Collaborative software or groupware is application software designed to help people working on a common task to attain their goals. One of the earliest definitions of groupware is "intentional group processes plus software to support them."
A management information system (MIS) is an information system used for decision-making, and for the coordination, control, analysis, and visualization of information in an organization. The study of the management information systems involves people, processes and technology in an organizational context.
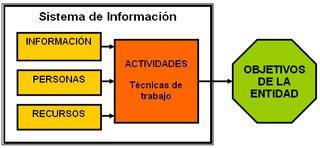
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure, and technology. Information systems can be defined as an integration of components for collection, storage and processing of data of which the data is used to provide information, contribute to knowledge as well as digital products that facilitate decision making.

Jay Wright Forrester was a pioneering American computer engineer, management theorist and systems scientist. He spent his entire career at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, entering as a graduate student in 1939, and eventually retiring in 1989.

Brainstorming is a group creativity technique by which efforts are made to find a conclusion for a specific problem by gathering a list of ideas spontaneously contributed by its members.

A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization and help people make decisions about problems that may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance—i.e. unstructured and semi-structured decision problems. Decision support systems can be either fully computerized or human-powered, or a combination of both.
The Association for Information Systems (AIS) is an international, not-for-profit, professional association for scholars of information systems that was established in 1994. The association publishes journals, organizes conferences, and provides a forum for information systems professors and managers. It has members in more than 100 countries.
Benn Konsynski has been the George S. Craft Distinguished University Professor of Information Systems and Operations Management at the Goizueta Business School at Emory University since 1994. Previously, he spent six years on the faculty at the Harvard Business School, where he taught in the MBA program and several executive programs. He also served as professor at the University of Arizona, where he was a co-founder of the university's multimillion-dollar group decision support laboratory. He holds a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Purdue University. He did a dissertation on "Computer Aided Logical Applications Software Design" under advisors Jay Frank Nunamaker, Jr. and Andrew Bernard Whinston. He was also named Baxter Research Fellow at Harvard, and Hewlett Fellow at The Carter Center.
William David Haseman was an American computer scientist who was an expert in Management Information Systems and Wisconsin Distinguished Professor of MIS of University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee (UWM). His expertise is Internet-based technologies.
Design science research is a research paradigm focusing on the development and validation of prescriptive knowledge in information science. Herbert Simon distinguished the natural sciences, concerned with explaining how things are, from design sciences which are concerned with how things ought to be, that is, with devising artifacts to attain goals. Design science research methodology refers to the research methodologies associated with this paradigm. It spans the methodologies of several research disciplines, for example information technology, which offers specific guidelines for evaluation and iteration within research projects.
Automated Decision Support, or ADS, systems are rule-based systems that are able to automatically provide solutions to repetitive management problems. ADSs are very closely related to business informatics and business analytics.
Media naturalness theory is also known as the psychobiological model. The theory was developed by Ned Kock and attempts to apply Darwinian evolutionary principles to suggest which types of computer-mediated communication will best fit innate human communication capabilities. Media naturalness theory argues that natural selection has resulted in face-to-face communication becoming the most effective way for two people to exchange information.
Hsinchun Chen is the Regents' Professor and Thomas R. Brown Chair of Management and Technology at the University of Arizona and the Director and founder of the Artificial Intelligence Lab. He also served as lead program director of the Smart and Connected Health program at the National Science Foundation from 2014 to 2015. He received a B.S. degree from National Chiao Tung University in Taiwan, an MBA from SUNY Buffalo and an M.S. and Ph.D. in Information Systems from New York University.
Varun Grover is an American Information systems researcher, who is the George & Boyce Billingsley Endowed Chair and distinguished professor at the Walton School of Business, University of Arkansas. From 2002-17, he was the William S. Lee Distinguished Professor of Information Systems at Clemson University, where he taught doctoral seminars on methods and information systems. He is consistently in the top 3 IS researchers in the world. He has an h-index of 100, among the top 5 in his field Grover has around 52,000 citations in Google Scholar and over 13,900 citations in Web of Science.
Robert P. Schumaker is an American academic and Professor of computer science at the University of Texas at Tyler, best known for creating AZFinText, a news-aware high-frequency stock trading system. Schumaker is also known as a Sports Analytics expert for his pioneering work using Twitter tweet sentiment to predict sports outcomes and is currently active in both prescription drug interactions and covid-19 vaccine allergies. Schumaker is also the founder and Director of the Data Analytics Lab.
Michael S. Scott Morton is a business theorist, and is the Jay W. Forrester Professor of Management (Emeritus) at MIT Sloan School of Management, known for his contributions to Strategic information systems and benchmarking e-learning.
In computer supported brainstorming, team members contribute their ideas through electronic means either synchronously or asynchronously. The brainstorming software selected by the team mediates the individual interactions and helps to organize and shape the products of the brainstorming session. Computer supported brainstorming can be implemented using a wide variety of electronic technologies.
Ephraim R. McLean is an American organizational theorist, and Professor of Information Systems at the J. Mack Robinson College of Business, known as one of the founders of the MIS discipline in the 1960s and for his work with William H. DeLone on the information systems success model.

Mark Keil is a Regents’ Professor and the John B. Zellars Professor of Computer Information Systems in the J. Mack Robinson College of Business at Georgia State University. He also holds appointments in the Department of Computer Science and the Institute of Health Administration at Georgia State University.
Alok Gupta is an American information scientist, economic engineer, and academic. He is the Professor of Information and Decision, a Senior Associate Dean of Faculty, Research and Administration, and Curtis L. Carlson School Wide Chair in Information Management in the Carlson School of Management at the University of Minnesota.




