Related Research Articles

The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between Europe's Balkan peninsula and Asia's Anatolia peninsula. The sea has an area of some 215,000 square kilometres. In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea and the Black Sea by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 3,544 meters, to the east of Crete. The Thracian Sea and the Myrtoan Sea are subdivisions of the Aegean Sea.

Naxos is a Greek island and the largest of the Cyclades. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. The island is famous as a source of emery, a rock rich in corundum, which until modern time was one of the best abrasives available.

Andros is the northernmost island of the Greek Cyclades archipelago, about 10 km (6 mi) southeast of Euboea, and about 3 km (2 mi) north of Tinos. It is nearly 40 km (25 mi) long, and its greatest breadth is 16 km (10 mi). It is for the most part mountainous, with many fruitful and well-watered valleys. The municipality, which includes the island Andros and several small, uninhabited islands, has an area of 380 km2 (146.719 sq mi). The largest towns are Andros (town), Gavrio, Batsi, and Ormos Korthiou.
Marco Sanudo was the creator and first Duke of the Duchy of the Archipelago, after the Fourth Crusade.

The Duchy of the Archipelago, also known as Duchy of Naxos or Duchy of the Aegean, was a maritime state created by Venetian interests in the Cyclades archipelago in the Aegean Sea, in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade, centered on the islands of Naxos and Paros. It included all the Cyclades. In 1537 it became a tributary of the Ottoman Empire, and was annexed by the Ottomans in 1579; however, Christian rule survived in islands such as Siphnos and Tinos.

Sifnos is an island municipality in the Cyclades island group in Greece. The main town, near the center, known as Apollonia, is home of the island's folklore museum and library. The town's name is thought to come from an ancient temple of Apollo on the site of the church of Panayia Yeraniofora. The second-largest town is Artemonas (800), thought to be named after an ancient temple of Apollo's sister-goddess Artemis, located at the site of the church of Panayia Kokhi. The village of Kastro (118), was the capital of the island during ancient times until 1836. It is built on top of a high cliff on the island's east shore and today has extensive medieval remains and is the location of the island's archeological museum. The port settlement, on the west coast of the island is known as Kamares (245).

The Battle of Halmyros, known by earlier scholars as the Battle of the Cephissus or Battle of Orchomenos, was fought on 15 March 1311, between the forces of the Frankish Duchy of Athens and its vassals under Walter of Brienne against the mercenaries of the Catalan Company, resulting in a decisive victory for the mercenaries.

Anafi, anciently, Anaphe, is a Greek island community in the Cyclades. In 2011, it had a population of 271. Its land area is 40.370 square kilometres. It lies east of the island of Thíra (Santorini). Anafi is part of the Thira regional unit.
The War of the Euboeote Succession was fought in 1256–1258 between the Prince of Achaea, William II of Villehardouin, and a broad coalition of other rulers from throughout Frankish Greece who felt threatened by William's aspirations. The war was sparked by William's attempt to gain control of a third of the island of Euboea, which was resisted by the local Lombard barons with the aid of the Republic of Venice. The Lord of Athens and Thebes, Guy I de la Roche, also entered the war against William, along with other barons of Central Greece. Their defeat at the Battle of Karydi in May/June 1258 effectively brought the war to an end in an Achaean victory, although a definite peace treaty was not concluded until 1262.
Angelo Sanudo was the second Duke of the Archipelago from 1227, when his father, Marco I, died, until his own death.
Marco II Sanudo was the third Duke of the Archipelago from 1262 to his death.
Florence Sanudo or Fiorenza, was Duchess of the Archipelago in 1362–1371, in co-regency with her second spouse.

Licario, called Ikarios by the Greek chroniclers, was a Byzantine admiral of Italian origin in the 13th century. At odds with the Latin barons of his native Euboea, he entered the service of the Byzantine emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos, and reconquered many of the Aegean islands for him in the 1270s. For his exploits, he was rewarded with Euboea as a fief and rose to the rank of megas konostaulos and megas doux, the first foreigner to do so.

Naxos is a city and a former municipality on the island of Naxos, in the Cyclades, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Naxos and Lesser Cyclades, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has 12,726 inhabitants, and the community 7,374 inhabitants. The Naxos municipal unit covers an area of 126.957 square kilometres (49.018 sq mi). It is located on the west side of Naxos Island in the Cyclades island group in the Aegean. It was the centre of archaic Cycladic culture. It shares the island of Naxos with the municipal unit of Drymalia.
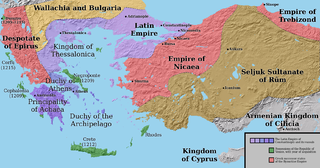
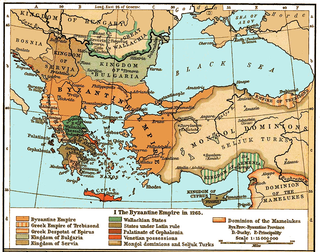
The Frankokratia, also known as Latinokratia and, for the Venetian domains, Venetokratia or Enetokratia, was the period in Greek history after the Fourth Crusade (1204), when a number of primarily French and Italian states were established by the Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae on the territory of the dissolved Byzantine Empire.
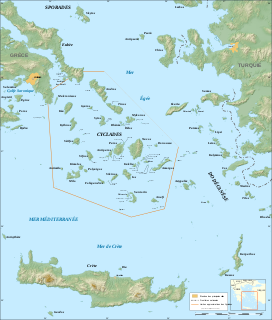
The Cyclades are Greek islands located in the southern part of the Aegean Sea. The archipelago contains some 2,200 islands, islets and rocks; just 33 islands are inhabited. For the ancients, they formed a circle around the sacred island of Delos, hence the name of the archipelago. The best-known are, from north to south and from east to west: Andros, Tinos, Mykonos, Naxos, Amorgos, Syros, Paros and Antiparos, Ios, Santorini, Anafi, Kea, Kythnos, Serifos, Sifnos, Folegandros and Sikinos, Milos and Kimolos; to these can be added the little Cyclades: Irakleia, Schoinoussa, Koufonisi, Keros and Donoussa, as well as Makronisos between Kea and Attica, Gyaros, which lies before Andros, and Polyaigos to the east of Kimolos and Thirassia, before Santorini. At times they were also called by the generic name of Archipelago.
Maria Sanudo was lady of the island of Andros in the Duchy of the Archipelago in 1372-1383, and lady of the island of Paros and of one third of Negroponte in 1383-1426 in co-regency with her spouse, Gaspare Sommaripa.
Francesco I Crispo, Patrizio Veneto was the tenth Duke of the Archipelago through his marriage and the will of Venice.
Paros is an island of the Cyclades group in the central Aegean Sea, which in 1389 became a separate lordship within the Duchy of the Archipelago that lasted until the Duchy's conquest by the Ottoman Empire in 1537.
The War of the Donkey was a conflict in 1286 between the rival noble families of the Ghisi and the Sanudo in the Duchy of the Archipelago in the Aegean Sea, over the ownership of a donkey.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Miller 1908, p. 584.
- 1 2 Freely 2006, p. 50.
- ↑ Miller 1908, p. 141.