Related Research Articles

A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same.

Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms.
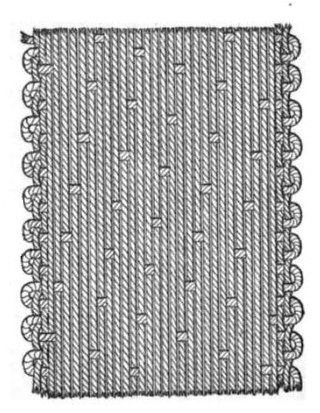
A satin weave is a type of fabric weave that produces a characteristically glossy, smooth or lustrous material, typically with a glossy top surface and a dull back; it is not durable, as it tends to snag. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves alongside plain weave and twill weave.
Ikat is a dyeing technique originating from Indonesia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to dyeing and weaving the fabric.

Warp and weft are the two basic components used in weaving to turn thread or yarn into fabric. The lengthwise or longitudinal warp yarns are held stationary in tension on a frame or loom while the transverse weft is drawn through and inserted over and under the warp. A single thread of the weft crossing the warp is called a pick. Terms vary. Each individual warp thread in a fabric is called a warp end or end.

Damask is a reversible patterned fabric of silk, wool, linen, cotton, or synthetic fibers, with a pattern formed by weaving. Damasks are woven with one warp yarn and one weft yarn, usually with the pattern in warp-faced satin weave and the ground in weft-faced or sateen weave. Twill damasks include a twill-woven ground or pattern.

Double cloth or double weave is a kind of woven textile in which two or more sets of warps and one or more sets of weft or filling yarns are interconnected to form a two-layered cloth. The movement of threads between the layers allows complex patterns and surface textures to be created.
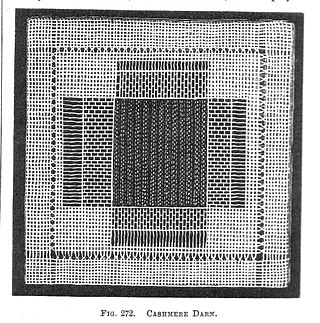
Darning is a sewing technique for repairing holes or worn areas in fabric or knitting using needle and thread alone. It is often done by hand, but it is also possible to darn with a sewing machine. Hand darning employs the darning stitch, a simple running stitch in which the thread is "woven" in rows along the grain of the fabric, with the stitcher reversing direction at the end of each row, and then filling in the framework thus created, as if weaving. Darning is a traditional method for repairing fabric damage or holes that do not run along a seam, and where patching is impractical or would create discomfort for the wearer, such as on the heel of a sock.

Pile weave is a form of textile created by weaving. This type of fabric is characterized by a pile—a looped or tufted surface that extends above the initial foundation, or 'ground' weave. The pile is formed by supplemental yarn running in the direction of the length of the fabric or the width of the fabric. Pile weaves include velvet and corduroy fabrics and machine-woven Berber carpets.

Kasuri (絣) is the Japanese term for fabric that has been woven with fibers dyed specifically to create patterns and images in the fabric, typically referring to fabrics produced within Japan using this technique. It is a form of ikat dyeing, traditionally resulting in patterns characterized by their blurred or brushed appearance.

Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can be more readily constructed into smaller pieces, making it ideal for socks and hats.

A selvage or selvedge is a "self-finished" edge of a piece of fabric which keeps it from unraveling and fraying. The term "self-finished" means that the edge does not require additional finishing work, such as hem or bias tape, to prevent fraying.

Silk In India, about 97% of the raw mulberry silk is produced in the Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. Mysore and North Bangalore, the upcoming site of a US$20 million "Silk City", contribute to a majority of silk production. Another emerging silk producer is Tamil Nadu where mulberry cultivation is concentrated in Salem, Erode and Dharmapuri districts. Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh and Gobichettipalayam, Tamil Nadu were the first locations to have automated silk reeling units.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.
Band weaving refers to the hand production of narrow woven fabric. This fabric may be called tape, band, inkle, strap, belt, back strap, trim, and more. It can be accomplished on a variety of types of looms, including inkle, band, tape, backstrap, and rigid heddle looms. Hole and slot heddles are also designed to weave bands. Depending on which loom is used, the material could be warp-faced or a balanced weave.

Shot silk is a fabric which is made up of silk woven from warp and weft yarns of two or more colours producing an iridescent appearance. A "shot" is a single throw of the bobbin that carries the weft thread through the warp, and shot silk colours can be described as "[warp colour] shot with [weft colour]." The weaving technique can also be applied to other fibres such as cotton, linen, and synthetics.
Textile manufacturing is one of the oldest human activities. The oldest known textiles date back to about 5000 B.C. In order to make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fibre from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving to create cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. Cloth is finished by what are described as wet process to become fabric. The fabric may be dyed, printed or decorated by embroidering with coloured yarns.

Salish are skilled weavers and knitters of the Pacific Northwest. They are most noted for their beautiful twill blankets many of which are very old. The adoption of new fabrics, dyes, and weaving techniques allow us to study a wide variety of Salish weavings today.

Leno weave is a weave in which two warp yarns are woven around the weft yarns to provide a strong yet sheer fabric. The standard warp yarn is paired with a skeleton or 'doup' yarn; these twisted warp yarns grip tightly to the weft which causes the durability of the fabric. Leno weave produces an open fabric with almost no yarn slippage or misplacement of threads.
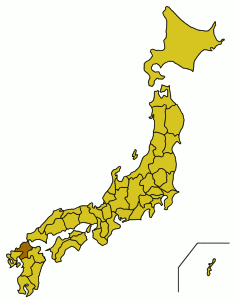
Hakata-ori (博多織) is a traditional Japanese textile that has been produced in Fukuoka Prefecture for more than 770 years.
References
- ↑ "The Magic of Invisible Mending". kottke.org. Retrieved 2023-04-13.