It is an independent profession considered an "allied health profession" or allied health profession by professional bodies like the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) and Speech Pathology Australia. Allied health professions include audiology, optometry, occupational therapy, rehabilitation psychology, physical therapy and others.

The Atlanta Speech School is a language and literacy school located in Atlanta, Georgia, established in 1938. The school provides educational and clinical programs. The Atlanta Speech School's Rollins Center provides professional development for teachers and educators in partner schools and preschools. The Rollins Center focuses on the eradication of illiteracy. The Rollins Center has an online presence called Cox Campus, which is an online learning environment with coursework targeted for the education of children age 0–8.
Auditory processing disorder (APD), rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes sounds. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the outer, middle, and inner ear. However, they cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system.
Aural rehabilitation is the process of identifying and diagnosing a hearing loss, providing different types of therapies to clients who are hard of hearing, and implementing different amplification devices to aid the client’s hearing abilities. Aural rehab includes specific procedures in which each therapy and amplification device has as its goal the habilitation or rehabilitation of persons to overcome the handicap (disability) caused by a hearing impairment or deafness.
Marion Downs was an American audiologist and Professor Emerita at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, who pioneered universal newborn hearing screening in the early 1960s, then spent more than 30 years trying to convince her peers to adopt the testing in hospitals and to place hearing aids on infants who showed hearing loss. She worked to alert the medical world to the developmental problems associated with childhood deafness. As a result of her efforts, 95 percent of all newborns in America today are screened for hearing loss. She devoted her professional life to the promotion of early identification of hearing loss in newborns, infants, and young children and to helping deaf and hard of hearing individuals lead fulfilling lives.
Speech-Language & Audiology Canada (SAC), formerly known as the Canadian Association of Speech-Language Pathologists and Audiologists (CASLPA), is a national organization supporting and representing speech-language pathologists, audiologists and communication health assistants. The association adopted its new name and logo on February 5, 2014.
Tele-audiology is the utilization of telemedicine to provide audiological services and may include the full scope of audiological practice.
Online speech therapy or telepractice is the use of technology to provide speech therapy via high speed internet, webcam, headset with microphone or any other form of communication. Online therapy is a clinical arrangement where the patient and a speech-language certified pathologist communicate and interact face-to-face over the Internet. The session involves a suite of therapeutic exercises including listening, speaking, reading and writing. The recorded videos are assessed by the pathologist to generate an activity report for evaluating progress and usage.

The National Institute of Speech and Hearing (NISH) is an institute devoted to the education and rehabilitation of individuals with speech-language and hearing impairments located in Thiruvananthapuram, the capital city in the Indian state of Kerala. It was established in 1997 on the initiative of the state of Kerala and is a self-financing affiliate college of the University of Kerala. Academics at NISH is unique in the sense that NISH has an integrated campus where students with hearing impairment and students with normal hearing share the same campus. Bachelor's level courses exclusively for students with hearing impairment include Degree courses in Fine Arts, Computer Science and Commerce affiliated to University of Kerala. On the other hand, NISH also provides RCI approved professional courses at undergraduate level and graduate level in Audiology and Speech Language Pathology as well as diploma courses affiliated to Kerala Health University (KUHS)
The Institute of Health Sciences, Bhubaneswar commonly known as I.H.S. Bhubaneswar, is a medical graduate college in Odisha. Founded in 1999, it offers medical degree courses in rehabilitation sciences, namely "Bachelor in Physiotherapy" (BPT), "Bachelor in Audiology & Speech Language Pathology" (BASLP), and, "Master in Audiology & Speech Language Pathology" (MASLP). The courses are recognized by the Government of Odisha, affiliated to Utkal University & approved by the RCI, New Delhi.
Despite having the largest economy in South America or Central America, Brazil is still considered a developing country due to its low gross domestic product, or GDP, per capita, low living standards, high infant mortality rate and other factors. "With regard to hearing health, the Brazilian government established the national policy for giving attention to hearing health in 2004, in which the Ministry of Health, considering the social magnitude of hearing impairment in the Brazilian population and its consequences, presented the proposal to structure a network of services set up by regions and in hierarchy that aims to be implemented in all federative units of Brazil, with integrated actions to promote ear health, hearing impairment prevention, treatment and rehabilitation organized and managed by the National Health System, Sistema Único de Saúde (SUS), in Portuguese," writes Bevilacqua et al. (2010)
Audiology and hearing health professionals in India is made up of Indian healthcare professional that focus on audiological and hearing problems.
Institute for Communicative and Cognitive Neurosciences (ICCONS) is an autonomous not-for-profit neuroscience speciality hospital & research institute established under Health and Family Welfare Department, Government of Kerala. There are two centres, one in Shoranur, Palakkad district and another in Pulayanarkotta, Thiruvananthapuram




