Related Research Articles

Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

Europium(III) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula EuCl3. The anhydrous compound is a yellow solid. Being hygroscopic it rapidly absorbs water to form a white crystalline hexahydrate, EuCl3·6H2O, which is colourless. The compound is used in research.
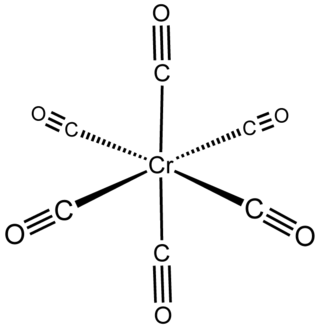
Chromium hexacarbonyl is a chromium(0) organometallic compound with the formula Cr(CO)6. It is a homoleptic complex, which means that all the ligands are identical. It is a colorless crystalline air-stable solid, with a high vapor pressure.

Robert Howard Crabtree is a British-American chemist. He is serving as Conkey P. Whitehead Professor Emeritus of Chemistry at Yale University in the United States. He is a naturalized citizen of the United States. Crabtree is particularly known for his work on "Crabtree's catalyst" for hydrogenations, and his textbook on organometallic chemistry.

Titanocene dichloride is the organotitanium compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2TiCl2, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiCl2. This metallocene is a common reagent in organometallic and organic synthesis. It exists as a bright red solid that slowly hydrolyzes in air. It shows antitumour activity and was the first non-platinum complex to undergo clinical trials as a chemotherapy drug.

Tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0) or [Pd2(dba)3] is an organopalladium compound. The compound is a complex of palladium(0) with dibenzylideneacetone (dba). It is a dark-purple/brown solid, which is modestly soluble in organic solvents. Because the dba ligands are easily displaced, the complex is used as a homogeneous catalyst in organic synthesis.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Frank Albert Cotton FRS was an American chemist. He was the W.T. Doherty-Welch Foundation Chair and Distinguished Professor of Chemistry at Texas A&M University. He authored over 1600 scientific articles. Cotton was recognized for his research on the chemistry of the transition metals.

Dicarbonylbis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium is the chemical compound with the formula (η5-C5H5)2Ti(CO)2, abbreviated Cp2Ti(CO)2. This maroon-coloured, air-sensitive species is soluble in aliphatic and aromatic solvents. It has been used for the deoxygenation of sulfoxides, reductive coupling of aromatic aldehydes and reduction of aldehydes.

Group 2 organometallic chemistry refers to the chemistry of compounds containing carbon bonded to any group 2 element. By far the most common group 2 organometallic compounds are the magnesium-containing Grignard reagents which are widely used in organic chemistry. Other organmetallic group 2 compounds are rare and are typically limited to academic interests.
Organoscandium chemistry is an area with organometallic compounds focused on compounds with at least one carbon to scandium chemical bond. The interest in organoscandium compounds is mostly academic but motivated by potential practical applications in catalysis, especially in polymerization. A common precursor is scandium chloride, especially its THF complex.
Bernt Krebs is a German scientist. He is conducting research at the Faculty of Chemistry, University of Münster.

Stephen James Lippard is the Arthur Amos Noyes Emeritus Professor of Chemistry at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is considered one of the founders of bioinorganic chemistry, studying the interactions of nonliving substances such as metals with biological systems. He is also considered a founder of metalloneurochemistry, the study of metal ions and their effects in the brain and nervous system. He has done pioneering work in understanding protein structure and synthesis, the enzymatic functions of methane monooxygenase (MMO), and the mechanisms of cisplatin anticancer drugs. His work has applications for the treatment of cancer, for bioremediation of the environment, and for the development of synthetic methanol-based fuels.
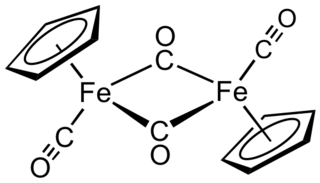
Cyclopentadienyliron dicarbonyl dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(η5-C5H5)Fe(CO)2]2, often abbreviated to Cp2Fe2(CO)4, [CpFe(CO)2]2 or even Fp2, with the colloquial name "fip dimer". It is a dark reddish-purple crystalline solid, which is readily soluble in moderately polar organic solvents such as chloroform and pyridine, but less soluble in carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is insoluble in but stable toward water. Cp2Fe2(CO)4 is reasonably stable to storage under air and serves as a convenient starting material for accessing other Fp (CpFe(CO)2) derivatives (described below).
Ruthenium anti-cancer drugs are coordination complexes of ruthenium complexes that have anticancer properties. They promise to provide alternatives to platinum-based drugs for anticancer therapy. No ruthenium anti-cancer drug has been commercialized.
Gregory S. Girolami is the William H. and Janet G. Lycan Professor of Chemistry at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. His research focuses on the synthesis, properties, and reactivity of new inorganic, organometallic, and solid state species. Girolami has been elected a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, the Royal Society of Chemistry, and the American Chemical Society.
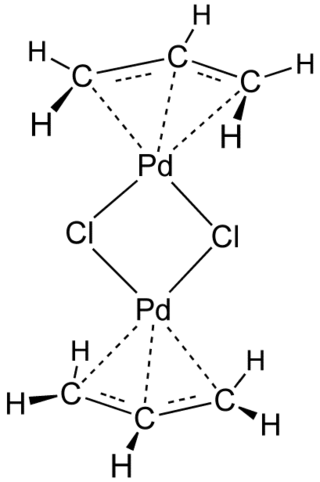
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures.
In chemistry, compounds of palladium(III) feature the noble metal palladium in the unusual +3 oxidation state (in most of its compounds, palladium has the oxidation state II). Compounds of Pd(III) occur in mononuclear and dinuclear forms. Palladium(III) is most often invoked, not observed in mechanistic organometallic chemistry.
William B. Tolman an American inorganic chemist focusing on the synthesis and characterization of model bioinorganic systems, and organometallic approaches towards polymer chemistry. He has served as Editor in Chief of the ACS journal Inorganic Chemistry, and as a Senior Investigator at the NSF Center for Sustainable Polymers. Tolman is a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and the American Chemical Society.

In chemistry, a polytelluride usually refers to anions of the formula (Ten)2-. Many main group and transition metals form complexes with polytelluride anions.
References
- ↑ "ACA IN MEMORIAM for James Ibers".
- ↑ Ukai, Toshinao; Kawazura, Hiroshi; Ishii, Yoshio; Bonnet, J. J.; Ibers, James A. "Chemistry of dibenzylideneacetone-palladium(0) complexes. I. Novel tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(solvent) complexes and their reactions with quinones" Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 1974, volume 65, pp. 253-66. doi : 10.1016/S0022-328X(00)91277-4
- ↑ Ray, Gigi B.; Li, Xiao Yuan; Ibers, James A.; Sessler, Jonathan L.; Spiro, Thomas G. "How far can proteins bend the FeCO unit? Distal polar and steric effects in heme proteins and models" Journal of the American Chemical Society 1994, volume 116, pp. 162-76. doi : 10.1021/ja00080a019
- ↑ Sunshine, Steven A.; Kang, Doris; Ibers, James A. "A new low-temperature route to metal polychalcogenides: solid-state synthesis of potassium titanium sulfide (K4Ti3S14), a novel one-dimensional compound" Journal of the American Chemical Society 1987, volume 109, pp. 6202-4. doi : 10.1021/ja00254a060