
Isosporiasis, also known as cystoisosporiasis, is a human intestinal disease caused by the parasite Cystoisospora belli. It is found worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical areas. Infection often occurs in immuno-compromised individuals, notably AIDS patients, and outbreaks have been reported in institutionalized groups in the United States. The first documented case was in 1915. It is usually spread indirectly, normally through contaminated food or water (CDC.gov).

Eimeria is a genus of apicomplexan parasites that includes various species capable of causing the disease coccidiosis in animals such as cattle, poultry and smaller ruminants including sheep and goats. Eimeria species are considered to be monoxenous because the life cycle is completed within a single host, and stenoxenous because they tend to be host specific, although a number of exceptions have been identified. Species of this genus infect a wide variety of hosts. Thirty-one species are known to occur in bats (Chiroptera), two in turtles, and 130 named species infect fish. Two species infect seals. Five species infect llamas and alpacas: E. alpacae, E. ivitaensis, E. lamae, E. macusaniensis, and E. punonensis. A number of species infect rodents, including E. couesii, E. kinsellai, E. palustris, E. ojastii and E. oryzomysi. Others infect poultry, rabbits and cattle. For full species list, see below.

Oryzomys is a genus of semiaquatic rodents in the tribe Oryzomyini living in southern North America and far northern South America. It includes eight species, two of which—the marsh rice rat (O. palustris) of the United States and O. couesi of Mexico and Central America—are widespread; the six others have more restricted distributions. The species have had eventful taxonomic histories, and most species were at one time included in the marsh rice rat; additional species may be recognized in the future. The name Oryzomys was established in 1857 by Spencer Fullerton Baird for the marsh rice rat and was soon applied to over a hundred species of American rodents. Subsequently, the genus gradually became more narrowly defined until its current contents were established in 2006, when ten new genera were established for species previously placed in Oryzomys.

Sarcocystis is a genus of protozoan parasites, with many species infecting mammals, reptiles and birds. Its name is dervived from Greek sarx = flesh and kystis = bladder.
Eimeria kinsellai is an apicomplexan parasite of the genus Eimeria that infects the marsh rice rat. It was discovered in 1970 at Paynes Prairie, Alachua County, Florida. A different Eimeria, Eimeria palustris, has been found in Alabama marsh rice rats. E. kinsellai differs from other Eimeria found in rice rats, such as Eimeria couesii, Eimeria oryzomysi, Eimeria ojastii, and E. palustris, in anatomical details. It was named after parasitologist John M. Kinsella.
Eimeria palustris is an apicomplexan parasite of the genus Eimeria that infects the marsh rice rat. It was discovered in 1970 at Tuskegee National Forest, Macon County, Alabama. A different Eimeria, Eimeria kinsellai, has been found in Florida marsh rice rats. E. palustris differs from other Eimeria found in rice rats, such as Eimeria couesii, Eimeria oryzomysi, Eimeria ojastii, and E. kinsellai, in anatomical details. Its specific epithet refers to that of its type host, Oryzomys palustris.
Skrjabinoclava kinsellai is a parasitic nematode worm that infects the marsh rice rat in Florida.
Lyperosomum intermedium is a parasitic trematode belonging to the subclass Digenea that infects the marsh rice rat. The species was first described in 1972 by Denton and Kinsella, who wrote that it was closest to Lyperosomum sinuosum, known from birds and raccoons in the United States and Brazil. Three years later, Denton and Kissinger placed the two, together with a number of other species, in a new subgenus of Lyperosomum, Sinuosoides. Species of Lyperosomum mainly infect birds; L. intermedium is one of the few species to infect a mammal.
Eimeria couesii is an apicomplexan parasite of the genus Eimeria that infects the intestine of the rice rat Oryzomys couesi in Mexico. It has an oocyst residuum and Stieda bodies, structures that are absent in some other Eimeria.
Maritrema heardi is a parasitic fluke that infects the marsh rice rat in a salt marsh at Cedar Key, Florida. It was first listed as Maritrema sp. II in 1988, then described as the only species of a new genus, Floridatrema heardi, in 1994, and eventually reassigned in 2003 to Maritrema as Maritrema heardi. Its intermediate host is the fiddler crab Uca pugilator and it lives in the intestine of the marsh rice rat, its definitive host. Together with two other species of Maritrema, it is very common in affected marsh rice rats; it infects 19% of studied rats at Cedar Key. According to Tkach and colleagues, M. heardi is probably primarily a parasite of birds that has secondarily infected the marsh rice rat. Floridatrema was distinguished from Maritrema on the basis of its possession of loops of the uterus that extend forward to the place where the intestine is forked or even to the pharynx. Genetically, M. heardi may be closest to the morphologically similar M. neomi, which infects Neomys water shrews in the Carpathians.
Aonchotheca forresteri is a parasitic nematode that infects the marsh rice rat in Florida. Occurring mainly in adults, it inhabits the stomach. It is much more common during the wet season, perhaps because its unknown intermediate host is an earthworm that only emerges when it rains. The worm was discovered in 1970 and formally described in 1987. Originally classified in the genus Capillaria, it was reclassified in Aonchotheca in 1999. A. forresteri is small and narrow-bodied, with a length of 13.8 to 19.4 mm in females and 6.8 to 9.2 mm in males. Similar species such as A. putorii differ in features of the alae and spicule, the size of the female, and the texture of the eggs.
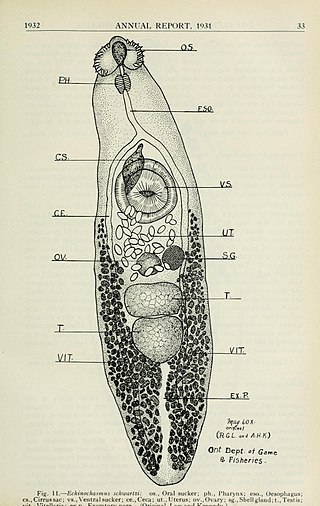
Echinochasmus schwartzi is a fluke that infects dogs, muskrats, and marsh rice rats. It uses Fundulus fish as its intermediate host. Adults are similar to Echinochasmus microcaudatus, but differ in features of the oral sucker.
Urotrema scabridum is a fluke in the genus Urotrema of family Urotrematidae. Recorded hosts include:
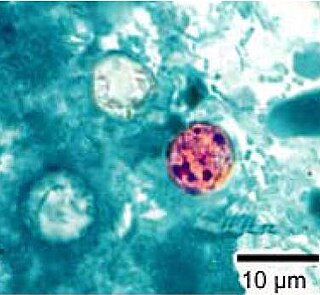
Cyclospora is a genus of apicomplexan parasites. It includes the species Cyclospora cayetanensis, the causative agent of cyclosporiasis. Members of Cyclospora are characterized as having oocysts with two sporocysts, each containing two sporozoites.
Nephroisospora is a genus of parasites that infects bats
Lankesterella is a genus in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect amphibians, reptiles and birds.

Cystoisospora belli, previously known as Isospora belli, is a parasite that causes an intestinal disease known as cystoisosporiasis. This protozoan parasite is opportunistic in immune suppressed human hosts. It primarily exists in the epithelial cells of the small intestine, and develops in the cell cytoplasm. The distribution of this coccidian parasite is cosmopolitan, but is mainly found in tropical and subtropical areas of the world such as the Caribbean, Central and S. America, India, Africa, and S.E. Asia. In the U.S., it is usually associated with HIV infection and institutional living.
Hammondia hammondi is a species of obligate heteroxenous parasitic alveolates of domestic cats. Intracellular cysts develop mainly in striated muscle. After the ingestion of cysts by cats, a multiplicative cycle precedes the development of gametocytes in the epithelium of the small intestine. Oocyst shedding persists for 10 to 28 days followed by immunity. Cysts in skeletal muscle measure between 100 and 340 μm in length and 40 and 95 μm in width. Some of the intermediate hosts develop low levels of antibody and some cross-immunity against Toxoplasma.
Cystoisospora canis, previously known as Isospora canis, is a microscopic, coccidian parasite that causes an intestinal tract infection in dogs. The intestinal tract infection is coccidiosis caused by a protozoa called coccidia.






