Related Research Articles
An oratorio is a musical composition with dramatic or narrative text for choir, soloists and orchestra or other ensemble.
Throughout his life as a musician, Johann Sebastian Bach composed cantatas for both secular and sacred use. His church cantatas are cantatas which he composed for use in the Lutheran church, mainly intended for the occasions of the liturgical year.

Günter Kunert was a German writer. Based in East Berlin, he published poetry from 1947, supported by Bertold Brecht. After he had signed a petition against the deprivation of the citizenship of Wolf Biermann in 1976, he lost his SED membership, and moved to the West two years later. He is regarded as a versatile German writer who wrote short stories, essays, autobiographical works, film scripts and novels. He received international honorary doctorates and awards.
Since the 18th century Berlin has been an influential musical center in Germany and Europe. First as an important trading city in the Hanseatic League, then as the capital of the electorate of Brandenburg and the Prussian Kingdom, later on as one of the biggest cities in Germany it fostered an influential music culture that remains vital until today. Berlin can be regarded as the breeding ground for the powerful choir movement that played such an important role in the broad socialization of music in Germany during the 19th century.

Carl Martin Reinthaler was a German organist, conductor and composer.

Das Floß der Medusa is a 1967 secular oratorio by the German composer Hans Werner Henze. It is regarded as a seminal work in the composer's alignment with left-wing politics.
Volkslied is a genre of popular songs in German which are traditionally sung. While many of them were first passed orally, several collections were published from the late 18th century. Later, some popular songs were also included in this classification.

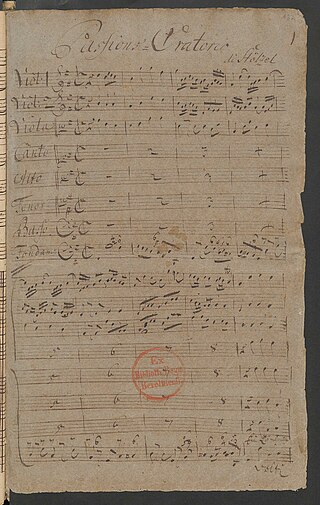
Wer ist der, so von Edom kömmt is a pasticcio Passion oratorio based on compositions by Carl Heinrich Graun, Georg Philipp Telemann, Johann Sebastian Bach and others. The pasticcio was assembled around 1750.

Gustav Alexander Wilhelm Nicolai was a Prussian writer and composer.

Peter Reulein is a German composer, organ improviser, academic teacher and church musician, from 2000 at the church Liebfrauen in Frankfurt am Main. In 2016 he composed for the Catholic Diocese of Limburg the Franciscan oratorio Laudato si'.
Ein Lämmlein geht und trägt die Schuld, also known by the title of its earliest extant printed libretto, Die leidende und am Creutz sterbende Liebe Jesu, is a Passion oratorio by Gottfried Heinrich Stölzel, composed in 1720. Its opening chorus is based on Paul Gerhardt's "Ein Lämmlein geht und trägt die Schuld" and its usual hymn tune, Wolfgang Dachstein's "An Wasserflüssen Babylon" melody.

Der Messias, K. 572, is Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart's 1789 German-language version of Messiah, George Frideric Handel's 1741 oratorio. On the initiative of Gottfried van Swieten, Mozart adapted Handel's work for performances in Vienna.

"Ein Lämmlein geht und trägt die Schuld" is a Lutheran Passion hymn in German by Paul Gerhardt. The hymn text was first published in Johann Crüger's Praxis Pietatis Melica, starting from the lost 1647 edition. Wolfgang Dachstein's 16th-century "An Wasserflüssen Babylon" melody is commonly indicated as its hymn tune, although other settings exist.
Das Sühnopfer des neuen Bundes is an 1847 passion oratorio by Carl Loewe after a libretto by Wilhelm Telschow (1809—1872). The libretto contains poetic-dramatic paraphrasing of the biblical Passion stories.

Antigone oder die Stadt is an opera in two acts, written in collaboration by composer Georg Katzer and librettist Gerhard Müller. They based it on Antigone, the play by Sophocles. Conceived in the German Democratic Republic (GDR) in 1988 as a comment of the East German system, the opera premiered, after German reunification, at the Komische Oper Berlin on 19 November 1991, staged by Harry Kupfer and conducted by Jörg-Peter Weigle.
Günter Neubert was a German composer and tonmeister.
Bruder Martin is an oratorio composed by Thomas Gabriel to a libretto in German by Eugen Eckert. The work in seven scenes and a prologue is based on the life of Martin Luther. It was written for the 500th anniversary of the Reformation in 2017. The composition is set for narrator, soloists, mixed choir, band and orchestra, and includes both Luther hymns and pop ballads. Bruder Martin was premiered open air in Tecklenburg on 17 September 2017, with the performers dressed in period costumes. It was published by Strube Verlag.

Helmut Koch was a German conductor, choir leader, composer, and academic teacher. He was recording manager for the Berliner Rundfunk from 1945, where he founded the Solistenvereinigung Berlin, the Kammerorchester Berlin and the Großer Chor des Berliner Rundfunks. He conducted a recording of Monteverdi's L'Orfeo in 1949, and later also contemporary classical music by composers including Hanns Eisler, Fritz Geißler, Ernst Hermann Meyer and Ruth Zechlin. He was professor at the Hochschule für Musik "Hanns Eisler" from its beginning. After working as a regular guest conductor at the Staatsoper Berlin, he became Generalmusikdirektor. He was the first conductor of the Berliner Singakademie in East Berlin, and held the position until his death.
The Rheinische Kantorei is a German vocal ensemble of baroque music accompanied by an instrumental ensemble called Das Kleine Konzert.
References
- ↑ JPC Auf ein Libretto von August Zeune schuf Carl Loewe das Werk und brachte es am 16. Dezember 1841 in und mit der Berliner Singakademie zur Uraufführung.
- ↑ Die Reformation zwischen Revolution und Renaissance: Wolfgang Behringer, Wolfgang Kraus, Roland Marti · 2019 p42 "Nicht Martin Luther, sondern Jan Hus war erstmals Thema eines Oratoriums von Carl Loewe, 1841 komponiert und am 16. 12. 1841 in der Berliner Singakademie uraufgeführt, 1842 schließlich veröffentlicht. Es ist eins von 16 Oratorien, ..."
- ↑ Scheiterhaufen mit Kontrapunkt 17. Oktober 2022 Die Arcis-Vocalisten entdecken Carl Loewes Oratorium "Jan Hus". von Michael Stallknecht, München