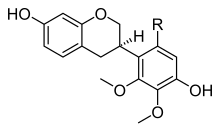
Flavonoids are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.

Daidzein is a naturally occurring compound found exclusively in soybeans and other legumes and structurally belongs to a class of compounds known as isoflavones. Daidzein and other isoflavones are produced in plants through the phenylpropanoid pathway of secondary metabolism and are used as signal carriers, and defense responses to pathogenic attacks. In humans, recent research has shown the viability of using daidzein in medicine for menopausal relief, osteoporosis, blood cholesterol, and lowering the risk of some hormone-related cancers, and heart disease. Despite the known health benefits, the use of both puerarin and daidzein is limited by their poor bioavailability and low water solubility.
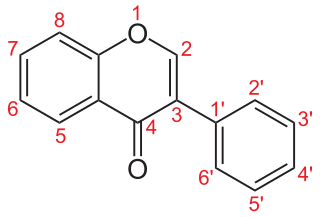
Isoflavonoids are a class of flavonoid phenolic compounds, many of which are biologically active. Isoflavonoids and their derivatives are sometimes referred to as phytoestrogens, as many isoflavonoid compounds have biological effects via the estrogen receptor.
In enzymology, a 4'-methoxyisoflavone 2'-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.14.89, Formerly EC 1.14.13.53) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isoflavone 2'-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.14.90, Formerly EC 1.14.13.89) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an isoflavone 3'-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.14.88, Formerly EC 1.14.13.52) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-apiosyl-beta-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.161) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
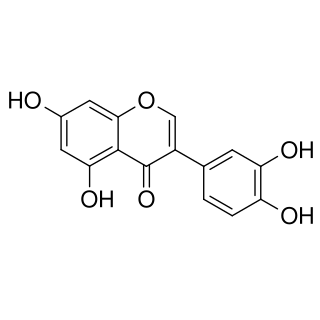
Orobol is one of several known isoflavones. It can be isolated from Aspergillus niger or Streptomyces neyagawaensis. It is a potent inhibitor of Phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
Philenoptera laxiflora, synonym Lonchocarpus laxiflorus, is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae. The tree grows to 4–8 meters in height, has grey or yellowish bark and compound leaves. New leaves are accompanied by purple flowers on multi-branched panicles. The fruit is a glabrous papery pod, usually containing one seed. Ph. laxiflorus is widely distributed in West Africa, Central Africa, the African Great Lakes, and Northeast Africa. It is found in savanna woodlands and dry forested areas, particularly fringing forest near water courses.

Isovitexin is a flavone. the apigenin-6-C-glucoside. In this case, the prefix 'iso' does not imply an isoflavonoid, but the position of the glucoside on the flavone.

Formononetin is an O-methylated isoflavone.

Puerarin, one of several known isoflavones, is found in a number of plants and herbs, such as the root of the kudzu plant
Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is the thioester of coenzyme-A and coumaric acid. Coumaroyl-coenzyme A is a central intermediate in the biosynthesis of myriad natural products found in plants. These products include lignols, flavonoids, isoflavonoids, coumarins, aurones, stilbenes, catechin, and other phenylpropanoids.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Enterodiol</span> Lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Enterodiol.png/320px-Enterodiol.png)
Enterodiol is an organic compound with the formula [HOC6H4CH2CH(CH2OH)]2.

Medicarpin is a pterocarpan, a derivative of isoflavonoids.
The biosynthesis of isoflavonoids involves several enzymes; These are:

Glabridin is a chemical compound that is found in the root extract of licorice. Glabridin is an isoflavane, a type of isoflavonoid. This product is part of a larger family of plant-derived molecules, the natural phenols. Glabridin effectively inhibits platelet activation, so it might become therapeutic agent for thromboembolic disorders.
2-hydroxyisoflavanone synthase (EC 1.14.13.136, CYT93C, IFS, isoflavonoid synthase) is an enzyme with systematic name liquiritigenin,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (hydroxylating, aryl migration). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reactions:
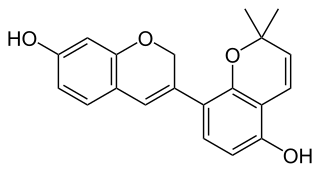
Glabrene is an isoflavonoid that is found in Glycyrrhiza glabra (licorice). It has estrogenic activity, showing estrogenic effects on breast, vascular, and bone tissue, and hence is a phytoestrogen (IC50 for estrogen receptor binding = 1 μM). It has also been found to act as a tyrosinase inhibitor (IC50 = 3.5 μM) and to inhibit the formation of melanin in melanocytes, and for these reasons, has been suggested as a potential skin-lightening agent.

Mirificin, also known as daidzein 8-C-(6-apiofuranosylglucoside), is an isoflavone that is found in Pueraria mirifica and Pueraria lobata. It has estrogenic activity and hence is a phytoestrogen.









![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Enterodiol</span> Lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Enterodiol.png/320px-Enterodiol.png)