Related Research Articles

Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year.

Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses pipes, valves, plumbing fixtures, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. Heating and cooling (HVAC), waste removal, and potable water delivery are among the most common uses for plumbing, but it is not limited to these applications. The word derives from the Latin for lead, plumbum, as the first effective pipes used in the Roman era were lead pipes.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

Celanese Corporation, formerly known as Hoechst Celanese, is an American technology and specialty materials company headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is a Fortune 500 corporation. The company is the world's leading producer of acetic acid, producing about 1.95 million tonnes per year, representing approximately 25% of global production. Celanese is also the world's largest producer of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM).

Phthalates, or phthalate esters, are esters of phthalic acid. They are mainly used as plasticizers, i.e., substances added to plastics to increase their flexibility, transparency, durability, and longevity. They are used primarily to soften polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Note that while phthalates are usually plasticizers, not all plasticizers are phthalates. The two terms are specific and unique and cannot be used interchangeably.

Polymer degradation is the reduction in the physical properties of a polymer, such as strength, caused by changes in its chemical composition. Polymers and particularly plastics are subject to degradation at all stages of their product life cycle, including during their initial processing, use, disposal into the environment and recycling. The rate of this degradation varies significantly; biodegradation can take decades, whereas some industrial processes can completely decompose a polymer in hours.

Salvador V. Vassallo was the president and CEO of Vassallo Industries, headquartered in Ponce, Puerto Rico. The company produces PVC injection moulded and extruded goods, and markets them worldwide.

High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, HDPE is used in the production of plastic bottles, corrosion-resistant piping, geomembranes and plastic lumber. HDPE is commonly recycled, and has the number "2" as its resin identification code.

Artificial leather, also called synthetic leather, is a material intended to substitute for leather in upholstery, clothing, footwear, and other uses where a leather-like finish is desired but the actual material is cost prohibitive or unsuitable, or for ethical concerns. Artificial leather is known under many names, including leatherette, imitation leather, faux leather, vegan leather, PU leather (polyurethane), and pleather.
Cross-linked polyethylene, commonly abbreviated PEX, XPE or XLPE, is a form of polyethylene with cross-links. It is used predominantly in building services pipework systems, hydronic radiant heating and cooling systems, domestic water piping, insulation for high tension electrical cables, and baby play mats. It is also used for natural gas and offshore oil applications, chemical transportation, and transportation of sewage and slurries. PEX is an alternative to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) or copper tubing for use as residential water pipes.

A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.

Formosa Plastics Corporation is a Taiwanese plastics company based in Taiwan that primarily produces polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resins and other intermediate plastic products. It is the corporation around which influential businessman Wang Yung-ching formed the Formosa Plastics Group, and it remains central to the Group's petrochemical operations. The president of Formosa Plastics Corp. (FPC) is Jason Lin (林健男).
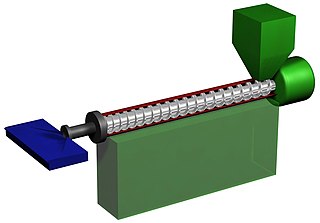
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, Plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.

A plastic bottle is a bottle constructed from high-density or low density plastic. Plastic bottles are typically used to store liquids such as water, soft drinks, motor oil, cooking oil, medicine, shampoo, milk, ink, etc. They come in a range of sizes, from very small bottles to large carboys. Consumer blow molded containers often have integral handles or are shaped to facilitate grasping.

Plastic pipe is a tubular section, or hollow cylinder, made of plastic. It is usually, but not necessarily, of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow—liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipes are far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.

Industrias Vassallo, Inc. is a "worldwide leader" in the manufacture and distribution of PVC injection moulded and extruded goods, and manufacturer and distributor of PVC pipes and accessories, related plastics products, and resin furniture. The company is located in Barrio Coto Laurel in Ponce, Puerto Rico. In 2004, the company had a workforce of 300 employees and revenues of $51M USD. Its president is Rafael Vassallo. Salvador Vassallo was the company's CEO and president until his death in 2007.

Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be molded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to their widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives.
VinyLoop is a proprietary physical plastic recycling process for polyvinyl chloride (PVC). It is based on dissolution in order to separate PVC from other materials or impurities.

Conservation and restoration of objects made from plastics is work dedicated to the conservation of objects of historical and personal value made from plastics. When applied to cultural heritage, this activity is generally undertaken by a conservator-restorer.
References
- ↑ "Plastics News - Pipe, Profile & Tubing Extruders". Plastics News. 4 July 2011. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ↑ "J-M Manufacturing to celebrate 30 years in Pueblo West" . Retrieved 13 January 2012.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Members Committee 100" . Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ "PW Eagle to be bought by J-M Manufacturing". Reuters. 15 January 2007. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ↑ "JM Eagle Completes Move to Los Angeles". National Driller. Retrieved 13 January 2012.
- ↑ "States and water districts join qui tam suit against PVC pipe manufacturer". Phillips & Cohen. 2010-02-16.
- ↑ Walsh, Mary Williams (12 February 2010). "Bursting Pipes Lead to a Legal Battle". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331.
- ↑ "Whistleblower lawsuit claims PVC company knowingly sold faulty pipes". Daily News. 21 May 2010.
- ↑ "JM Eagle Faces Billions In Damages After Jury Finds JM Liable For Fraud For Making And Selling Faulty Water System Pipes". www.wateronline.com. 15 November 2013.
- ↑ Roulo, Candace (1 October 2010). "PVC pipe class action lawsuit filed against JM Eagle". www.contractormag.com.
- ↑ Fisher, Daniel (6 June 2014). "Law Firm Can Be Sued Over Claims In Post-Verdict News Release, Judge Says". Forbes.
- ↑ Kavanaugh, Catherine (17 November 2018). "Whistleblower case against JM Eagle ends in mistrial". Plastics News.
- ↑ "Manufacturing Company Inc. v. Phillips Cohen LLP". Findlaw.
- ↑ Fisher, Daniel (30 April 2014). "Taiwanese Plastics Heir Fights Cancer, Litigation To Build World's Biggest Pipemaker". Forbes.
- ↑ Marinello, Mitchell L. (6 December 2018). "Ethics Misstep Leads to Fee Award Being Vacated". www.americanbar.org.
- ↑ Cutler, Joyce E. (5 June 2018). "Sheppard Mullin Conflict Waiver Case Puts $4M Fee at Stake". news.bloomberglaw.com.
- ↑ Jarvis, Peter R.; Rich, Trisha M. (7 September 2018). "Calif. Supreme Court Breaks New Ground on Arbitrability, Future Waivers and Quantum Meruit | Insights | Holland & Knight". www.hklaw.com.
- ↑ "JM Eagle CEO Walter Wang Tours Millennium Villages in East Africa" . Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ "JMM Brings Clean Water To Small Village In Honduras". JM Eagle Official Website. Archived from the original on 17 November 2011. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ↑ "Next step in 21st century education for students in Africa" . Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ "UCLA - The Optimists" . Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ "UCLA Foundation names new board members" . Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ "Emphasizing the 'Family' in Family Business" . Retrieved 14 June 2020.
- ↑ "A Tradition of Closeness and Compassion" (PDF). Retrieved 14 June 2020.[ permanent dead link ]