
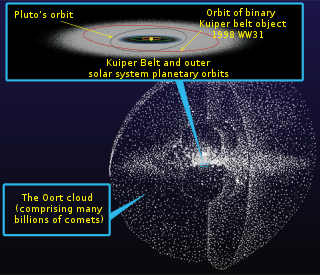
The Oort cloud, sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, is theorized to be a vast cloud of icy planetesimals surrounding the Sun at distances ranging from 2,000 to 200,000 AU. The concept of such a cloud was proposed in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, in whose honor the idea was named. Oort proposed that the bodies in this cloud replenish and keep constant the number of long-period comets entering the inner Solar System—where they are eventually consumed and destroyed during close approaches to the Sun.

Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar was an Indian-American theoretical physicist who spent his professional life in the United States. He shared the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics with William A. Fowler for "...theoretical studies of the physical processes of importance to the structure and evolution of the stars". His mathematical treatment of stellar evolution yielded many of the current theoretical models of the later evolutionary stages of massive stars and black holes. Many concepts, institutions, and inventions, including the Chandrasekhar limit and the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, are named after him.

Hannes Olof Gösta Alfvén was a Swedish electrical engineer, plasma physicist and winner of the 1970 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on magnetohydrodynamics (MHD). He described the class of MHD waves now known as Alfvén waves. He was originally trained as an electrical power engineer and later moved to research and teaching in the fields of plasma physics and electrical engineering. Alfvén made many contributions to plasma physics, including theories describing the behavior of aurorae, the Van Allen radiation belts, the effect of magnetic storms on the Earth's magnetic field, the terrestrial magnetosphere, and the dynamics of plasmas in the Milky Way galaxy.

Hans Albrecht Bethe was a German-American theoretical physicist who made major contributions to nuclear physics, astrophysics, quantum electrodynamics, and solid-state physics, and who won the 1967 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis. For most of his career, Bethe was a professor at Cornell University.

Plasma cosmology is a non-standard cosmology whose central postulate is that the dynamics of ionized gases and plasmas play important, if not dominant, roles in the physics of the universe at interstellar and intergalactic scales. In contrast, the current observations and models of cosmologists and astrophysicists explain the formation, development, and evolution of large-scale structures as dominated by gravity.

Jan Hendrik Oort was a Dutch astronomer who made significant contributions to the understanding of the Milky Way and who was a pioneer in the field of radio astronomy. The New York Times called him "one of the century's foremost explorers of the universe"; the European Space Agency website describes him as "one of the greatest astronomers of the 20th century" and states that he "revolutionised astronomy through his ground-breaking discoveries." In 1955, Oort's name appeared in Life magazine's list of the 100 most famous living people. He has been described as "putting the Netherlands in the forefront of postwar astronomy."

Wojciech Hubert Zurek is a theoretical physicist and a leading authority on quantum theory, especially decoherence and non-equilibrium dynamics of symmetry breaking and resulting defect generation.
Gliese 710, or HIP 89825, is an orange 0.6 M☉ star in the constellation Serpens Cauda. It is projected to pass near the Sun in about 1.29 million years at a predicted minimum distance of 0.051 parsecs—0.1663 light-years – about 1/25th of the current distance to Proxima Centauri. Such a distance would make for a similar brightness to the brightest planets, optimally reaching an apparent visual magnitude of about −2.7. The star's proper motion will peak around one arcminute per year, a rate of apparent motion that would be noticeable over a human lifespan. This is a timeframe, based on data from Gaia DR3, well within the parameters of current models which cover the next 15 million years.

In astrophysics, accretion is the accumulation of particles into a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter, typically gaseous matter, into an accretion disk. Most astronomical objects, such as galaxies, stars, and planets, are formed by accretion processes.
Fred C. Adams is an American astrophysicist who has made contributions to the study of physical cosmology.

Stirling Auchincloss Colgate was an American nuclear physicist at the Los Alamos National Laboratory and a professor emeritus of physics at the New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology from 1965 to 1974, of which he also served its president.

In astronomy, the Hills cloud is a vast theoretical circumstellar disc, interior to the Oort cloud, whose outer border would be located at around 20,000 to 30,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, and whose inner border, less well defined, is hypothetically located at 250–1500 AU, well beyond planetary and Kuiper Belt object orbits—but distances might be much greater. If it exists, the Hills cloud contains roughly 5 times as many comets as the Oort cloud.

HD 204521 is a star in the northern constellation of Cepheus. In the sky it positioned just to the west of the magnitude 3.2 star Beta Cephei. This object has a yellow hue similar to the Sun but is too faint to be visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 7.26. It is located at a distance of 86 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and has an absolute magnitude of 5.15. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −77 km/s, and is predicted to come to within 7.96 light-years in 334,000 years. At that distance the star can have a relatively small perturbing effect on comets in the Oort cloud.
Francis Harvey Harlow was an American theoretical physicist known for his work in the field of fluid dynamics. He was a researcher at Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico. Harlow is credited with establishing the science of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) as an important discipline.
Tyche was a hypothetical gas giant located in the Solar System's Oort cloud, first proposed in 1999 by astrophysicists John Matese, Patrick Whitman and Daniel Whitmire of the University of Louisiana at Lafayette. They argued that evidence of Tyche's existence could be seen in a supposed bias in the points of origin for long-period comets. More recently, Matese and Whitmire re-evaluated the comet data and noted that Tyche, if it existed, would be detectable in the archive of data that was collected by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) telescope. In 2014, NASA announced that the WISE survey had ruled out any object with Tyche's characteristics, indicating that Tyche as hypothesized by Matese, Whitman, and Whitmire does not exist.
An exocomet, or extrasolar comet, is a comet outside the Solar System, which includes rogue comets and comets that orbit stars other than the Sun. The first exocomets were detected in 1987 around Beta Pictoris, a very young A-type main-sequence star. There are now a total of 27 stars around which exocomets have been observed or suspected.

Alexander V. Balatsky is a USSR-born American physicist. He is the professor of theoretical physics at NORDITA and University of Connecticut. He served as the founding director of the Institute for Materials Science (IMS) at Los Alamos National Laboratory in 2014–2017.

Johndale C. Solem is an American theoretical physicist and Fellow of Los Alamos National Laboratory. Solem has authored or co-authored over 185 technical papers in many different scientific fields. He is known for his work on avoiding comet or asteroid collisions with Earth and on interstellar spacecraft propulsion.
Joel Edward Tohline is an American astrophysicist, specializing in computer simulation of complex fluid flows in astrophysical systems.
Robert Everett Ecke is an American experimental physicist who is a laboratory fellow and director emeritus of the Center for Nonlinear Studies (CNLS) at Los Alamos National Laboratory and Affiliate Professor of Physics at the University of Washington. His research has included chaotic nonlinear dynamics, pattern formation, rotating Rayleigh-Bénard convection, two-dimensional turbulence, granular materials, and stratified flows. He is a Fellow of the American Physical Society (APS) and of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), was chair of the APS Topical Group on Statistical and Nonlinear Physics, served in numerous roles in the APS Division of Fluid Dynamics, and was the Secretary of the Physics Section of the AAAS.















