Related Research Articles
HMS Daring was a 12-gun gun-brig of the Archer class of the British Royal Navy. She was launched in 1804 and served in the Channel and North Sea, capturing a number of merchant vessels. In 1813 she was serving on the West Africa Station when her crew had to scuttle her to prevent her capture.

The Lively class were a successful class of sixteen British Royal Navy 38-gun sailing frigates.

The Pallas class constituted the standard design of 40-gun frigates of the French Navy during the Napoleonic Empire period. Jacques-Noël Sané designed them in 1805, as a development of his seven-ship Hortense class of 1802, and over the next eight years the Napoléonic government ordered in total 62 frigates to be built to this new design. Of these some 54 were completed, although ten of them were begun for the French Navy in shipyards within the French-occupied Netherlands or Italy, which were then under French occupation; these latter ships were completed for the Netherlands or Austrian navies after 1813.
Ten ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Confiance:

The Bucentaure class was a class of 80-gun French ships of the line built to a design by Jacques-Noël Sané from 1802 onwards, of which at least 29 were ordered but only 21 ships were launched. They were a development from his earlier Tonnant class.
The Conway class sailing sixth rates were a series of ten Royal Navy post ships built to an 1812 design by Sir William Rule. All ten were ordered on 18 January 1812, and nine of these were launched during 1814, at the end of the Napoleonic War; the last (Tees) was delayed and was launched in 1817.
The Apollo-class sailing frigates were a series of twenty-seven ships that the British Admiralty commissioned be built to a 1798 design by Sir William Rule. Twenty-five served in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, two being launched too late.
William Pitt was a three-decker sailing ship, built in Liverpool in 1803. She made three complete voyages for the British East India Company (EIC), and on the first of these she transported convicts to New South Wales. In December 1813 she was lost in a gale to the east of Algoa Bay while homeward bound from her fourth voyage.
HMS Pheasant was an 18-gun merlin class sloop of the Royal Navy.
Rear-Admiral Hood Hanway Christian was a British naval officer who reached the rank of Rear-Admiral. He fought in several naval engagements during the Napoleonic Wars between 1800 and 1814. Later he was Commodore of the naval squadron based on the Cape of Good Hope.
Lord Melville was launched in 1803 as an East Indiaman for the British East India Company (EIC). She made six voyages for the company before she was sold for a hulk in 1817.
Lord Forbes was launched at Chester in 1803 as a West Indiaman. She soon became an "armed defense ship", but by 1805 had returned to being a West Indiaman. She made two voyages as an "extra" ship for the British East India Company (EIC). She continued trading with India until 1817 when she sustained damage on her way to Bengal. There she was surveyed, condemned and sold.
HMS Vulture was launched in 1801 at South Shields as Warrior. The Royal Navy purchased her in 1803 as a sloop and renamed her. From 1808 through 1813 she was a floating battery at Jersey,. The Navy sold her in 1814 and she returned to mercantile service as Warrior. She was last listed in 1820, but does not seem to have sailed again after returning from east of the Cape in 1817.

HMS Minerva was a 32-gun fifth-rate Thames-class frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1805 at Deptford. Her namesake was the Roman goddess Minerva.
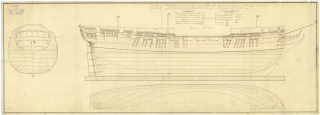
The Thames-class frigate was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate class of eight ships of the Royal Navy based on the Richmond-class frigate designed by William Bately. The ships were ordered to the older design, which was of a smaller type of ship compared to more modern designs, so that they could be built quickly and cheaply in time to assist in defending against Napoleon's expected invasion of Britain. The class received several design changes to the Richmond class, being built of fir instead of oak, with these changes making the class generally slower and less weatherly than their predecessors, especially when in heavy weather conditions. The first two ships of the class, Pallas and Circe, were ordered on 16 March 1804 with two more ordered on 1 May and the final four on 12 July. The final ship of the class, Medea, was cancelled on 22 October before construction could begin but the other seven ships of the class were commissioned between 1804 and 1806.
HMS Thames was a 32-gun fifth-rate Thames-class frigate of the Royal Navy, launched in 1805 at Chatham.

Sir William Rule (c.1750–1816) was a shipbuilder and designer to the Royal Navy who rose to be Surveyor of the Navy.
References
- ↑ "Ships Named Ipswich". Planet Ipswich: A bridge between the Ipswiches of the world. Stefrapes Productions. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- ↑ "Provincial Occurrences". The Monthly Magazine. R. Phillips. 35: 473. 1813.